|
Baudhayana Sulba Sutra
The (Sanskrit: बौधायन) are a group of Vedic Sanskrit texts which cover dharma, daily ritual, mathematics and is one of the oldest Dharma-related texts of Hinduism that have survived into the modern age from the 1st-millennium BCE. They belong to the ''Taittiriya'' branch of the Krishna Yajurveda school and are among the earliest texts of the genre.. In relative chronology, they predate Āpastamba, which is dated by Robert Lingat to the ''sutra'' period proper, between c. 500 to 200 BCE. Robert Lingat, The Classical Law of India, (Munshiram Manoharlal Publishers Pvt Ltd, 1993), p. 20 The Baudhayana sūtras consist of six texts: # the , probably in 19 (questions), # the in 20 (chapters), # the in 4 , # the Grihyasutra in 4 , # the in 4 and # the in 3 . The ' is noted for containing several early mathematical results, including an approximation of the square root of 2 and the statement of the Pythagorean theorem. Baudhāyana Shrautasūtra His Śr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedic Sanskrit
Vedic Sanskrit was an ancient language of the Indo-Aryan subgroup of the Indo-European language family. It is attested in the Vedas and related literature compiled over the period of the mid- 2nd to mid-1st millennium BCE. It was orally preserved, predating the advent of writing by several centuries. Extensive ancient literature in the Vedic Sanskrit language has survived into the modern era, and this has been a major source of information for reconstructing Proto-Indo-European and Proto-Indo-Iranian history. In the pre-historic era, Proto-Indo-Iranian split into Proto-Iranian and Proto-Indo-Aryan and the two languages evolved independently of each other. History Prehistoric derivation The separation of Proto-Indo-Iranian language into Proto-Iranian and Proto-Indo-Aryan is estimated, on linguistic grounds, to have occurred around or before 1800 BCE. The date of composition of the oldest hymns of the Rigveda is vague at best, generally estimated to roughly 1500 BCE. Both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iyengar
Iyengar (also spelt Ayyangar or Aiyengar, pronounced ) refers to the name of an ethnoreligious community of Tamil-speaking Hindu Brahmins, whose members follow Sri Vaishnavism and the Visishtadvaita philosophy propounded by Ramanuja. Found mostly in the Southern Indian states of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh, Iyengars are divided into two denominations, the Vadakalai and the Tenkalai. The community belongs to the Pancha Dravida Brahmana classification of Brahmins in India. Etymology There are several opinions regarding the etymology of the term ''Iyengar'', which is the anglicized form of the Dravidian word ''Aiyaṅgār'' (, ). One is that it derives from the Proto-Dravidian word ''ayya-gāru'' ( 𑀅𑀬𑀕𑀭𑀼), which became ''Ayyangāru'' (), and later ''Ayengar''. The term ''ayya'' is the Tamil equivalent of the Sanskrit word ''ārya,'' ( 𑀆𑀭𑁆𑀬/आर्य) which in Sanskrit means ''noble''. ''Gāru'' refers to a form of the Pali term ''gā ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Triangle
A right triangle (American English) or right-angled triangle (British), or more formally an orthogonal triangle, formerly called a rectangled triangle ( grc, ὀρθόσγωνία, lit=upright angle), is a triangle in which one angle is a right angle (that is, a 90-degree angle), i.e., in which two sides are perpendicular. The relation between the sides and other angles of the right triangle is the basis for trigonometry. The side opposite to the right angle is called the ''hypotenuse'' (side ''c'' in the figure). The sides adjacent to the right angle are called ''legs'' (or ''catheti'', singular: ''cathetus''). Side ''a'' may be identified as the side ''adjacent to angle B'' and ''opposed to'' (or ''opposite'') ''angle A'', while side ''b'' is the side ''adjacent to angle A'' and ''opposed to angle B''. If the lengths of all three sides of a right triangle are integers, the triangle is said to be a Pythagorean triangle and its side lengths are collectively known as a ''Pythagor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
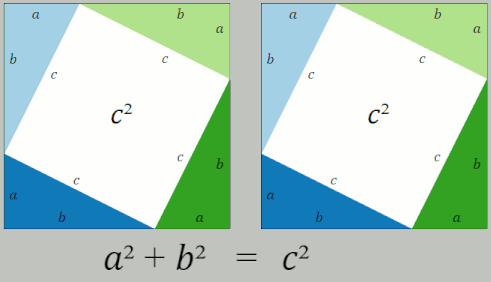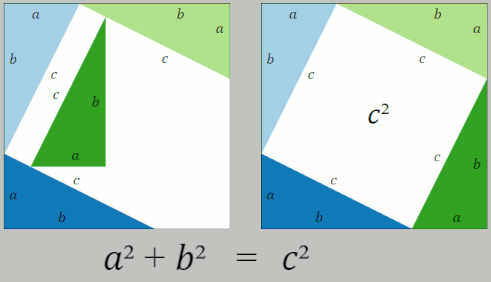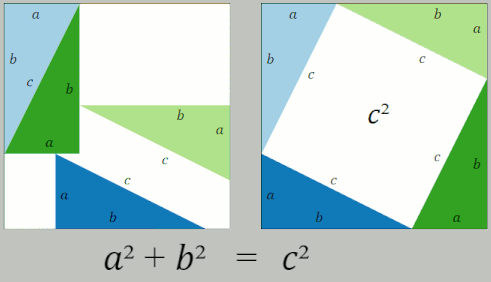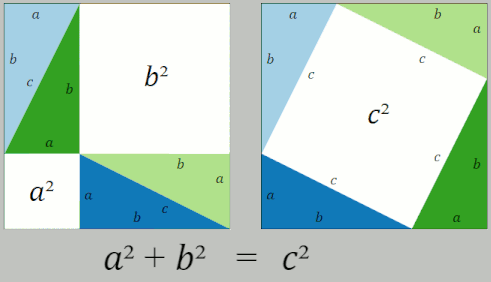
