|
Bedaux Unit
The Bedaux Unit emerged from the U.S. scientific management movement. It remains in daily use in measuring and comparing manual labor to this day. F. W. Taylor's time studies While Frederick Winslow Taylor, F. W. Taylor remains famous for conducting time and motion studies, time studies on employees, these studies' influence on subsequent workplaces have long been harder to determine. argues that 'A comprehensive and detailed outline of the principles of Taylorism is essential to our narrative, not because of the things for which it is popularly known - stopwatch, speed-up, etc. - but because behind these commonplaces there lies a theory which is nothing less than the explicit verbalization of the capitalist mode of production ... It is impossible to overestimate the importance of the scientific management movement in the shaping of the modern corporation and indeed all institutions of capitalist society which carry on labor processes ... Taylorism dominates the world of production. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Management
Scientific management is a theory of management that analyzes and synthesizes workflows. Its main objective is improving economic efficiency, especially labor productivity. It was one of the earliest attempts to apply science to the engineering of processes to management. Scientific management is sometimes known as Taylorism after its pioneer, Frederick Winslow Taylor. Mitcham, Carl and Adam, Briggle ''Management'' in Mitcham (2005) p. 1153 Taylor began the theory's development in the United States during the 1880s and 1890s within manufacturing industries, especially steel. Its peak of influence came in the 1910s. Although Taylor died in 1915, by the 1920s scientific management was still influential but had entered into competition and syncretism with opposing or complementary ideas. Although scientific management as a distinct theory or school of thought was obsolete by the 1930s, most of its themes are still important parts of industrial engineering and management today. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl K
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. The title originates in the Old English word ''eorl'', meaning "a man of noble birth or rank". The word is cognate with the Scandinavian form ''jarl'', and meant "chieftain", particularly a chieftain set to rule a territory in a king's stead. After the Norman Conquest, it became the equivalent of the continental count (in England in the earlier period, it was more akin to a duke; in Scotland, it assimilated the concept of mormaer). Alternative names for the rank equivalent to "earl" or "count" in the nobility structure are used in other countries, such as the '' hakushaku'' (伯爵) of the post-restoration Japanese Imperial era. In modern Britain, an earl is a member of the peerage, ranking below a marquess and above a viscount. A feminine form of ''earl'' never developed; instead, ''countess'' is used. Etymology The term ''earl'' has been compared to the name of the Heruli, and to runic '' erilaz''. Proto-Norse ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Standard
British Standards (BS) are the standards produced by the BSI Group which is incorporated under a royal charter and which is formally designated as the national standards body (NSB) for the UK. The BSI Group produces British Standards under the authority of the charter, which lays down as one of the BSI's objectives to: Formally, as stated in a 2002 memorandum of understanding between the BSI and the United Kingdom Government, British Standards are defined as: Products and services which BSI certifies as having met the requirements of specific standards within designated schemes are awarded the Kitemark. History BSI Group began in 1901 as the ''Engineering Standards Committee'', led by James Mansergh, to standardize the number and type of steel sections, in order to make British manufacturers more efficient and competitive. Over time the standards developed to cover many aspects of tangible engineering, and then engineering methodologies including quality systems, safety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BSI Group
The British Standards Institution (BSI) is the national standards body of the United Kingdom. BSI produces technical standards on a wide range of products and services and also supplies certification and standards-related services to businesses. History BSI was founded as the Engineering Standards Committee in London in 1901.Robert C McWilliam. BSI: The first hundred years. 2001. Thanet Press. London It subsequently extended its standardization work and became the British Engineering Standards Association in 1918, adopting the name British Standards Institution in 1931 after receiving a Royal Charter in 1929. In 1998 a revision of the Charter enabled the organization to diversify and acquire other businesses, and the trading name was changed to BSI Group. The Group now operates in 195 countries. The core business remains standards and standards related services, although the majority of the Group's revenue comes from management systems assessment and certification work. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Francis Leopold Brech
Edward Francis Leopold Brech (26 February 1909 – 22 September 2006) was a British management consultant, and author of management theory and practice books, known for his work on the history of management. Life and work Brech was born in Kennington to a Hungarian father, who worked as catering manager, and a Bavarian mother. After grammar school, Brech was selected by the Roman Catholic bishop of Southwark to be educated as priest. At that time there was a pilot scheme, that required a university graduation before entering the church. In 1929 Brech obtained his BA in humanities at the London University, declined priesthood, and continued to study economics at London University obtaining his BA in 1932.Peter Starbuck. "Obituary : Edward Brech, Management studies for the benefit of all," in: ''The Guardian,'' Tuesday 10 October 2006 At the age of 85 Brech earned his doctorate in British management history through Britain's Open University, where he also was a Visiting Research F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyndall Urwick
Lyndall Fownes Urwick (3 March 1891 – 5 December 1983) was a British management consultant and business thinker. He is recognised for integrating the ideas of earlier theorists like Henri Fayol into a comprehensive theory of management administration. He wrote an influential book called ''The Elements of Business Administration'', published in 1943. With Luther Gulick, he founded the academic journal ''Administrative Science Quarterly''. Biography Youth and military service Urwick was born in Worcestershire, the son of a partner in Fownes Brothers, a long-established glove-making firm. He was educated at Boxgrove Primary School, Repton School and New College, Oxford, where he read History. He saw active service in the trenches during the First World War, rising to the rank of Major, and being awarded the Military Cross. Though he did not himself attend the military Staff College at Camberley, his respect for military training would affect his outlook on management in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rowntree's
Rowntree's is a British confectionery brand and former business based in York, England. Rowntree developed the Kit Kat (introduced in 1935), Aero (introduced in 1935), Fruit Pastilles (introduced in 1881), Smarties (introduced in 1937) brands, and the Rolo and Quality Street brands when it merged with Mackintosh's in 1969 to form Rowntree Mackintosh Confectionery. Rowntree's also launched After Eight thin mint chocolates in 1962. The Yorkie and Lion bars were introduced in 1976. Rowntree's also pioneered the festive selection box (a gift consisting of assorted bars and sweets) which in the UK have been a staple gift at Christmas for over a century. Founded in 1862, the company developed strong associations with Quaker philanthropy. Throughout much of the 19th and 20th centuries, it was one of the big three confectionery manufacturers in the United Kingdom, alongside Cadbury and Fry, both also founded by Quakers. In 1981, Rowntree's received the Queen's Award for Ent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American National Biography
The ''American National Biography'' (ANB) is a 24-volume biographical encyclopedia set that contains about 17,400 entries and 20 million words, first published in 1999 by Oxford University Press under the auspices of the American Council of Learned Societies. Background A 400-entry supplement appeared in 2002. Additional funding came from the Rockefeller Foundation, the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation and the National Endowment for the Humanities. The ''ANB'' bills itself as the successor of the ''Dictionary of American Biography'', which was first published between 1926 and 1937. It is not, however, a strict superset of this older publication; the selection of topics was made anew. It is commonly available in the reference sections of United States libraries, and is available online by subscription (see external links). Awards and reception In 1999, the American Library Association awarded the ''American National Biography'' its Dartmouth Medal as a reference work of outstand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
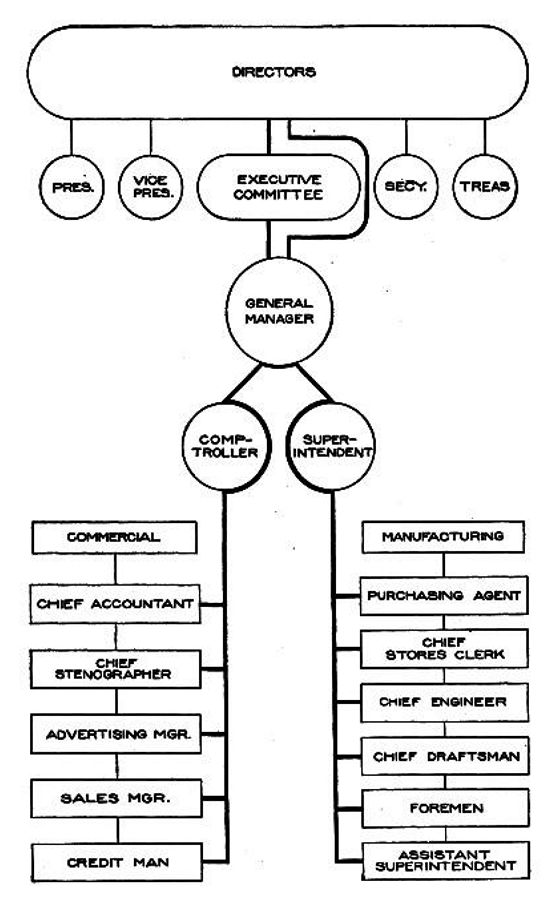
Bedaux System
The efficiency movement was a major movement in the United States, Britain and other industrial nations in the early 20th century that sought to identify and eliminate waste in all areas of the economy and society, and to develop and implement best practices. The concept covered mechanical, economic, social, and personal improvement. The quest for efficiency promised effective, dynamic management rewarded by growth. As a result of the influence of an early proponent, it is more often known as Taylorism. United States The efficiency movement played a central role in the Progressive Era in the United States, where it flourished 1890–1932. Adherents argued that all aspects of the economy, society and government were riddled with waste and inefficiency. Everything would be better if experts identified the problems and fixed them. The result was strong support for building research universities and schools of business and engineering, municipal research agencies, as well as reform of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Bedaux
Charles Eugène Bedaux (10 October 1886 – 18 February 1944) was a French-American millionaire who made his fortune developing and implementing the work measurement aspect of scientific management, notably the Bedaux System. Bedaux was friends with British royalty and Nazis alike, and was a management consultant, big game hunter and explorer. Early years Charles Bedaux was born in the Charenton-le-Pont commune of Paris, France.Steven Kreis, 'Charles E. Bedaux' in ''American National Biography'online/ref> One of five children, his father worked for the French railroad system, and though his two brothers Daniel and Gaston became engineers, Charles became a school dropout. Charles worked a series of menial jobs before befriending Henri Ledoux, a successful pimp from the infamous Pigalle district. The mysterious Ledoux apparently taught Bedaux lessons on proper dress, confidence and street-fighting, but was murdered in 1906.Gaston Bedaux, ''La Vie Ardente de Charles Bedaux'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Winslow Taylor
Frederick Winslow Taylor (March 20, 1856 – March 21, 1915) was an American mechanical engineer. He was widely known for his methods to improve industrial efficiency. He was one of the first management consultants. In 1909, Taylor summed up his efficiency techniques in his book ''The Principles of Scientific Management'' which, in 2001, Fellows of the Academy of Management voted the most influential management book of the twentieth century. His pioneering work in applying engineering principles to the work done on the factory floor was instrumental in the creation and development of the branch of engineering that is now known as industrial engineering. Taylor made his name, and was most proud of his work, in scientific management; however, he made his fortune patenting steel-process improvements. As a result, scientific management is sometimes referred to as ''Taylorism''. Biography Taylor was born in 1856 to a Quaker family in Germantown, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Taylor's f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Edward Knoeppel
Charles Edward (C. E.) Knoeppel (15 April 1881 – 29 November 1936)Knoeppel, Charles Edward (1881–1936) in: Morgen Witzel, ed. The Encyclopedia of the History of American Management'' 2005, p. 303 was an American organizational theorist and consultant, who was among the foremost writers on management techniques early 20th century. Yehouda A. Shenhav (2002). ''Manufacturing Rationality: The Engineering Foundations of the Managerial Revolution''. Oxford University Press. p. 221 Biography Knoeppel was born in Milwaukee, Wisconsin as son of John C. Knoeppel, a practical molder and foundryman, who had received some patents in 1878, 1881, and later on in 1909. The family moved to Buffalo, New York, where he attended school. Financially unable to continue college, he started to work. Knoeppel was journalist for a short while, before he started working his way up in an ironworks from laborer to draughtsman and designer to manager in 1904 at the age of 23. The next years he started ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)