|
Bearing Pressure
Bearing pressure is a particular case of contact mechanics often occurring in cases where a convex surface (male cylinder or sphere) contacts a concave surface (female cylinder or sphere: bore or hemispherical cup). Excessive contact pressure can lead to a typical bearing failure such as a plastic deformation similar to peening. This problem is also referred to as bearing resistance.EN 1993-1-8:2005 '' Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-8: Design of joints'' Hypotheses A contact between a male part (convex) and a female part (concave) is considered when the radii of curvature are close to one another. There is no tightening and the joint slides with no friction therefore, the contact forces are normal to the tangent of the contact surface. Moreover, bearing pressure is restricted to the case where the charge can be described by a radial force pointing towards the center of the joint. Case of a cylinder-cylinder contact In the case of a revolute joint or of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Mechanics
Solid mechanics, also known as mechanics of solids, is the branch of continuum mechanics that studies the behavior of solid materials, especially their motion and deformation under the action of forces, temperature changes, phase changes, and other external or internal agents. Solid mechanics is fundamental for civil, aerospace, nuclear, biomedical and mechanical engineering, for geology, and for many branches of physics such as materials science. It has specific applications in many other areas, such as understanding the anatomy of living beings, and the design of dental prostheses and surgical implants. One of the most common practical applications of solid mechanics is the Euler–Bernoulli beam equation. Solid mechanics extensively uses tensors to describe stresses, strains, and the relationship between them. Solid mechanics is a vast subject because of the wide range of solid materials available, such as steel, wood, concrete, biological materials, textiles, geological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrostatic Pressure
Fluid statics or hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies the condition of the equilibrium of a floating body and submerged body "fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and the pressure in a fluid, or exerted by a fluid, on an immersed body". It encompasses the study of the conditions under which fluids are at rest in stable equilibrium as opposed to fluid dynamics, the study of fluids in motion. Hydrostatics is a subcategory of fluid statics, which is the study of all fluids, both compressible or incompressible, at rest. Hydrostatics is fundamental to hydraulics, the engineering of equipment for storing, transporting and using fluids. It is also relevant to geophysics and astrophysics (for example, in understanding plate tectonics and the anomalies of the Earth's gravitational field), to meteorology, to medicine (in the context of blood pressure), and many other fields. Hydrostatics offers physical explanations for many phenomena of everyday life, such as why ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Trigonometric Identities
In trigonometry, trigonometric identities are equalities that involve trigonometric functions and are true for every value of the occurring variables for which both sides of the equality are defined. Geometrically, these are identities involving certain functions of one or more angles. They are distinct from triangle identities, which are identities potentially involving angles but also involving side lengths or other lengths of a triangle. These identities are useful whenever expressions involving trigonometric functions need to be simplified. An important application is the integration of non-trigonometric functions: a common technique involves first using the substitution rule with a trigonometric function, and then simplifying the resulting integral with a trigonometric identity. Pythagorean identities The basic relationship between the sine and cosine is given by the Pythagorean identity: :\sin^2\theta + \cos^2\theta = 1, where \sin^2 \theta means (\sin \theta)^2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler's Formula
