|
Battle Of Sufetula (546 Or 547)
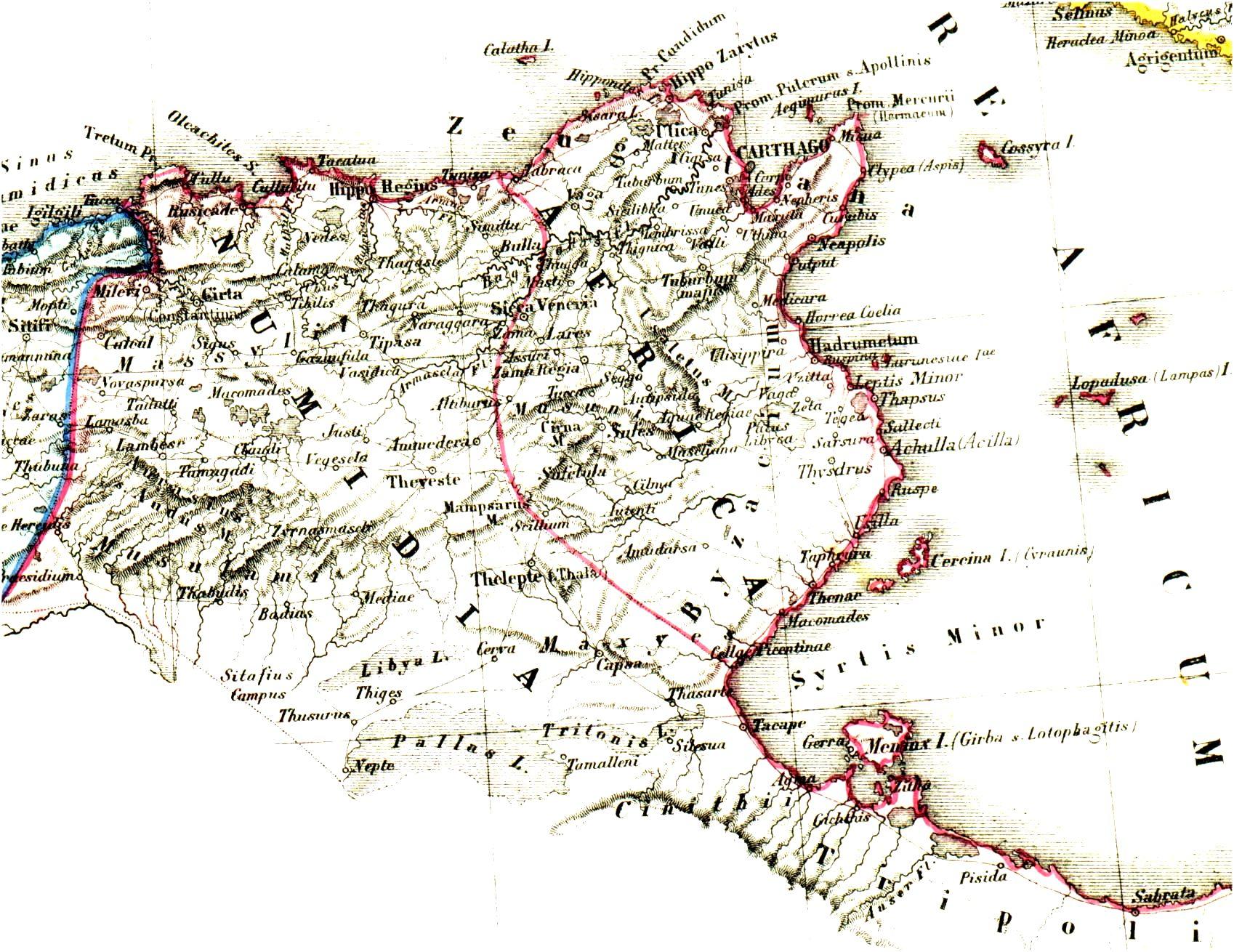
The Battle of Sufetula was a battle that took place in either late 546 or early 547, at Sufetula in Byzacena, a province of Byzantine Empire, in what is now Tunisia during the Moorish uprisings against the Byzantines. It was fought by Byzantine forces led by John Troglita, against Moorish rebels led by Antalas. The battle resulted in a crushing Byzantine victory: the Berbers suffered heavy losses, and the battle-standards lost at the battle of Cillium in 544 were recovered by the Byzantines. Before the battle In late 546, when John Troglita reached Carthage, the situation was dire: the imperial troops, under Marcentius the ''dux'' of Byzacena and Gregory the Armenian in Carthage, were few in number and demoralized. They held out in the coastal cities, blockaded by the Moors of Byzacena under their chieftain Antalas, while the Leuathae and Austurae tribes from Tripolitania were raiding Byzacena with impunity. Diplomatic efforts, however, secured the allegiance of the Moorish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sbeitla
Sbeitla or Sufetula ( ber, Sbitla or Seftula, ar, سبيطلة ') is a small town in west-central Tunisia. Nearby are the Byzantine ruins of Sufetula, containing the best preserved Byzantine forum temples in Tunisia. It was the entry point of the Muslim conquest of North Africa. Sbeitla is the capital of the largest delegation in Kasserine Governorate with an area of 1133.5 km2. It is located in 33 km in the west of the governorate, and 264 km to Tunis. It has a population of 23,844 (2014 estimate). Sbeitla is mentioned in Noman Douglas's '' Fountains in the Sand'' as being wooded by junipers and Aleppo pines as late as the 19th century, though he found them "bleak and bare" in the early 20th century. History The oldest traces of civilisation in the zone are Punic megaliths and funereal stelae. The region was inhabited by nomadic tribes until the Legio III Augusta established a camp at Ammaedara. Through the surrender of the Berber leader Tacfarinas, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classical world. The city developed from a Canaanite Phoenician colony into the capital of a Punic empire which dominated large parts of the Southwest Mediterranean during the first millennium BC. The legendary Queen Alyssa or Dido, originally from Tyre, is regarded as the founder of the city, though her historicity has been questioned. According to accounts by Timaeus of Tauromenium, she purchased from a local tribe the amount of land that could be covered by an oxhide. As Carthage prospered at home, the polity sent colonists abroad as well as magistrates to rule the colonies. The ancient city was destroyed in the nearly-three year siege of Carthage by the Roman Republic during the Third Punic War in 146 BC and then re-developed as Roman Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine North Africa
The Exarchate of Africa was a division of the Byzantine Empire around Carthage that encompassed its possessions on the Western Mediterranean. Ruled by an exarch (viceroy), it was established by the Emperor Maurice in the late 580s and survived until the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb in the late 7th century. It was, along with the Exarchate of Ravenna, one of two exarchates established following the western reconquests under Emperor Justinian I to administer the territories more effectively. History Background In the Vandalic War of 533, Byzantine forces under Belisarius reconquered the Maghreb along with Corsica and Sardinia and the Balearic Islands. Emperor Justinian I () organized the recovered territories as the Praetorian prefecture of Africa, which included the provinces of Africa Proconsularis, Byzacena, Tripolitania, Numidia, Mauretania Caesariensis and Mauretania Sitifensis, and was centered at Carthage. In the 550s, a Roman expedition succeeded in regaining pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving The Byzantine Empire
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
540s Conflicts
54 may refer to: * 54 (number) * one of the years 54 BC, AD 54, 1954, 2054 * ''54'' (novel), a 2002 novel by Wu Ming * Studio 54 Studio 54 is a Broadway theater and a former disco nightclub at 254 West 54th Street in the Midtown Manhattan neighborhood of New York City. Operated by the Roundabout Theatre Company, Studio 54 has 1,006 seats on two levels. The theater was ..., a New York City nightclub from 1977 until 1981 * ''54'' (film), a 1998 American drama film about the club * ''54'' (album), a 2010 album by Metropole Orkest * "Fifty Four", a song by Karma to Burn from the album '' Arch Stanton'', 2014 * 54th Division (other) * 54th Regiment of Foot (other) * 54th Infantry (other) {{number disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Fields Of Cato
John Troglita ( la, Ioannes Troglita, el, ) was a 6th-century Byzantine general. He participated in the Vandalic War and served in North Africa as a regional military governor during the years 533–538, before being sent east to the wars with the Sassanid Persians. As ''dux Mesopotamiae'', Troglita distinguished himself in several battles, and was noticed by agents of the Byzantine emperor, Justinian I ( r. 527–565). In summer 546, Justinian chose John Troglita to assume overall command of Byzantine forces in Africa, where a succession of revolts by the indigenous Moorish tribes and within the imperial army itself had seriously reduced the Byzantine position. Troglita quickly secured an initial victory in the winter of 546/547 against the Moors of Byzacena, but was defeated in summer 547 by the tribes of Tripolitania, and Africa was once again laid open to destructive raids. Troglita reorganized his army and secured the assistance of some tribal leaders, and confronted and deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Marta
John Troglita ( la, Ioannes Troglita, el, ) was a 6th-century Byzantine general. He participated in the Vandalic War and served in North Africa as a regional military governor during the years 533–538, before being sent east to the wars with the Sassanid Persians. As ''dux Mesopotamiae'', Troglita distinguished himself in several battles, and was noticed by agents of the Byzantine emperor, Justinian I ( r. 527–565). In summer 546, Justinian chose John Troglita to assume overall command of Byzantine forces in Africa, where a succession of revolts by the indigenous Moorish tribes and within the imperial army itself had seriously reduced the Byzantine position. Troglita quickly secured an initial victory in the winter of 546/547 against the Moors of Byzacena, but was defeated in summer 547 by the tribes of Tripolitania, and Africa was once again laid open to destructive raids. Troglita reorganized his army and secured the assistance of some tribal leaders, and confronted and deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marmarica
Marmarica (Greek Μαρμαρική) in ancient geography was a littoral area in Ancient Libya, located between ''Cyrenaica'' and ''Aegyptus''. It corresponds to what is now the Libya and Egypt frontier, including the towns of Bomba (ancient ''Phthia''), Timimi (ancient ''Paliurus''), Tobruk (ancient ''Antipyrgus''), Acroma (ancient ''Gonia''), Bardiya, As-Salum, and Sidi Barrani (ancient ''Zygra''). The territory stretched to the far south, encompassing the Siwa Oasis, which at the time was known for its sanctuary to the deity Amun. The eastern part of Marmarica, by some geographers considered a separate district between Marmarica and Aegyptus, was known as ''Libycus Nomus''. In late antiquity, Marmarica was also known as ''Libya Inferior'', while Cyrenaica was known as ''Libya Superior''. ''Libya'' is found in Africa and is located west of the Nile, more precisely west of the mouth of the Nile at Canopus. The ''Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax'' names the Adyrmachidae as the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: the ''Eclogues'' (or ''Bucolics''), the ''Georgics'', and the epic ''Aeneid''. A number of minor poems, collected in the ''Appendix Vergiliana'', were attributed to him in ancient times, but modern scholars consider his authorship of these poems as dubious. Virgil's work has had wide and deep influence on Western literature, most notably Dante's ''Divine Comedy'', in which Virgil appears as the author's guide through Hell and Purgatory. Virgil has been traditionally ranked as one of Rome's greatest poets. His ''Aeneid'' is also considered a national epic of ancient Rome, a title held since composition. Life and works Birth and biographical tradition Virgil's biographical tradition is thought to depend on a lost biography by the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cataphracts
A cataphract was a form of armored heavy cavalryman that originated in Persia and was fielded in ancient warfare throughout Eurasia and Northern Africa. The English word derives from the Greek ' (plural: '), literally meaning "armored" or "completely enclosed" (the prefix ''kata-''/''cata-'' implying "intense" or "completely"). Historically, the cataphract was a very heavily armored horseman, with both the rider and mount almost completely covered in scale armor, and typically wielding a kontos or lance as his primary weapon. Cataphracts served as the elite cavalry force for most empires and nations that fielded them, primarily used for charges to break through opposing heavy cavalry and infantry formations. Chronicled by many historians from the earliest days of antiquity up until the High Middle Ages, they may have influenced the later European knights, through contact with the Eastern Roman Empire.Nell, Grant S. (1995) ''The Savaran: The Original Knights''. University o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Archers
A horse archer is a cavalryman armed with a bow and able to shoot while riding from horseback. Archery has occasionally been used from the backs of other riding animals. In large open areas, it was a highly successful technique for hunting, for protecting the herds, and for war. It was a defining characteristic of the Eurasian nomads during antiquity and the medieval period, as well as the Iranian peoples, (Alans, Scythians, Sarmatians, Parthians, Sassanid Persians) and Indians in antiquity, and by the Hungarians, Mongols, Chinese, and the Turkic peoples during the Middle Ages. By the expansion of these peoples, the practice also spread to Eastern Europe (via the Sarmatians and the Huns), Mesopotamia, and East Asia. In East Asia, horse archery came to be particularly honored in the samurai tradition of Japan, where horse archery is called Yabusame. The term mounted archer occurs in medieval English sources to describe a soldier who rode to battle but who dismounted to shoot. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iaudas
Iaudas or Iabdas was a Berber leader of the sixth century and king of the Kingdom of the Aurès who held the Byzantines in check for a long time in the Aurès, and played an important role in the Berber revolts following the Moorish wars, Byzantine reconquest. Biography Iaudas was the son-in-law of Méphanias, another tribal chief, whom he assassinated, and the brother-in-law of Massônas, son of Méphanias. According to Corippus, he was the ''dux'' of the ''Aurasitana manus'', i.e. the leader of the Auresian army, and according to Procopius, the leader of the Berbers of Aurasion. The latter also describes him as being “of all the Moors the handsomest and most valiant”. At the beginning of 535, while the Byzantine general Solomon (magister militum), Solomon was busy dealing with the revolt of the Berbers of Byzacena, led by the chiefs Cutzinas, Esdilasas, :fr:Medisinissas, Medisinissas and :fr:Iourphouthès, Iourphouthès, Iaudas took the opportunity to take his 30,000 warrior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
