|
Battle Of Čegar
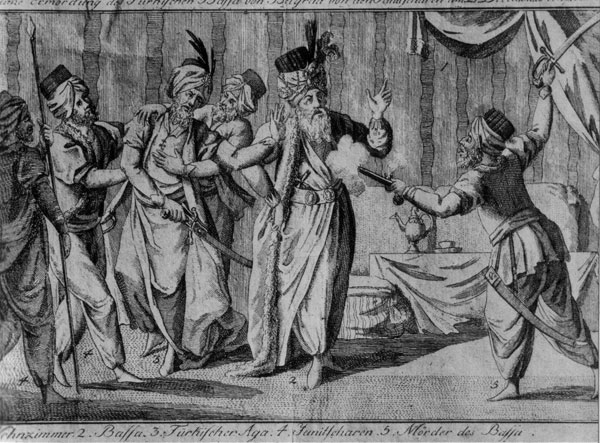
The Battle of Čegar ( sr, Битка на Чегру/Bitka na Čegru), also known as the Battle of Kamenica (Бој на Каменици/Boj na Kamenici) was a battle of the First Serbian Uprising between the Serbian Revolutionaries and Ottoman forces near the Niš Fortress on 31 May 1809. Fought on the Čegar hill situated between the villages of Donji Matejevac and Kamenica near Niš in what is today southeastern Serbia, it ended in an Ottoman victory. Commander Stevan Sinđelić famously blew up the gunpowder magazine when the Ottomans overtook his trench, killing everyone in it. Skulls of dead Serb rebels were embedded into the Skull Tower. Background On April 15, 1809, the 10,000 Serbian rebels approached the villages of Kamenica, Donji and Gornji Matejevac, near the Fortress of Niš with Miloje Petrović as Commander-in-chief. They made six trenches. The first and the biggest one was on Čegar Hill in charge of ''vojvoda'' Stevan Sinđelić. The second one was in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Serbian Uprising
The First Serbian Uprising ( sr, Prvi srpski ustanak, italics=yes, sr-Cyrl, Први српски устанак; tr, Birinci Sırp Ayaklanması) was an uprising of Serbs in the Sanjak of Smederevo against the Ottoman Empire from 14 February 1804 to 7 October 1813. Initially a local revolt against renegade janissaries who had seized power through a coup, it evolved into a war for independence (the Serbian Revolution) after more than three centuries of Ottoman rule and short-lasting Austrian occupations. The janissary commanders murdered the Ottoman Vizier in 1801 and occupied the sanjak, ruling it independently from the Ottoman Sultan. Tyranny ensued; the janissaries suspended the rights granted to Serbs by the Sultan earlier, increased taxes, and imposed forced labor, among other things. In 1804 the janissaries feared that the Sultan would use the Serbs against them, so they murdered many Serbian chiefs. Enraged, an assembly chose Karađorđe as leader of the uprising, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names in other languages) is the third largest city in Serbia and the administrative center of the Nišava District. It is located in southern part of Serbia. , the city proper has a population of 183,164, while its administrative area (City of Niš) has a population of 260,237 inhabitants. Several Roman emperors were born in Niš or used it as a residence: Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor and the founder of Constantinople, Constantius III, Constans, Vetranio, Julian, Valentinian I, Valens; and Justin I. Emperor Claudius Gothicus decisively defeated the Goths at the Battle of Naissus (present-day Niš). Later playing a prominent role in the history of the Byzantine Empire, the city's past would earn it the nickname ''Imperial City.'' After about 400 years of Ottoman rule, the city was liberated in 1878 and became part of the Principality of Serbia, though not without great bloodshed—remnants of which can be found thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 1809
Conflict may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Conflict'' (1921 film), an American silent film directed by Stuart Paton * ''Conflict'' (1936 film), an American boxing film starring John Wayne * ''Conflict'' (1937 film), a Swedish drama film directed by Per-Axel Branner * ''Conflict'' (1938 film), a French drama film directed by Léonide Moguy * ''Conflict'' (1945 film), an American suspense film starring Humphrey Bogart * ''Catholics: A Fable'' (1973 film), or ''The Conflict'', a film starring Martin Sheen * ''Judith'' (1966 film) or ''Conflict'', a film starring Sophia Loren * ''Samar'' (1999 film) or ''Conflict'', a 1999 Indian film by Shyam Benegal Games * ''Conflict'' (series), a 2002–2008 series of war games for the PS2, Xbox, and PC * ''Conflict'' (video game), a 1989 Nintendo Entertainment System war game * '' Conflict: Middle East Political Simulator'', a 1990 strategy computer game Literature and periodicals * ''Conflict'' (novel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Involving Serbia
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Đorđe Krstić
Đorđe Krstić also Djordje Krstić (, ; 19 April 1851 – 30 October 1907) was a Serbian realist painter and academic. He is often ranked alongside his contemporaries, Paja Jovanović and Uroš Predić. Biography Krstić finished his education in Munich, Germany, where he began his early works under the influence of German realism up until 1883. Some significant works of this early period include ''The Drowning Maiden'', ''Anatomist'', and ''The Gospel Writer''. In Serbia, Krstić moved his style of painting from a realist tone to a more idyllic one, with paintings such as '' Kosovo Field Landscape'', ''From the Surroundings of Čačak'', ''From Leskovac'', '' Studenica'', and ''Žiča''. In his later years, Krstić began painting a number of iconostases in Čurug and Niš, working with architect Mihailo Valtrović, of which include the controversial ''Death of Prince Lazar''. Krstić painted more than 50 works based on Serbian folk art and traditional clothing. Legacy He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miloš Obrenović
Miloš, Milos, Miłosz or spelling variations thereof is a masculine given name and a surname. It may refer to: Given name Sportsmen * Miłosz Bernatajtys, Polish rower * Miloš Bogunović, Serbian footballer * Miloš Budaković, Serbian footballer * Miloš Ćuk, Serbian water polo player, Olympic champion * Miloš Dimitrijević, Serbian footballer * Miloš Holuša, Czech race walker * Miloš Jojić, Serbian footballer * Miloš Korolija, Serbian water polo player * Miloš Krasić, Serbian footballer * Miloš Marić, Serbian footballer * Miloš Milošević, Croatian swimmer * Miloš Milutinović, Serbian footballer and manager * Miloš Nikić, Serbian volleyball player * Miloš Ninković, Serbian footballer * Miloš Pavlović (racing driver), Serbian racing driver * Milos Raonic, Montenegrin-born Canadian tennis player * Miloš Stanojević (rower), Serbian rower * Miloš Šestić, Serbian footballer * Miloš Teodosić, Serbian basketball player * Miloš Terzić, Serbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Serbian Uprising
The Second Serbian Uprising ( sr, Други српски устанак / ''Drugi srpski ustanak'', tr, İkinci Sırp Ayaklanması) was the second phase of the Serbian Revolution against the Ottoman Empire, which erupted shortly after the re-annexation of the country to the Ottoman Empire in 1813. The occupation was enforced following the defeat of the First Serbian Uprising (1804–1813), during which Serbia existed as a ''de facto'' independent state for over a decade. The second revolution ultimately resulted in Serbian semi-independence from the Ottoman Empire. The Principality of Serbia was established, governed by its own parliament, constitution and royal dynasty. ''De jure'' independence, however, was attained in 1878, following the decisions of the Congress of Berlin. Background The First Serbian Uprising liberated the country for a significant time (1804–1813) from the Ottoman Empire; for the first time in three centuries, Serbs governed themselves without the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه , alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth ( Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ("the Great City"), Πόλις ("the City"), Kostantiniyye or Konstantinopolis (Turkish) , image = Byzantine Constantinople-en.png , alt = , caption = Map of Constantinople in the Byzantine period, corresponding to the modern-day Fatih district of Istanbul , map_type = Istanbul#Turkey Marmara#Turkey , map_alt = A map of Byzantine Istanbul. , map_size = 275 , map_caption = Constantinople was founded on the former site of the Greek colony of Byzantion, which today is known as Istanbul in Turkey. , coordinates = , location = Fatih, İstanbul, Turkey , region = Marmara Region , type = Imperial city , part_of = , length = , width ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skull Tower 1863
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium and the viscerocranium (facial skeleton) that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton. Functions of the skull include protection of the brain, fixing the distance between the eyes to allow stereoscopic vision, and fixing the position of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. In some animals, such as horned ungulates (mammals with hooves), the skull also has a defensive function by providing the mount (on the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hajduk-Veljko
Veljko Petrović ( sr-cyr, Вељко Петровић, ; c. 1780 – 1813), known simply as Hajduk Veljko (Хајдук Вељко, ǎjduːk v̞ɛ̌ːʎkɔ, was one of the '' vojvodas'' (military commanders) of the Serbian Revolutionary forces in the First Serbian Uprising against the Ottoman Empire, in charge of the Negotin area. He was one of the most prominent leaders of the uprising.Vojska, Vol. 13, Issue 622–630 (2004) Biography Early life He was born in , near Zaječar, in the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
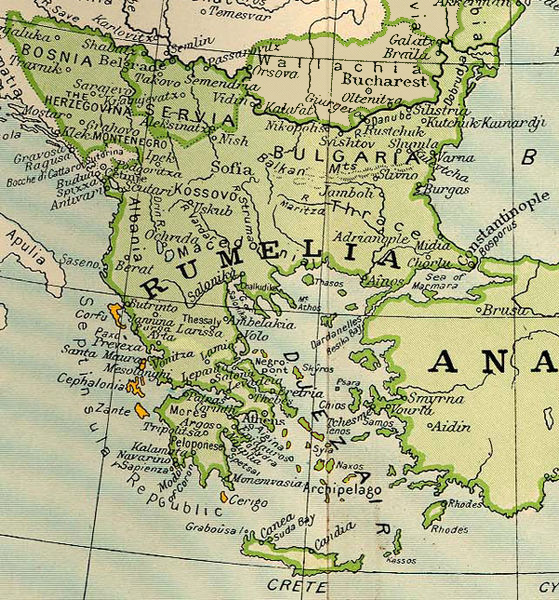
Rumelia
Rumelia ( ota, روم ايلى, Rum İli; tr, Rumeli; el, Ρωμυλία), etymologically "Land of the Romans", at the time meaning Eastern Orthodox Christians and more specifically Christians from the Byzantine rite, was the name of a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and vassals in Europe that would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans". During the period of its existence, it was more often known in English as Turkey in Europe. Etymology ''Rûm'' in this context means "Greek", or a Christian Greek speaker and ''ėli'' means "land" and ''Rumelia'' ( ota, روم ايلى, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means "Land of the Romans" in Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans, which formerly belonged to the Byzantine Empire, known by its contemporaries as the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortress Of Niš
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its ' cyclopean' walls). A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |