|
Battle Of The Hellespont (321 BC)
The Battle of the Hellespont took place in 321 BC between the armies of Craterus and Neoptolemus against Eumenes. It was part of the wars between Alexander's successors. Eumenes and Neoptolemus were sent by Perdiccas to prevent Craterus crossing the Hellespont into Asia, but Neoptolemus deserted to join Craterus. Eumenes won the battle, and both Craterus and Neoptolemus were killed. Prelude The death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC threw his empire into a state of political and military turmoil, with his generals and governors splitting up the empire as his “Successors” (the Diadochi). Perdiccas inherited the main Macedonian army and the title ‘regent of the Asiatic Empire.’ He also tried to marry Alexander’s sister Cleopatra of Macedon, which would have given him a claim to the Macedonian throne. Because of this a coalition of other successors formed against him. An army under Craterus was sent to Asia to confront Perdiccas and his allies. Perdiccas sent Eumenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wars Of The Diadochi
The Wars of the Diadochi ( grc, Πόλεμοι τῶν Διαδόχων, '), or Wars of Alexander's Successors, were a series of conflicts that were fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule his Macedonia (ancient kingdom)#Empire, empire following his death. The fighting occurred between 322 and 281 BC. Background Alexander the Great died on June 10, 323 BC, leaving behind an empire that stretched from Macedon and the rest of Hellenistic Greece, Greece in Europe to the Indus valley in South Asia. The empire had no clear successor, with the Argead dynasty, Argead family, at this point, consisting of Alexander's mentally disabled half-brother, Philip III of Macedon, Arrhidaeus; his unborn son Alexander IV of Macedon, Alexander IV; his reputed illegitimate son Heracles, son of Alexander, Heracles; his mother Olympias; his sister Cleopatra of Macedon, Cleopatra; and his half-sisters Thessalonike of Macedon, Thessalonike and Cynan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altıkulaç Sarcophagus Combat Scene (detail) , a 4th-century sarcophagus
{{disambig ...
Altıkulaç can refer to: * Altıkulaç, Abana, a village in Turkey * Altıkulaç, Çan * Altıkulaç Sarcophagus The Altıkulaç Sarcophagus, or Çan sarcophagus, is an early 4th century BCE (400-375 BCE) sarcophagus. It is sometimes said to be in the Greco-Persian style. The sarcophagus was found in 1998 in a circular corbel-vaulted tomb within the Çing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
321 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 321 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Calvinus and Caudinus (or, less frequently, year 433 '' Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 321 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Macedonian Empire * Antipater appoints Antigonus commander in chief of his army in Asia Minor and sends him with Craterus to fight against Eumenes, the satrap of Cappadocia and a supporter of Perdiccas. * Leaving Eumenes to hold Asia Minor against Craterus and Antigonus, Perdiccas marches against Ptolemy, but when he fails to cross the Nile he is murdered by mutinous officers. Prominent among the mutineers is Seleucus. A truce is arranged, leaving Ptolemy in power in Egypt and Seleucus in power in Babylon. * The key remaining generals (diadochi) of the late Alexander the Great agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Lives
Plutarch's ''Lives of the Noble Greeks and Romans'', commonly called ''Parallel Lives'' or ''Plutarch's Lives'', is a series of 48 biographies of famous men, arranged in pairs to illuminate their common moral virtues or failings, probably written at the beginning of the second century AD. The surviving ''Parallel Lives'' (Greek: Βίοι Παράλληλοι, ''Bíoi Parállēloi'') comprises 23 pairs of biographies, each pair consisting of one Greek and one Roman of similar destiny, such as Alexander the Great and Julius Caesar, or Demosthenes and Cicero. It is a work of considerable importance, not only as a source of information about the individuals described, but also about the times in which they lived. Motivation ''Parallel Lives'' was Plutarch's second set of biographical works, following the Lives of the Roman Emperors from Augustus to Vitellius. Of these, only the Lives of Galba and Otho survive. As he explains in the first paragraph of his ''Life of Alexander'', Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Life Early life Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His name is derived from Pluto (πλοῦτον), an epithet of Hades, and Archos (ἀρχός) meaning "Master", the whole name meaning something like "Whose master is Pluto". His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipater
Antipater (; grc, , translit=Antipatros, lit=like the father; c. 400 BC319 BC) was a Macedonian general and statesman under the subsequent kingships of Philip II of Macedon and his son, Alexander the Great. In the wake of the collapse of the Argead house, his son Cassander would eventually come to rule Macedonia as a king in his own right. In 320 BC, Antipater was elected regent of all of Alexander the Great's Empire but died the following year. In a perplexing turn of events, he chose an infantry officer named Polyperchon as his successor instead of his son Cassander, and a two-year-long power struggle ( the Second War of the Diadochi) ensued. Career under Philip and Alexander Nothing is known of his early career until 342 BC, when he was appointed by Philip to govern Macedon as his regent while the former left for three years of hard and successful campaigning against Thracian and Scythian tribes, which extended Macedonian rule as far as the Hellespont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled by the royal Argead dynasty, which was followed by the Antipatrid and Antigonid dynasties. Home to the ancient Macedonians, the earliest kingdom was centered on the northeastern part of the Greek peninsula,. and bordered by Epirus to the west, Paeonia to the north, Thrace to the east and Thessaly to the south. Before the 4th century BC, Macedonia was a small kingdom outside of the area dominated by the great city-states of Athens, Sparta and Thebes, and briefly subordinate to Achaemenid Persia. During the reign of the Argead king PhilipII (359–336 BC), Macedonia subdued mainland Greece and the Thracian Odrysian kingdom through conquest and diplomacy. With a reformed army containing phalanxes wielding the ''sarissa'' pike, PhilipII d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
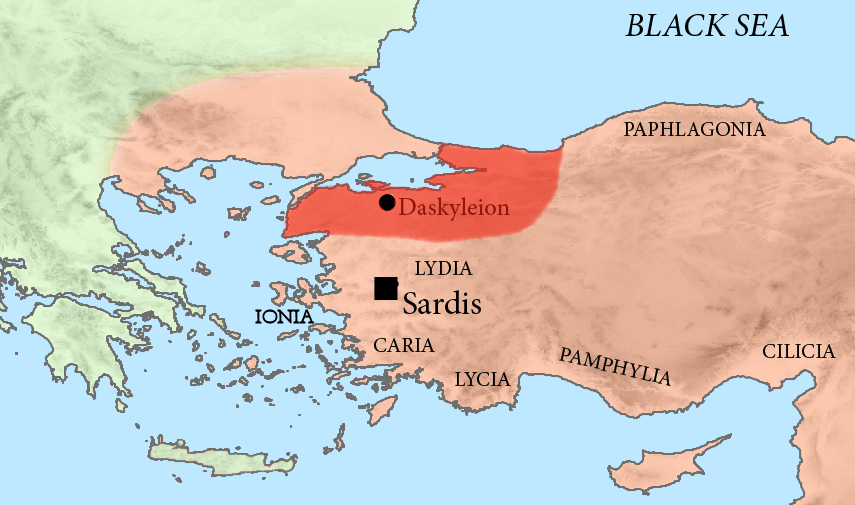
Pharnabazus Of Phrygia
Pharnabazus III (Old Iranian: ''Farnabāzu'', Ancient Greek: ''Φαρνάβαζος''; c. 370 BC - after 320 BC) was a Persian satrap who fought against Alexander the Great. His father was Artabazus II, and his mother a Greek from Rhodes. Youth in Macedonia Pharnabazus was the son of Artabazus, satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia. However, Artabazus was exiled after a failed rebellion against Artaxerxes III in 358 BC. From 352 to 342, the family went into exile to Macedonia, in the capital of Pella, under the rule of king Philip II (360-336), where they met the young Prince Alexander, future Alexander the Great. With Artabazus and Pharnabazus was Memnon of Rhodes, a Greek mercenary and relative by marriage. Artabazus, Pharnabazus and Memnon were later allowed to return to Persia, in 343 BC. Memnon obtained the command of the Persian navy in the Aegean sea in 334 BC, with Pharnabazus joining him. War against Alexander When Alexander invaded the Persian empire, Memnon defended the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonian Phalanx
The Macedonian phalanx ( gr, Μακεδονική φάλαγξ) was an infantry formation developed by Philip II from the classical Greek phalanx, of which the main innovation was the use of the sarissa, a 6 meter pike. It was famously commanded by Philip's son Alexander the Great during his conquest of the Achaemenid Empire between 334 and 323 BC. The Macedonian phalanx model then spread throughout the Hellenistic world, where it became the standard battle formation for pitched battles. During the Macedonian Wars against the Roman Republic (214–148 BC), the phalanx appeared obsolete against the more manoeuvrable Roman legions. Development In 359 BC, following the Macedonian defeat by the Illyrians, which killed the majority of Macedonia's army and King Perdiccas III of Macedon, Perdiccas' brother Philip II took the throne. Philip II was a hostage in Thebes for much of his youth (367–360), where he witnessed the combat tactics of the general Epaminondas, which then influence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artabazos II
Artabazos II (in Greek Ἀρτάβαζος) ( fl. 389 – 328 BC) was a Persian general and satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia. He was the son of the Persian satrap of Hellespontine Phrygia Pharnabazus II, and younger kinsman (most probably nephew) of Ariobarzanes of Phrygia who revolted against Artaxerxes II around 356 BC. His first wife was an unnamed Greek woman from Rhodes, sister of the two mercenaries Mentor of Rhodes and Memnon of Rhodes. Towards the end of his life, he became satrap of Bactria for Alexander the Great. Revolt of Datames In 362 BC, Artabazos was sent by Artaxerxes II to capture Datames, the satrap of Cappadocia, who had joined in the Satraps' revolt in which Artabazus' brother, Ariobarzanes, was a participant. However, Artabazos was defeated by Datames. Artaxerxes II ultimately prevailed, and Ariobarzanes was crucified and Datames assassinated. Rebellion against Artaxerxes III Following the capture and death of his brother, Artabazos was made satr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrygia
In classical antiquity, Phrygia ( ; grc, Φρυγία, ''Phrygía'' ) was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Asian Turkey, centered on the Sangarios River. After its conquest, it became a region of the great empires of the time. Stories of the heroic age of Greek mythology tell of several legendary Phrygian kings: * Gordias, whose Gordian Knot would later be cut by Alexander the Great * Midas, who turned whatever he touched to gold * Mygdon, who warred with the Amazons According to Homer's ''Iliad'', the Phrygians participated in the Trojan War as close allies of the Trojans, fighting against the Achaeans. Phrygian power reached its peak in the late 8th century BC under another, historical, king Midas, who dominated most of western and central Anatolia and rivaled Assyria and Urartu for power in eastern Anatolia. This later Midas was, however, also the last independent king of Phrygia before Cimmerians sacked the Phrygian capital, Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleopatra Of Macedon
Cleopatra of Macedonia (Greek: Κλεοπάτρα της Μακεδονίας; c. 355/354 BC – 308 BC), or Cleopatra of Epirus (Greek: Κλεοπάτρα της Ηπείρου) was an ancient Macedonian princess and later queen regent of Epirus. The daughter of Philip II of Macedon and Olympias of Epirus, she was the only full sibling of Alexander the Great. Her other siblings include half sisters Thessalonike and Cynane, and half-brother Philip III of Macedon. Cleopatra grew up in the care of her mother in Pella. In 338 BC, Cleopatra stayed in Pella with her father while her mother Olympias fled to exile in Epirus with her Molossian brother Alexander I of Epirus (Cleopatra's uncle), and Cleopatra's brother Alexander fled to Illyria. Soon Philip felt he had to ally himself to Alexander I by offering his daughter's hand in marriage. A large wedding between Cleopatra and her uncle Alexander I was held in 336 BC. It was at the celebration of her nuptials, which took place on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)