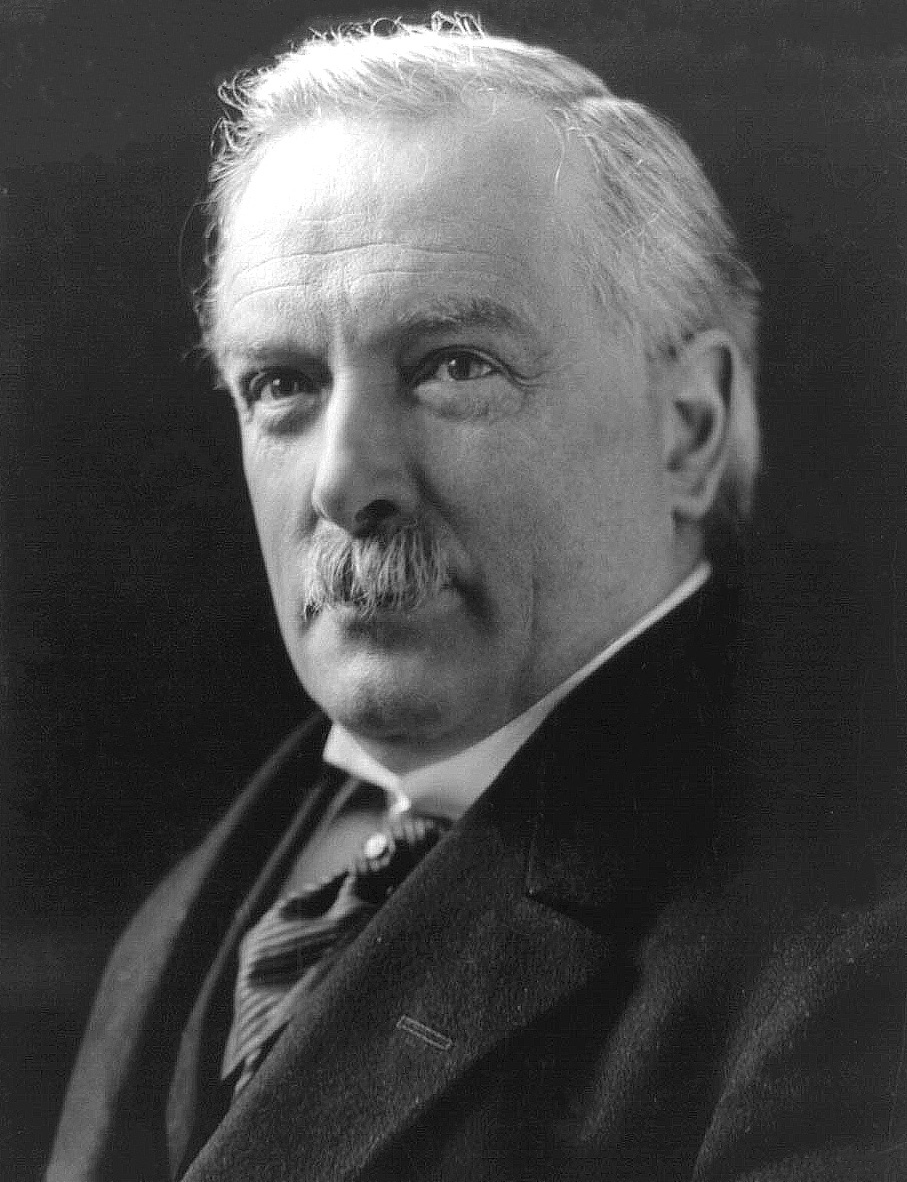|
Belfast Brigade, Irish Republican Army
The Belfast Brigade of the Irish Republican Army (IRA) was formed in March 1921 during the Irish War of Independence, when the IRA was re-organised by its leadership in Dublin into Divisions and Joe McKelvey was appointed commander of the Third Northern Division, responsible for Belfast and the surrounding area. There were three battalions within the Brigade, the 1st in West Belfast, the 2nd in North Belfast and the Third in East Belfast. Most of the Brigade's attacks on Crown forces were carried out by an Active Service Unit within the 1st battalion, led by Roger McCorley. McCorley and Seamus Woods were leaders of a very active IRA Active Service Unit in Belfast (consisted of 32 men) which targeted the Royal Irish Constabulary (RIC) - Auxiliaries and Black and Tans. The Brigade was strengthened during the period between the end of hostilities between the IRA and British forces in July 1921 and the outbreak of the Irish Civil War in June 1922. During this time, Michael Collins, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Republican Army
The Irish Republican Army (IRA) is a name used by various paramilitary organisations in Ireland throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Organisations by this name have been dedicated to irredentism through Irish republicanism, the belief that all of Ireland should be an independent republic free from British rule. The original Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), often now referred to as the "old IRA", was raised in 1917 from members of the Irish Volunteers and the Irish Citizen Army later reinforced by Irishmen formerly in the British Army in World War I, who returned to Ireland to fight against Britain in the Irish War of Independence. In Irish law, this IRA was the army of the revolutionary Irish Republic as declared by its parliament, Dáil Éireann, in 1919. In the century that followed, the original IRA was reorganised, changed and split on multiple occasions, to such a degree that many subsequent paramilitary organisations have been known by that title – most not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belfast Pogrom
Belfast ( , ; from ga, Béal Feirste , meaning 'mouth of the sand-bank ford') is the capital and largest city of Northern Ireland, standing on the banks of the River Lagan on the east coast. It is the 12th-largest city in the United Kingdom and the second-largest in Ireland. It had a population of 345,418 . By the early 19th century, Belfast was a major port. It played an important role in the Industrial Revolution in Ireland, briefly becoming the biggest linen-producer in the world, earning it the nickname " Linenopolis". By the time it was granted city status in 1888, it was a major centre of Irish linen production, tobacco-processing and rope-making. Shipbuilding was also a key industry; the Harland and Wolff shipyard, which built the , was the world's largest shipyard. Industrialisation, and the resulting inward migration, made Belfast one of Ireland's biggest cities. Following the partition of Ireland in 1921, Belfast became the seat of government for Northern Ireland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Campaign (Irish Republican Army)
The Northern campaign was a series of attacks by the Irish Republican Army (IRA) Northern Command between September 1942 and December 1944 against the security forces in Northern Ireland. The action taken by the Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland governments as a result of these attacks shattered the IRA and resulted in the former being free from IRA activity by the end of World War II. The campaign The Taoiseach of the Irish Free State, Éamon de Valera, complained about the occupation of Irish soil with the arrival of American soldiers in Northern Ireland as part of the war effort against Nazi Germany. This influx of foreign soldiers encouraged the northern command of the IRA, under the auspices of newly appointed commander Hugh McAteer, to reorganise and on 25 March 1942 agree a new campaign against the British military and war effort in Northern Ireland. Over the first few months of the campaign, a few attacks against the Royal Ulster Constabulary (RUC) in Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denis Ireland
Denis Liddell Ireland (29 July 1894 – 23 September 1974) was an Irish essayist and political activist. A northern Protestant, after service in the First World War he embraced the cause of Irish independence. He also advanced the social credit ideas of C. H. Douglas. In Belfast, his efforts to encourage Protestants in the exploration of Irish identity and interest were set back when in 1942 his Ulster Union Club was found to have been infiltrated by a successful recruiter for the Irish Republican Army. In Dublin, where he argued economic policy had failed to "see independence through," he entered the Seanad Eireann, the Irish Senate, in 1948 for the republican and social-democratic Clann na Poblachta. He was the first member of the Oireachtas, the Irish Parliament, to be resident in Northern Ireland. Early years Ireland was born in Malone Park, Belfast, the son of a linen manufacturer, Adam Liddell Ireland (recalled as "a mild-mannered man . . . who rarely took time off from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of Ireland
The Church of Ireland ( ga, Eaglais na hÉireann, ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Kirk o Airlann, ) is a Christian church in Ireland and an autonomous province of the Anglican Communion. It is organised on an all-Ireland basis and is the second largest Christian church on the island after the Roman Catholic Church. Like other Anglican churches, it has retained elements of pre-Reformation practice, notably its episcopal polity, while rejecting the primacy of the Pope. In theological and liturgical matters, it incorporates many principles of the Reformation, particularly those of the English Reformation, but self-identifies as being both Reformed and Catholic, in that it sees itself as the inheritor of a continuous tradition going back to the founding of Christianity in Ireland. As with other members of the global Anglican communion, individual parishes accommodate different approaches to the level of ritual and formality, variously referred to as High and Low Church. Overvie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Graham (Irish Republican)
John S.S. Graham (1915, in Belfast, Ireland – 29 December 1997) was an important Irish Republican Army (IRA) activist in the 1940s. He was a member of a Protestant group (including George Gilmore and George Plant) who joined the IRA, and for a time in the 1940s they formed a company of the IRA in Belfast. He rose to become Belfast Commander and Northern Director of Intelligence. Graham was arrested in September 1942 and sentenced to 12 years in prison. While in HM Prison Crumlin Road he (and 21 other Irish Republicans) went on a "strip strike" asking for treatment as political prisoners. The strip strike began in mid June 1943 and was called off in early September. The strike attracted little attention due to war time censorship. Graham was jailed during the IRA "Border Campaign" of 1956-62. While in prison, he learned Irish, and started one of the first Irish language newspapers in Belfast (which is now discontinued). In the late 1970s, a book was written about him, in which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Army (Ireland)
The National Army, sometimes unofficially referred to as the Free State army or the Regulars, was the army of the Irish Free State from January 1922 until October 1924. Its role in this period was defined by its service in the Irish Civil War, in defence of the institutions established by the Anglo-Irish Treaty. Michael Collins was the army's first commander-in-chief until his death in August 1922. The army made its first public appearance on 31 January 1922, when command of Beggars Bush Barracks was handed over from the British Army. Its first troops were those volunteers of the Irish Republican Army (IRA) who supported the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the "Provisional Government of Ireland" formed thereunder. Conflict arose between the National Army and the anti-Treaty components of the IRA, which did not support the government of the Irish Free State. On 28 June 1922 the National Army commenced an artillery bombardment of anti-Treaty IRA forces who were occupying the Four Courts i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Irish Treaty
The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty ( ga , An Conradh Angla-Éireannach), commonly known in Ireland as The Treaty and officially the Articles of Agreement for a Treaty Between Great Britain and Ireland, was an agreement between the government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and representatives of the Irish Republic that concluded the Irish War of Independence. It provided for the establishment of the Irish Free State within a year as a self-governing dominion within the "community of nations known as the British Empire", a status "the same as that of the Dominion of Canada". It also provided Northern Ireland, which had been created by the Government of Ireland Act 1920, an option to opt out of the Irish Free State (Article 12), which the Parliament of Northern Ireland exercised. The agreement was signed in London on 6 December 1921, by representatives of the British government (which included Prime Minister David Lloyd George, who was head of the British delegates) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Treaty IRA
The 1921 Anglo-Irish Treaty ( ga , An Conradh Angla-Éireannach), commonly known in Ireland as The Treaty and officially the Articles of Agreement for a Treaty Between Great Britain and Ireland, was an agreement between the government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and representatives of the Irish Republic that concluded the Irish War of Independence. It provided for the establishment of the Irish Free State within a year as a self-governing dominion within the "community of nations known as the British Empire", a status "the same as that of the Dominion of Canada". It also provided Northern Ireland, which had been created by the Government of Ireland Act 1920, an option to opt out of the Irish Free State (Article 12), which the Parliament of Northern Ireland exercised. The agreement was signed in London on 6 December 1921, by representatives of the British government (which included Prime Minister David Lloyd George, who was head of the British delegates) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Released Belfast Hunger Strikers May 1920
Released may refer to: * ''Released'' (Jade Warrior album), 1971 * ''Released'' (Patti LaBelle album), 1980 * '' Released: 1985–1995'', an album by Kronos Quartet, 1995 * ''Released'', an album by Westlife, 2005 * "Released", a song by Norther from ''Dreams of Endless War ''Dreams of Endless War'' is the debut album by the Finnish melodic death metal band Norther. It was released on 18 July 2002 by Spinefarm Records. The songs; "Victorious One" and "Endless War" are demo songs from ''Warlord'', while the song "War ...'', 2002 See also * Release (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Argenta
HMS ''Argenta'' (originally the American cargo ship SS ''Argenta'') was a prison ship of the British Royal Navy. Construction The two deck steamer was laid down in July 1917 by the National Shipbuilding Company of Orange, Texas as Hull No. 245. Shortages of materials meant that she was wooden-hulled, with a steel keelson, stem and stern posts of oak, and timbers largely of yellow pine. This was due to shortages of metals. SS ''Argenta'' was launched in May 1919. Cargo ship ''Argenta''s career as a cargo ship was short. As early as November 1919, there were some signs of leakage, and the ship was out of service from late 1921. Condemned and declared unseaworthy in May 1922, she was then sold for use as a prison ship (a prison hulk) by the British Royal Navy. Prison ship During the 1920s, the vessel was used by the British government as a military base and prison ship for holding Irish Republicans as part of Britain's internment strategy following the events of "Bloody Sunday" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Republican
Irish republicanism ( ga, poblachtánachas Éireannach) is the political movement for the unity and independence of Ireland under a republic. Irish republicans view British rule in any part of Ireland as inherently illegitimate. The development of nationalist and democratic sentiment throughout Europe in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, distilled into the contemporary ideology known as republican radicalism, was reflected in Ireland in the emergence of republicanism, in opposition to British rule. Discrimination against Catholics and Protestant nonconformists, attempts by the British administration to suppress Irish culture, and the belief that Ireland was economically disadvantaged as a result of the Acts of Union were among the specific factors leading to such opposition. The Society of United Irishmen, formed in 1791 and led primarily by liberal Protestants, launched the 1798 Rebellion with the help of troops sent by Revolutionary France, but the uprising f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)