Euler's formula, named after Leonhard Euler, is a mathematical formula in complex analysis that establishes the fundamental relationship between the trigonometric functions and the complex exponential function. Euler's formula states that for any real number : e^ = \cos x + i\sin x, where is the base of the natural logarithm, is the imaginary unit, and and are the trigonometric functions cosine and sine respectively. This complex exponential function is sometimes denoted ("cosine plus i sine"). The formula is still valid if is a complex number, and so some authors refer to the more general complex version as Euler's formula. Euler's formula is ubiquitous in mathematics, physics, and engineering. The physicist Richard Feynman called the equation "our jewel" and "the most remarkable formula in mathematics". When , Euler's formula may be rewritten as , which is known as Euler's identity. History In 1714, the English mathematician Roger Cotes presented a geometrical ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Function
In Euclidean geometry, an affine transformation or affinity (from the Latin, ''affinis'', "connected with") is a geometric transformation that preserves lines and parallelism, but not necessarily Euclidean distances and angles. More generally, an affine transformation is an automorphism of an affine space (Euclidean spaces are specific affine spaces), that is, a function which maps an affine space onto itself while preserving both the dimension of any affine subspaces (meaning that it sends points to points, lines to lines, planes to planes, and so on) and the ratios of the lengths of parallel line segments. Consequently, sets of parallel affine subspaces remain parallel after an affine transformation. An affine transformation does not necessarily preserve angles between lines or distances between points, though it does preserve ratios of distances between points lying on a straight line. If is the point set of an affine space, then every affine transformation on can be repre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action De Contact Ligne Circulaire Avec Deformation Contenant
Action may refer to: * Action (narrative), a literary mode * Action fiction, a type of genre fiction * Action game, a genre of video game Film * Action film, a genre of film * ''Action'' (1921 film), a film by John Ford * ''Action'' (1980 film), a film by Tinto Brass * ''Action 3D'', a 2013 Telugu language film * ''Action'' (2019 film), a Kollywood film. Music * Action (music), a characteristic of a stringed instrument * Action (piano), the mechanism which drops the hammer on the string when a key is pressed * The Action, a 1960s band Albums * ''Action'' (B'z album) (2007) * ''Action!'' (Desmond Dekker album) (1968) * ''Action Action Action'' or ''Action'', a 1965 album by Jackie McLean * ''Action!'' (Oh My God album) (2002) * ''Action'' (Oscar Peterson album) (1968) * ''Action'' (Punchline album) (2004) * ''Action'' (Question Mark & the Mysterians album) (1967) * ''Action'' (Uppermost album) (2011) * ''Action'' (EP), a 2012 EP by NU'EST * ''Action'', a 1984 albu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radian
The radian, denoted by the symbol rad, is the unit of angle in the International System of Units (SI) and is the standard unit of angular measure used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly an SI supplementary unit (before that category was abolished in 1995). The radian is defined in the SI as being a dimensionless unit, with 1 rad = 1. Its symbol is accordingly often omitted, especially in mathematical writing. Definition One radian is defined as the angle subtended from the center of a circle which intercepts an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle. More generally, the magnitude in radians of a subtended angle is equal to the ratio of the arc length to the radius of the circle; that is, \theta = \frac, where is the subtended angle in radians, is arc length, and is radius. A right angle is exactly \frac radians. The rotation angle (360°) corresponding to one complete revolution is the length of the circumference divided by the radius, which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscoplasticity
Viscoplasticity is a theory in continuum mechanics that describes the rate-dependent inelastic behavior of solids. Rate-dependence in this context means that the deformation of the material depends on the rate at which loads are applied. The inelastic behavior that is the subject of viscoplasticity is plastic deformation which means that the material undergoes unrecoverable deformations when a load level is reached. Rate-dependent plasticity is important for transient plasticity calculations. The main difference between rate-independent plastic and viscoplastic material models is that the latter exhibit not only permanent deformations after the application of loads but continue to undergo a creep flow as a function of time under the influence of the applied load. The elastic response of viscoplastic materials can be represented in one-dimension by Hookean spring elements. Rate-dependence can be represented by nonlinear dashpot elements in a manner similar to viscoelasticity. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscoelasticity
In materials science and continuum mechanics, viscoelasticity is the property of materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when undergoing deformation. Viscous materials, like water, resist shear flow and strain linearly with time when a stress is applied. Elastic materials strain when stretched and immediately return to their original state once the stress is removed. Viscoelastic materials have elements of both of these properties and, as such, exhibit time-dependent strain. Whereas elasticity is usually the result of bond stretching along crystallographic planes in an ordered solid, viscosity is the result of the diffusion of atoms or molecules inside an amorphous material.Meyers and Chawla (1999): "Mechanical Behavior of Materials", 98-103. Background In the nineteenth century, physicists such as Maxwell, Boltzmann, and Kelvin researched and experimented with creep and recovery of glasses, metals, and rubbers. Viscoelasticity was further examined in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elasticity (physics)
In physics and materials science, elasticity is the ability of a body to resist a distorting influence and to return to its original size and shape when that influence or force is removed. Solid objects will deform when adequate loads are applied to them; if the material is elastic, the object will return to its initial shape and size after removal. This is in contrast to ''plasticity'', in which the object fails to do so and instead remains in its deformed state. The physical reasons for elastic behavior can be quite different for different materials. In metals, the atomic lattice changes size and shape when forces are applied (energy is added to the system). When forces are removed, the lattice goes back to the original lower energy state. For rubbers and other polymers, elasticity is caused by the stretching of polymer chains when forces are applied. Hooke's law states that the force required to deform elastic objects should be directly proportional to the distance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
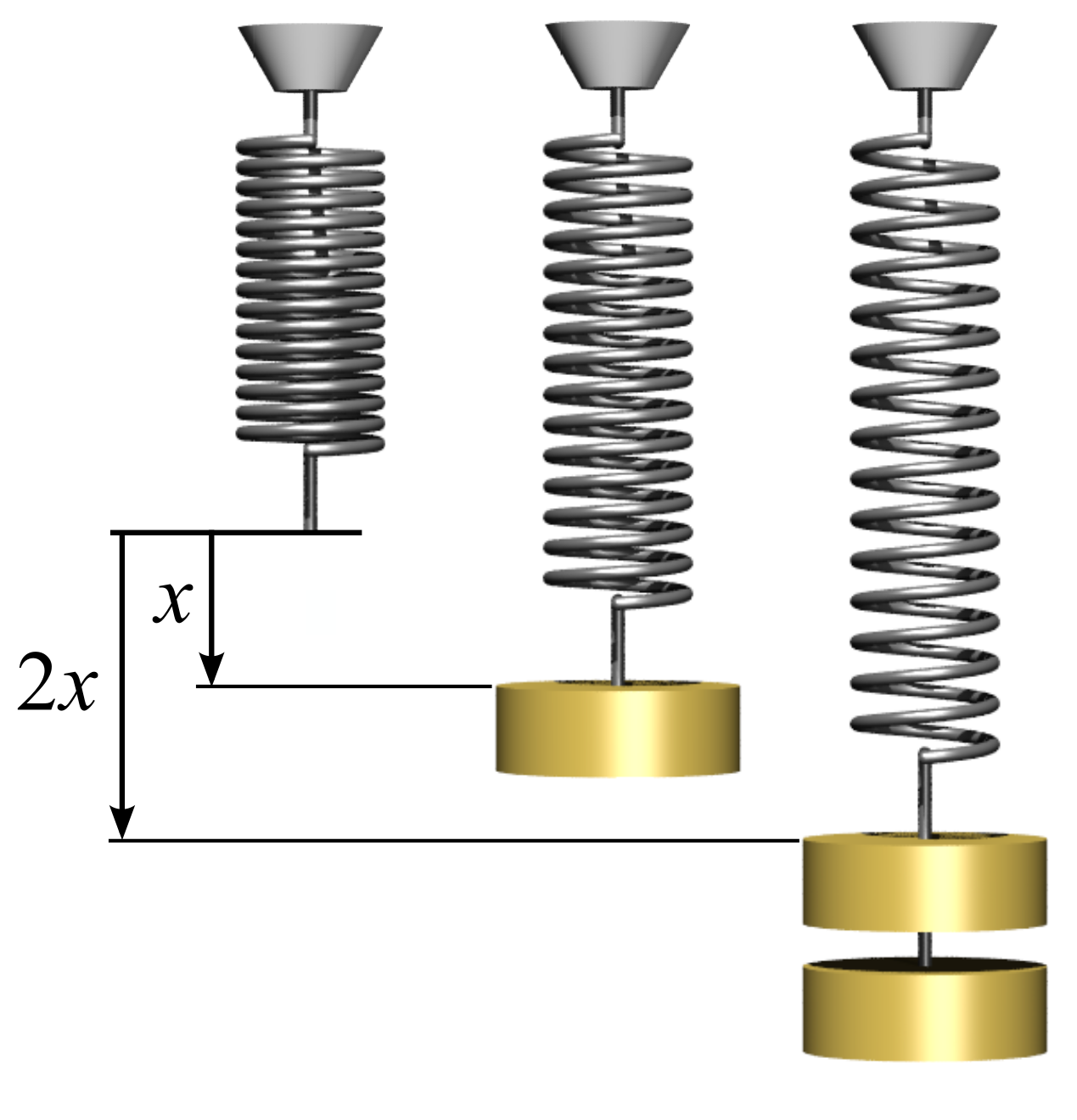
Hooke's Law
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring (device), spring by some distance () Proportionality (mathematics)#Direct_proportionality, scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of the spring (i.e., its stiffness), and is small compared to the total possible deformation of the spring. The law is named after 17th-century British physicist Robert Hooke. He first stated the law in 1676 as a Latin anagram. He published the solution of his anagram in 1678 as: ("as the extension, so the force" or "the extension is proportional to the force"). Hooke states in the 1678 work that he was aware of the law since 1660. Hooke's equation holds (to some extent) in many other situations where an elasticity (physics), elastic body is Deformation (physics), deformed, such as wind blowing on a tall building, and a musician plucking a string (music), string of a guitar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)