Pythagorean Theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. This theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides ''a'', ''b'' and the hypotenuse ''c'', often called the Pythagorean equation: :a^2 + b^2 = c^2 , The theorem is named for the Greek philosopher Pythagoras, born around 570 BC. The theorem has been proven numerous times by many different methods – possibly the most for any mathematical theorem. The proofs are diverse, including both geometric proofs and algebraic proofs, with some dating back thousands of years. When Euclidean space is represented by a Cartesian coordinate system in analytic geometry, Euclidean distance satisfies the Pythagorean relation: the squared dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Govindasvāmi
Govindasvāmi (or Govindasvāmin, Govindaswami) (c. 800 – c. 860) was an Indian mathematical astronomer most famous for his ''Bhashya'', a commentary on the ''Mahābhāskarīya'' of Bhāskara I, written around 830. The commentary contains many examples illustrating the use of a Sanskrit place-value system and the construction of a sine table. His works have been quoted extensively by Sankaranarayana (fl. 869), Udayadivakara (fl. 1073) and Nilakantha Somayaji (c. 1444-1544). Sankaranarayana was the director of the observatory founded in Mahodayapuram, the capital of the Chera kingdom, and is believed to be the student of Govindasvami. In his book, Sankaranarayana gives explanations to the insightful questions of the king Ravi Varma, then ruler of Mahodayapuram and from these references the period of Sankaranarayana is known. His work ''Govindakriti'' was a sequel to Āryabhaṭīya ''Aryabhatiya'' (IAST: ') or ''Aryabhatiyam'' ('), a Sanskrit astronomical treatise, is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Srautasutra
Kalpa ( sa, कल्प) means "proper, fit" and is one of the six disciplines of the Vedānga, or ancillary science connected with the Vedas – the scriptures of Hinduism. This field of study is focused on the procedures and ceremonies associated with Vedic ritual practice.James Lochtefeld (2002), "Kalpa" in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , p. 339. The major texts of Kalpa Vedanga are called ''Kalpa Sutras'' in Hinduism. The scope of these texts includes Vedic rituals, rites of passage rituals associated with major life events such as birth, wedding and death in family, as well as personal conduct and proper duties in the life of an individual. Most Kalpasutras texts have experienced interpolation, changes and consequent corruption over their history, and Apasthamba Kalpasutra ancillary to the Yajurveda may be the best preserved text in this genre. Kalpa Sutras are also found in other Indian traditions, such as Jainism. Etymology K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praśna
The Prashnopanishad ( sa, प्रश्नोपनिषद्, ) is an ancient Sanskrit text, embedded inside Atharva Veda, ascribed to ''Pippalada'' sakha of Vedic scholars. It is a Mukhya (primary) Upanishad, and is listed as number 4 in the Muktika canon of 108 Upanishads of Hinduism. The Prashna Upanishad contains six ''Prashna'' (questions), and each is a chapter with a discussion of answers.Robert HumePrasna Upanishad Thirteen Principal Upanishads, Oxford University Press, pages 378-390 The chapters end with the phrase, ''prasnaprativakanam'', which literally means, "thus ends the answer to the question". In some manuscripts discovered in India, the Upanishad is divided into three ''Adhyayas'' (chapters) with a total of six ''Kandikas'' (कण्डिका, short sections).Raksha BandhanRaksha BandhanBibliotheca Indica, Vol. XV, No. 41 and 50, Asiatic Society of Bengal, pages 119-141 The first three questions are profound metaphysical questions but, states Eduard R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalpa (Vedanga)
Kalpa ( sa, कल्प) means "proper, fit" and is one of the six disciplines of the Vedānga, or ancillary science connected with the Vedas – the scriptures of Hinduism. This field of study is focused on the procedures and ceremonies associated with Vedic ritual practice.James Lochtefeld (2002), "Kalpa" in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , p. 339. The major texts of Kalpa Vedanga are called ''Kalpa Sutras'' in Hinduism. The scope of these texts includes Vedic rituals, rites of passage rituals associated with major life events such as birth, wedding and death in family, as well as personal conduct and proper duties in the life of an individual. Most Kalpasutras texts have experienced interpolation, changes and consequent corruption over their history, and Apasthamba Kalpasutra ancillary to the Yajurveda may be the best preserved text in this genre. Kalpa Sutras are also found in other Indian traditions, such as Jainism. Etymology K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amavasya
Amāvásyā () is the lunar phase of the new moon in Sanskrit. Indian calendars use 30 lunar phases, called tithi in India. The dark moon tithi is when the Moon is within 12 degrees of the angular distance between the Sun and Moon before conjunction ( syzygy). The New Moon tithi (called Pratipada or Prathama) is the 12 angular degrees after syzygy. Amāvásyā is often translated as new moon since there is no standard term for the Moon before conjunction in English. Meaning of Amāvásyā In Sanskrit, "amā" means "together" and "vásya" means "to dwell" or "cohabit". It also means "na" +"ma"+"asya" meaning to "na" = "No, "ma"=Moon, "Asya"="There" in turn meaning to There is no Moon i.e., Moon is not visible. In the ''pūrṇimānta māna'' Hindu lunar calendar used in most parts of the Indian subcontinent, the lunar month starts on the day following the full moon or ''purnima'' and therefore Amāvásyā always falls in the middle of the month. However, in the '' amānta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one of the most popular and widely revered among Indian divinities. Krishna's birthday is celebrated every year by Hindus on Krishna Janmashtami according to the lunisolar Hindu calendar, which falls in late August or early September of the Gregorian calendar. The anecdotes and narratives of Krishna's life are generally titled as ''Krishna Leela''. He is a central character in the ''Mahabharata'', the '' Bhagavata Purana'', the ''Brahma Vaivarta Purana,'' and the '' Bhagavad Gita'', and is mentioned in many Hindu philosophical, theological, and mythological texts. They portray him in various perspectives: as a god-child, a prankster, a model lover, a divine hero, and the universal supreme being. Quote: "Krsna's various appearances as a di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kongu Vellalars
Kongu Vellalar is a community found in the Kongu region of Tamil Nadu, India. Etymology The Vellalar of the Kongu country came to be known as Kongu Vellalar. They are also known by names such as "Bupaalan", Gangavamsam, Kudiyaanavar and Vivasaayi, and use the title Gounder as a caste appellation in their personal names. Origin According to the ''Kongu Vellalar Puranam'', a 19th-century work by Mahavidwan Kandasamy Kavirayar, the Vellalar of the Kongu country trace their origin to Marabalan, a mythical figure who was created from the river Ganges to rid the world of hunger. Marabalan turned to agriculture and his descendants became the Vellalar. Marabalan had various titles such as Gangavamsa, Devar, Vellalar, Bupaalan, etc. Interestingly the Gandadikara Vokkaligas of the neighbouring parts of Karnataka also claim origin from the banks of the Ganges.:”Gangadikara is a contraction of the term Gangawadikara (A man of Gangavadi)” According to Burton Stein, the Gangadikara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerala
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Canara, and Thiruvithamkoor. Spread over , Kerala is the 21st largest Indian state by area. It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. With 33 million inhabitants as per the 2011 census, Kerala is the 13th-largest Indian state by population. It is divided into 14 districts with the capital being Thiruvananthapuram. Malayalam is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state. The Chera dynasty was the first prominent kingdom based in Kerala. The Ay kingdom in the deep south and the Ezhimala kingdom in the north formed the other kingdoms in the early years of the Common Era (CE). The region had been a prominent spic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |