|
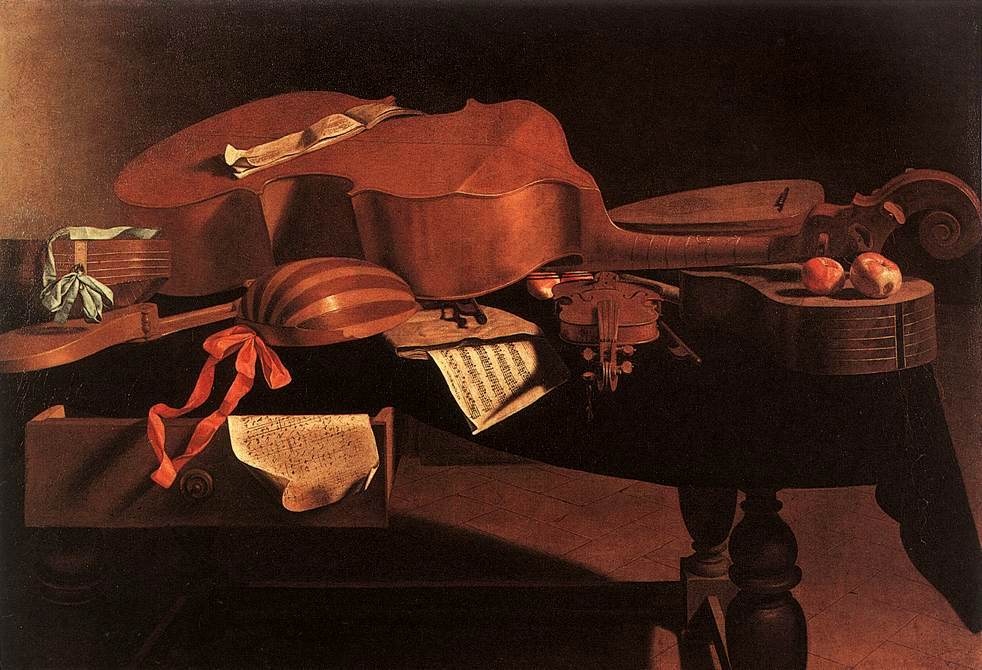
Bell Cittern
The Cithrinchen or Bell cittern was a distinctively shaped instrument of the renaissance and baroque periods. It was usually strung with doubled courses of thin, light tension brass or steel strings. It usually had 3 soundholes (with decorative roses) and 5 (or sometimes 6 or more) courses (pairs) of strings. It was popular in Germany, England England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ... and Sweden. Most such instruments built nowadays are reconstructions of historical instruments, or modern mandolin-type instruments which simply use the same body shape as the historical Cithrinchen. Gallery Image:Cittern MET DP163299.jpg, Cithrinchen in the Met Museum, New York, USA. Image:Cithrinchen BNM Mu 13.jpg, Cithrinchen in the Bayerisches Nationalmuseum, Munich, Germany Image:C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joachim Tielke
Joachim Tielke (14 October 1641 – 19 January 1719) was a German maker of musical instruments. He was born in Königsberg (now Kaliningrad), Duchy of Prussia a fief of Kingdom of Poland, and died in Hamburg. A publication was dedicated to him by Günther Hellwig. Hellwig lists the total number of 139 instruments still existing of Tielke's oeuvre, with lutes, angelicas, theorboes, bell citterns (Ger ''Hamburger Cithrinchen''), guitars, pochettes, violin The violin, sometimes known as a ''fiddle'', is a wooden chordophone (string instrument) in the violin family. Most violins have a hollow wooden body. It is the smallest and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in the family in regular ...s, viole d'amore without sympathetic strings, barytons, viole da gamba, and bows. The publications of 2011 and 2020 omit few instruments and the bows as unauthentic, but new findings raise the total number of instruments and fragments from the Tielke workshop to 174. More r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
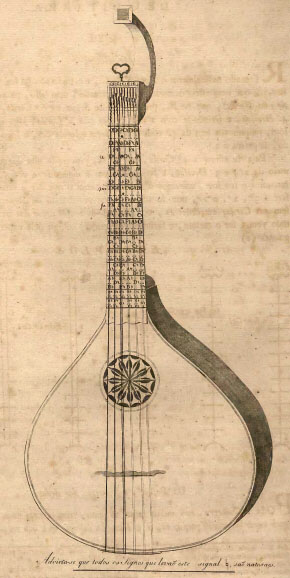
Cittern
The cittern or cithren ( Fr. ''cistre'', It. ''cetra'', Ger. ''Cister,'' Sp. ''cistro, cedra, cítola'') is a stringed instrument dating from the Renaissance. Modern scholars debate its exact history, but it is generally accepted that it is descended from the Medieval citole (or cytole). Its flat-back design was simpler and cheaper to construct than the lute. It was also easier to play, smaller, less delicate and more portable. Played by people of all social classes, the cittern was a premier instrument of casual music-making much as is the guitar today. History Pre-modern citterns The cittern is one of the few metal-strung instruments known from the Renaissance period. It generally has four courses (single, pairs or threes) of strings, one or more courses being usually tuned in octaves, though instruments with more or fewer courses were made. The cittern may have a range of only an octave between its lowest and highest strings and employs a re-entrant tuning – a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orpharion
The orpharion ( or ) or opherion is a plucked stringed instrument from the Renaissance, a member of the cittern family. Its construction is similar to the larger bandora and an ancestor of the guitar. The metal strings are tuned like a lute and are plucked with the fingers. The nut and bridge of an orpharion are typically sloped, so that the string length increases from treble to bass. Due to the extremely low-tension metal strings, which would easily distort the notes when pushed down, the frets were almost flush with the fingerboard, which was gently scalloped."Orpheoreon" in ''Groves Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' (1946). As with all metal-strung instruments of the era, a very light touch with the plucking hand was required, quite different from the sharper attack used on the lute. The orpharion was invented in England in the second half of the 16th century; in sources of English music it is often mentioned as an alternative to the lute. According to Stow's "Annals" (16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Guitar
The English guitar or guittar (also citra), is a stringed instrument – a type of cittern – popular in many places in Europe from around 1750–1850. It is unknown when the identifier "English" became connected to the instrument: at the time of its introduction to Great Britain, and during its period of popularity, it was apparently simply known as ''guitar'' or ''guittar''. The instrument was also known in Norway as a ''guitarre'' and France as ''cistre'' or ''guitarre allemande'' (German guitar). There are many examples in Norwegian museums, like the Norsk Folkemuseum and in British ones, including the Victoria and Albert Museum. The English guitar has a pear-shaped body, a flat base, and a short neck. The instrument is also related to the Portuguese guitar and the German waldzither. Early examples had tuning pegs (similar to a violin or lute), but many museum examples have what are commonly referred to now as Preston tuners, an innovation that appears closely linked with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Guitar
The Portuguese guitar or Portuguese guitarra ( pt, guitarra portuguesa, ) is a plucked string instrument with twelve steel strings, strung in six courses of two strings. It is one of the few musical instruments that still uses watch-key or Preston tuners. It is iconically associated with the musical genre known as Fado, and is now an icon for anything Portuguese. History The Portuguese guitar now known has undergone considerable technical modification in the last century (dimensions, mechanical tuning system, etc.) although it has kept the same number of courses, the string tuning and the finger technique characteristic of this type of instrument. It is a descendant of the Medieval citole, based on evidence of its use in Portugal since the thirteenth century (then known as 'cítole' in Portuguese) amongst troubadour and minstrel circles and in the Renaissance period, although initially it was restricted to noblemen in court circles. Later it became popular and references have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance Music
Renaissance music is traditionally understood to cover European music of the 15th and 16th centuries, later than the Renaissance era as it is understood in other disciplines. Rather than starting from the early 14th-century '' ars nova'', the Trecento music was treated by musicology as a coda to Medieval music and the new era dated from the rise of triadic harmony and the spread of the ' '' contenance angloise'' ' style from Britain to the Burgundian School. A convenient watershed for its end is the adoption of basso continuo at the beginning of the Baroque period. The period may be roughly subdivided, with an early period corresponding to the career of Guillaume Du Fay (c. 1397–1474) and the cultivation of cantilena style, a middle dominated by Franco-Flemish School and the four-part textures favored by Johannes Ockeghem (1410's or 20's – 1497) and Josquin des Prez (late 1450's – 1521), and culminating during the Counter-Reformation in the florid counterpoint of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Music
Baroque music ( or ) refers to the period or dominant style of Western classical music composed from about 1600 to 1750. The Baroque style followed the Renaissance period, and was followed in turn by the Classical period after a short transition, the galant style. The Baroque period is divided into three major phases: early, middle, and late. Overlapping in time, they are conventionally dated from 1580 to 1650, from 1630 to 1700, and from 1680 to 1750. Baroque music forms a major portion of the "classical music" canon, and is now widely studied, performed, and listened to. The term "baroque" comes from the Portuguese word ''barroco'', meaning " misshapen pearl". The works of George Frideric Handel and Johann Sebastian Bach are considered the pinnacle of the Baroque period. Other key composers of the Baroque era include Claudio Monteverdi, Domenico Scarlatti, Alessandro Scarlatti, Antonio Vivaldi, Henry Purcell, Georg Philipp Telemann, Jean-Baptiste Lully, Jean-Philippe Rame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Course (music)
A course, on a stringed musical instrument, is either one string or two or more adjacent strings that are closely spaced relative to the other strings, and typically played as a single string. The strings in each multiple-string course are typically tuned in unison or an octave. Normally, the term ''course'' is used to refer to a single string only on an instrument that also has multi-string courses. For example, a nine-string baroque guitar has five courses: most are two-string courses but sometimes the lowest or the highest consists of a single string. An instrument with at least one multiple-string course is referred to as ''coursed'', while one whose strings are all played individually is ''uncoursed''. Rationale and types Multiple string courses were probably originally employed to increase the volume of instruments, in eras in which electrical amplification did not exist, and stringed instruments might be expected to accompany louder instruments (such as woodwinds or bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its 16 constituent states have a total population of over 84 million in an area of . It borders Denmark to the north, Poland and Czechia to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its main financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Settlement in what is now Germany began in the Lower Paleolithic, with various tribes inhabiting it from the Neolithic onward, chiefly the Celts. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Eng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweden
Sweden, ; fi, Ruotsi; fit, Ruotti; se, Ruoŧŧa; smj, Svierik; sje, Sverji; sju, Sverje; sma, Sveerje or ; yi, שוועדן, Shvedn; rmu, Svedikko; rmf, Sveittiko. formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic country and the List of European countries by area, fifth-largest country in Europe. The Capital city, capital and largest city is Stockholm. Sweden has a population of 10.5 million, and a low population density of ; around 87% of Swedes reside in urban areas in the central and southern half of the country. Sweden’s urban areas together cover 1.5% of its land area. Because the country is so long, ranging from 55th parallel north, 55°N to 69th parallel north, 69°N, the climate of Sweden is diverse. Sweden has been inhabited since Prehistoric Sweden, prehistoric times, . T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Musical Instruments
Early may refer to: History * The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.: ** Early Christianity ** Early modern Europe Places in the United States * Early, Iowa * Early, Texas * Early Branch, a stream in Missouri * Early County, Georgia Other uses * ''Early'' (Scritti Politti album), 2005 * ''Early'' (A Certain Ratio album), 2002 * Early (name) * Early effect, an effect in transistor physics * Early Records, a record label * the early part of the morning Morning is the period from sunrise to noon. There are no exact times for when morning begins (also true of evening and night) because it can vary according to one's lifestyle and the hours of daylight at each time of year. However, morning stric ... See also * Earley (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |