|
Before The Dawn (Wade Book)
''Before the Dawn: Recovering the Lost History of Our Ancestors'' is a non-fiction book by Nicholas Wade, a science reporter for '' The New York Times''. It was published in 2006 by the Penguin Group. By drawing upon research on the human genome, the book attempts to piece together what Wade calls "two vanished periods": the five million years of human evolution from the development of bipedalism leading up to behavioural modernity around 50,000 years ago, and the 45,000 subsequent years of prehistory. Wade asserts that there is a clear continuity from the earlier apes of five million years ago to the anatomically modern humans who diverged from them, citing the genetic and social similarities between humans and chimpanzees. He attributes the divergence of the two species from a common ancestor to a change in their ecological niche; the ancestors of chimpanzees remained in the forests of equatorial Africa, whereas the ancestors of humans moved to open woodland and were e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Wade
Nicholas Michael Landon Wade (born 17 May 1942) is a British author and journalist. He is the author of numerous books, and has served as staff writer and editor for ''Nature'', ''Science'', and the science section of ''The New York Times''. His 2014 book '' A Troublesome Inheritance: Genes, Race and Human History'' was widely denounced by the scientific community for misrepresenting research into human population genetics. In May 2021, Wade published an article in support of the COVID-19 lab leak hypothesis, fueling the controversy around the origins of the virus. Wade's claims about the origin of COVID-19 are at odds with the prevailing view among scientists. Early life and education Wade was born in Aylesbury, England and educated at Eton College. He is a grandson of Lawrence Beesley, a survivor of the sinking of the ''Titanic''. He earned a Bachelor of Arts degree in Natural Sciences from King's College, Cambridge in 1964, and immigrated to the United States in 1970. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Pressure
Any cause that reduces or increases reproductive success in a portion of a population potentially exerts evolutionary pressure, selective pressure or selection pressure, driving natural selection. It is a quantitative description of the amount of change occurring in processes investigated by evolutionary biology, but the formal concept is often extended to other areas of research. In population genetics, selective pressure is usually expressed as a selection coefficient. Amino acids selective pressure It has been shown that putting an amino acid bio-synthesizing gene like ''HIS4'' gene under amino acid selective pressure in yeast causes enhancement of expression of adjacent genes which is due to the transcriptional co-regulation of two adjacent genes in Eukaryota. Antibiotic resistance Drug resistance in bacteria is an example of an outcome of natural selection. When a drug is used on a species of bacteria, those that cannot resist die and do not produce offspring, while th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knuckle-walking
Knuckle-walking is a form of quadrupedal walking in which the forelimbs hold the fingers in a partially flexed posture that allows body weight to press down on the ground through the knuckles. Gorillas, bonobos, and chimpanzees use this style of locomotion, as do anteaters and platypuses. Knuckle-walking helps with actions other than locomotion on the ground. For the gorilla, the fingers are used for the manipulation of food, and in chimpanzees, for the manipulation of food and climbing. In anteaters and pangolins, the fingers have large claws for opening the mounds of social insects. Platypus fingers have webbing that extend past the fingers to aid in swimming, thus knuckle-walking is used to prevent stumbling. Gorillas move around by knuckle-walking, although they sometimes walk bipedally for short distances while carrying food or in defensive situations. Mountain gorillas use knuckle-walking plus other parts of their hand—fist-walking does not use the knuckles, using the back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
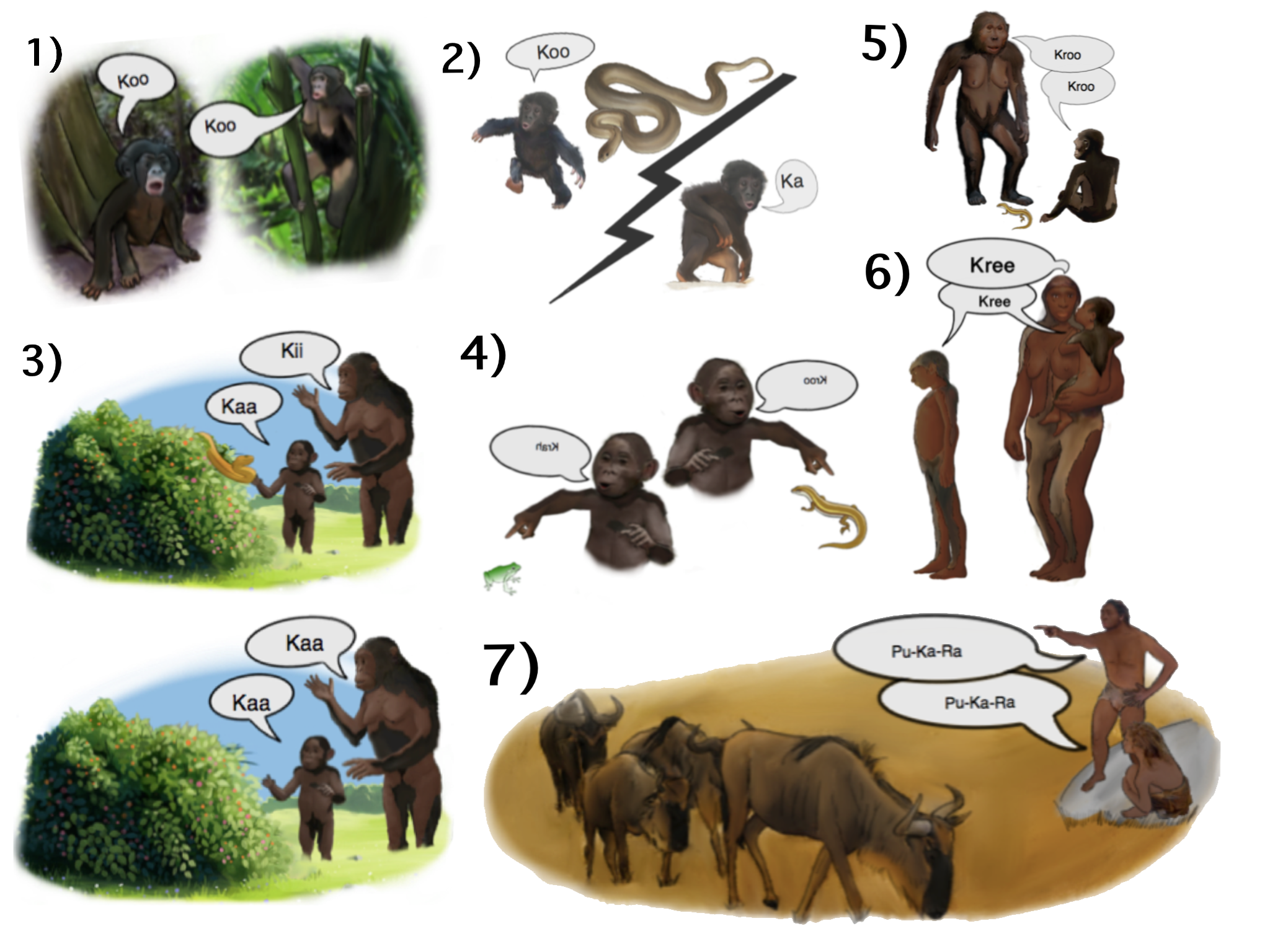
Origin Of Language
The origin of language (spoken and signed, as well as language-related technological systems such as writing), its relationship with human evolution, and its consequences have been subjects of study for centuries. Scholars wishing to study the origins of language must draw inferences from evidence such as the fossil record, archaeological evidence, contemporary language diversity, studies of language acquisition, and comparisons between human language and systems of communication existing among animals (particularly other primates). Many argue that the origins of language probably relate closely to the origins of modern human behavior, but there is little agreement about the facts and implications of this connection. The shortage of direct, empirical evidence has caused many scholars to regard the entire topic as unsuitable for serious study; in 1866, the Linguistic Society of Paris banned any existing or future debates on the subject, a prohibition which remained influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neanderthal
Neanderthals (, also ''Homo neanderthalensis'' and erroneously ''Homo sapiens neanderthalensis''), also written as Neandertals, are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. While the "causes of Neanderthal disappearance about 40,000 years ago remain highly contested," demographic factors such as small population size, inbreeding and genetic drift, are considered probable factors. Other scholars have proposed competitive replacement, assimilation into the modern human genome (bred into extinction), great climatic change, disease, or a combination of these factors. It is unclear when the line of Neanderthals split from that of modern humans; studies have produced various intervals ranging from 315,000 to more than 800,000 years ago. The date of divergence of Neanderthals from their ancestor ''H. heidelbergensis'' is also unclear. The oldest potential Neanderthal bones date to 430,000 years ago, but the classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
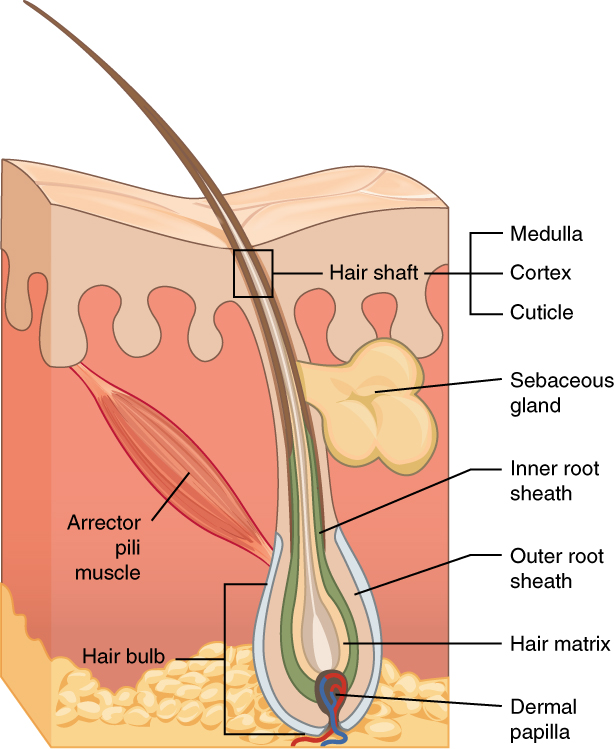
Hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals. The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and fine vellus hair. Most common interest in hair is focused on hair growth, hair types, and hair care, but hair is also an important biomaterial primarily composed of protein, notably alpha-keratin. Attitudes towards different forms of hair, such as hairstyles and hair removal, vary widely across different cultures and historical periods, but it is often used to indicate a person's personal beliefs or social position, such as their age, sex, or religion. Overview The word "hair" usually refers to two distinct structures: #the part beneath the skin, called the hair follicle, or, when pulled from the skin, the bulb or root. This organ is located in the dermis and maintains stem cells, which not only re-grow the hair after it falls out, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Association Of Science Writers
The National Association of Science Writers (NASW) was created in 1934 by a dozen science journalists and reporters in New York City. ''MIT New''. Retrieved 2016-01-10. The aim of the organization was to improve the craft of science journalism and to promote good science reportage. In June 1934, John J. O'Neill, William L. Laurence, |
Science In Society Journalism Award
The Science in Society Journalism Awards are awards created by the American National Association of Science Writers (NASW) to honor and encourage "outstanding investigative and interpretive reporting about the sciences and their impact for good and ill." Each year the NASW recognizes work in these categories: books, periodicals (newspaper and magazine), and electronic media (radio, television, and the Internet). Each winner receives $2,500. The first award was given in 1972. The Awards recognize not only reporting about science, but also thoughtful work that probes the ethical problems and social effects of science. The awards are considered especially prestigious because they are judged by accomplished peers. Starting in 2009 the award categories were changed. The book category will remain unchanged, while the other categories will morph into "Commentary and Opinion," "Science Reporting," and "Local Science Reporting." Except for the Book category, the awards will be platform indep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of productivity and displacement, and rely on social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Race (human Classification)
A race is a categorization of humans based on shared physical or social qualities into groups generally viewed as distinct within a given society. The term came into common usage during the 1500s, when it was used to refer to groups of various kinds, including those characterized by close kinship relations. By the 17th century, the term began to refer to physical (phenotypical) traits, and then later to national affiliations. Modern science regards race as a social construct, an identity which is assigned based on rules made by society. While partly based on physical similarities within groups, race does not have an inherent physical or biological meaning. The concept of race is foundational to racism, the belief that humans can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. Social conceptions and groupings of races have varied over time, often involving folk taxonomies that define essential types of individuals based on perceived traits. Today, scientists con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divergent Evolution
Divergent evolution or divergent selection is the accumulation of differences between closely related populations within a species, leading to speciation. Divergent evolution is typically exhibited when two populations become separated by a geographic barrier (such as in allopatric or peripatric speciation) and experience different selective pressures that drive adaptations to their new environment. After many generations and continual evolution, the populations become less able to interbreed with one another. The American naturalist J. T. Gulick (1832–1923) was the first to use the term "divergent evolution", with its use becoming widespread in modern evolutionary literature. Classic examples of divergence in nature are the adaptive radiation of the finches of the Galapagos or the coloration differences in populations of a species that live in different habitats such as with pocket mice and fence lizards. The term can also be applied in molecular evolution, such as to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Isolate
Introduction Geographic isolation or other factors that prevent reproduction have resulted in a population of organisms with a change in genetic diversity and ultimately leads to the genetic isolation of species. Genetic isolates form new species through an evolutionary process known as speciation. Today, all the species diversity present on earth is the product of genetic isolate and evolution. The current distribution of genetic differences and isolation within and among populations is also influenced by genetic processes, which can give significant input into evolution's basic principles. The resulting genetic diversity within a species' distribution range is frequently unequally distributed, and large disparities can occur at the series of ranges when population dispersion and isolation are critical for species survival. The interrelationship of genetic drift, gene flow, and natural selection determines the level and dispersion of genetic differences between populations and am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |