|
Bawan
Bawan is a large village and corresponding community development block in Hardoi district of Uttar Pradesh, India. It is located 10km west of Hardoi, on the south side of the road to Bazpur-Naktaura and the Sai Ghat. Bawan was historically the seat of a pargana since at least the time of the Mughal Emperor Akbar, and it is also the site of a mela held in honour of Darshan Debi on the first Sunday of Bhadon, at a site called the Suraj Kund. The main staple crops here are wheat, rice, and gram. Markets are held on Mondays and Thursdays. As of 2011, the population of Bawan is 13,524, in 2,230 households. History According to tradition, Bawan was founded by a person named Rajpal before the reign of Rama in Ayodhya. It is said that later, the 11th-century Muslim folk hero Ghazi Sayyid Salar Masud sent a force from Kannauj to conquer Bawan, and that the Muslim soldiers who died in the ensuing battle were buried near the Suraj Kund. Another one of Salar Masud's companions, Makhdum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
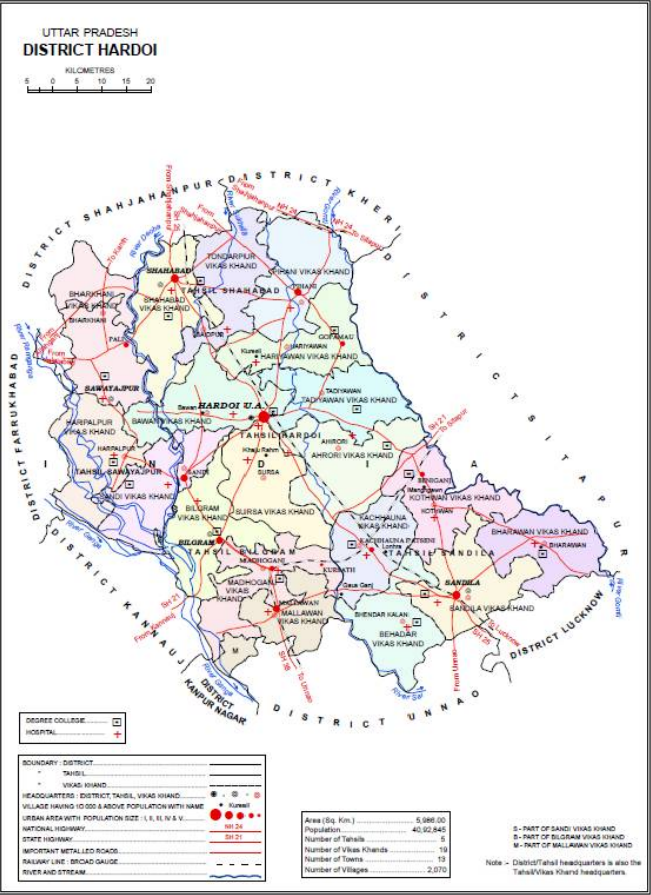
Hardoi District
Hardoi district is a district situated in the center of Uttar Pradesh, India. The district headquarters is in the city of Hardoi. Hardoi is the third largest district of Uttar Pradesh. It falls under Lucknow division in the history region of Awadh As of the 2011 census, the total population of Hardoi district is 4,092,845 people, in 730,442 households. It is the 13th-most populous district in Uttar Pradesh. History The present-day Hardoi district was created by the British after their takeover of Awadh in 1856. At the time of Akbar in the 1500s, the area of the modern district was divided between the sarkars of Lucknow and Khairabad. Five ''mahal''s were in Lucknow sarkar: Sandila, Mallanwan, Kachhandao, "Garanda" (probably a miscopying of Gundwa), and Bilgram. The Ain-i-Akbari does list a mahal of Hardoi in Lucknow district, but this was referring to the Hardoi in modern Rae Bareli district instead of the one in Hardoi district. As for the sarkar of Khairabad, the mahals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions. History Pre-independence The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region. The British Raj mostly retained the administrative structure of the preceding Mughal Empire. India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies), directly governed by the British, and princely states, which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held ''de facto'' sovereignty ( suzerainty) over the princely states. 1947–1950 Between 1947 and 1950 the territories of the princely states were politically integrated into the Indian union. Most were merged into existing provinces; others were organised into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeological record suggests that wheat was first cultivated in the regions of the Fertile Crescent around 9600 BCE. Botanically, the wheat kernel is a type of fruit called a caryopsis. Wheat is grown on more land area than any other food crop (, 2014). World trade in wheat is greater than for all other crops combined. In 2020, world production of wheat was , making it the second most-produced cereal after maize. Since 1960, world production of wheat and other grain crops has tripled and is expected to grow further through the middle of the 21st century. Global demand for wheat is increasing due to the unique viscoelastic and adhesive properties of gluten proteins, which facilitate the production of processed foods, whose consumption is inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is about and one hectare contains about . In 1795, when the metric system was introduced, the ''are'' was defined as 100 square metres, or one square decametre, and the hectare ("hecto-" + "are") was thus 100 ''ares'' or km2 (10,000 square metres). When the metric system was further rationalised in 1960, resulting in the International System of Units (), the ''are'' was not included as a recognised unit. The hectare, however, remains as a non-SI unit accepted for use with the SI and whose use is "expected to continue indefinitely". Though the dekare/decare daa (1,000 m2) and are (100 m2) are not officially "accepted for use", they are still used in some contexts. Description The hectare (), although not a unit of SI, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1981 Census Of India ...
The 1981 Census of India was the 12th in a series of censuses held in India every decade since 1872. The population of India was counted as 685,184,692 people. Population by state Religious demographics ;Population trends for major religious groups in India (1981) See also *Demographics of India References External links * {{Census of India Census Of India, 1978 Censuses in India Political history of India India India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acre
The acre is a unit of land area used in the imperial Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism. Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to: Places United States * Imperial, California * Imperial, Missouri * Imperial, Nebraska * Imperial, Pennsylvania * Imperial, Texa ... and United States customary units#Units of area, US customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one Chain (unit), chain by one furlong (66 by 660 feet), which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the International yard and pound, international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".National Institute of Standards and Technolog(n.d.) General Tables of Units of Measurement . Traditionally, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1961 Census Of India
The 1961 Census of India was the tenth in a series of censuses held in India every decade since 1872. The population of India was counted as 438,936,918 people. Population by state Language data The 1961 census recognized 1,652 ''mother tongues'', counting all declarations made by any individual at the time when the census was conducted. However, the declaring individuals often mixed names of languages with those of dialects, sub-dialects and dialect clusters or even castes, professions, religions, localities, regions, countries and nationalities. The list therefore includes "languages" with barely a few individual speakers as well as 530 unclassified "mother tongues" and more than 100 idioms that are non-native to India, including linguistically unspecific demonyms such as "African", "Canadian" or "Belgian". Modifications were done by bringing in two additional components- place of birth i.e. village or town and duration of stay ( if born elsewhere). See also *Demographics o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmin
Brahmin (; sa, ब्राह्मण, brāhmaṇa) is a varna as well as a caste within Hindu society. The Brahmins are designated as the priestly class as they serve as priests (purohit, pandit, or pujari) and religious teachers (guru or acharya). The other three varnas are the Kshatriya, Vaishya and Shudra. The traditional occupation of Brahmins is that of priesthood at the Hindu temples or at socio-religious ceremonies, and rite of passage rituals such as solemnising a wedding with hymns and prayers.James Lochtefeld (2002), Brahmin, The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , page 125 Traditionally, the Brahmins are accorded the highest ritual status of the four social classes. Their livelihood is prescribed to be one of strict austerity and voluntary poverty ("A Brahmin should acquire what just suffices for the time, what he earns he should spend all that the same day"). In practice, Indian texts suggest that some Brahmins historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweetmeats
Confectionery is the Art (skill), art of making confections, which are food items that are rich in sugar and carbohydrates. Exact definitions are difficult. In general, however, confectionery is divided into two broad and somewhat overlapping categories: bakers' confections and sugar confections. The occupation of confectioner encompasses the categories of cooking performed by both the French ''Pâtissier, patissier'' (pastry chef) and the ''confiseur'' (sugar worker). Bakers' confectionery, also called flour confections, includes principally sweet pastries, cakes, and similar Baking, baked goods. Baker's confectionery excludes everyday Bread, breads, and thus is a subset of products produced by a baker. Sugar confectionery includes candies (also called ''sweets'', short for ''sweetmeats'', in many English-speaking countries), candied nuts, chocolates, chewing gum, bubble gum, pastillage, and other confections that are made primarily of sugar. In some cases, chocolate conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makhdum Abdul Qasim
Makhdoom ( ar, مخدوم, meaning ''one who is served'' and sometimes spelled Makhdum, bn, মখদুম, Mokhdum) is an Arabic word meaning "Teacher of Sunnah." It is a title for Pirs, in South and Central Asia. People with the title Makhdoom * Makhdoom Yahya Maneri (1263 - 1379 AD) – a mystic who lived in Bihar Sharif * Makhdoom Jahaniyan Jahangasht (1308- 1384 AD) - a world-traveling Sufi Saint who was spiritual master of king Firoz Shah Tughlaq, Ashraf Jahangir Simnani and 80 makhdooms of his time. * Hamza Makhdoom – a mystic from Kashmir (d. 1563 AD) * Makhdoom Mian Mir – a Sufi mystic from Lahore who laid first foundation of the Golden Temple in Amritsar * Makhdoom Ali Mahimi – a Sufi saint from the Konkan in India *\ Makhdoom Syed Yousaf Raza Gillani – a former Prime Minister of Pakistan * Makhdoom Muhammad Ameen Faheem – a former Pakistani politician and leader of PPP * Makhdoom Syed Faisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannauj
Kannauj ( Hindustani pronunciation: ənːɔːd͡ʒ is a city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city's name is a corrupted form of the classical name ''Kanyakubja''. It was also known as ''Mahodaya'' during the time of Mihira Bhoja Kannauj is an ancient city. It is said that the Kanyakubja Brahmins who included Shandilya (teacher of Rishi Bharadwaja) were held one of the three prominent families originally from Kannauj. In Classical India, it served as the center of imperial Indian dynasties. The earliest of these was the Maukhari dynasty, and later, Emperor Harsha of the Vardhana dynasty.Tripathi, ''History of Kanauj'', p. 192 The city later came under the Gahadavala dynasty, and under the rule of Govindachandra, the city reached "unprecedented glory". Kannauj was also the main place of war in the Tripartite struggle between the Gurjara-Pratihara, the Palas and the Rashtra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghazi Sayyid Salar Masud
Ghazi Salar Masud or Ghazi Miyan (1014 – 1034 CE) was a semi-legendary Muslim figure from India. By the 12th century, he had become reputed as a warrior, and his tomb (''dargah'') at Bahraich, Uttar Pradesh, India, had become a place of pilgrimage. The main source of information about him is the chivalric romance ''Mirat-i-Masudi'' ("Mirror of Masud"), a Persian-language hagiography written by Abdur Rahman Chishti in the 1620s. According to this biography, he was a nephew of the Ghaznavid invader Mahmud, and accompanied his uncle in the conquest of India during the early 11th century. However, the Ghaznavid chronicles do not mention him, and other claims in ''Mirat-i-Masudi'' are also of doubtful historicity. ''Mirat-i-Masudi'' legend The ''Mirat-i-Masudi'' narrates the legend of Salar Masud as follows: Early life In 1011 CE, the Muslims of Jalgaon, whose rights were being infringed upon by the local Hindu rulers, appealed Sultan Mahmud of Ghazni for help. Mahmud agreed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Bhumi_Puja%2C_yajna.jpg)

