|
Battle Of Yangcun
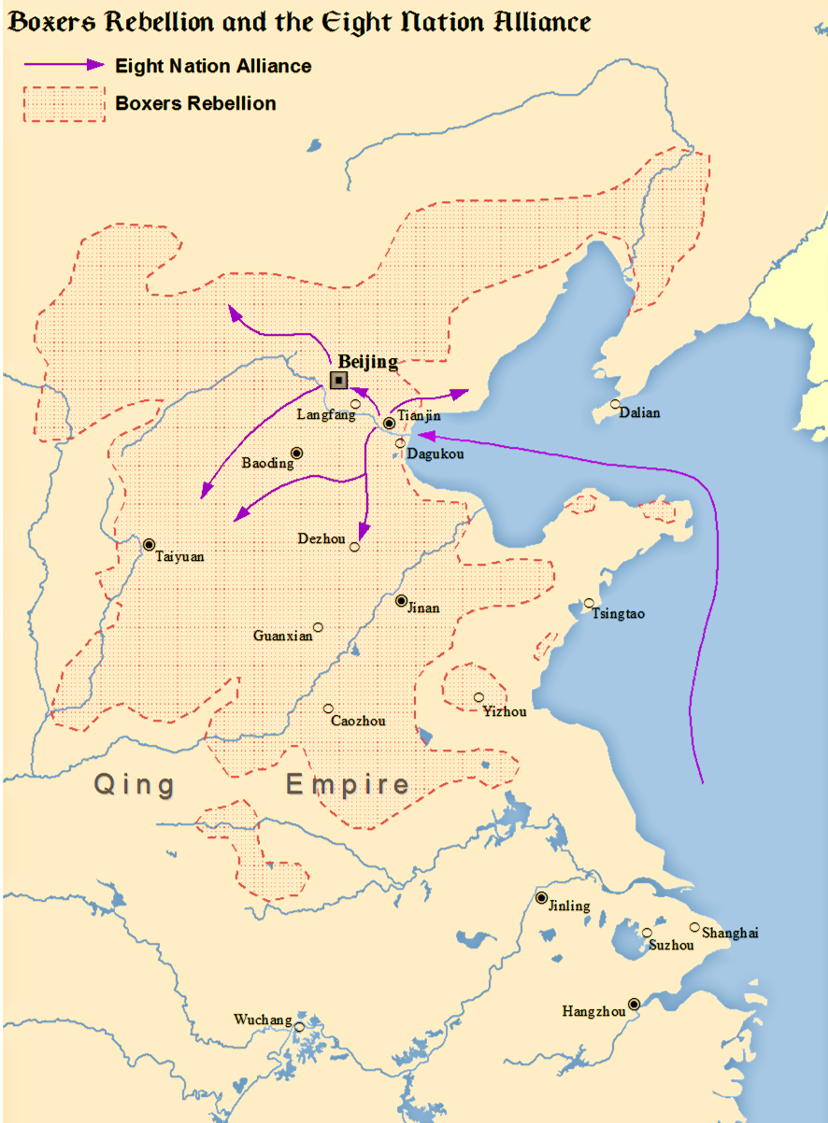
The Battle of Yangcun was a battle during the march of Eight-Nation Alliance forces from Tianjin to Beijing during the Boxer Rebellion. The Alliance forces defeated the Qing and were able to continue their march towards Peking. Background On August 4, 1900, the soldiers of the Eight-Nation Alliance left the city of Tianjin to march to Beijing to relieve the Siege of the Legations. The army consisted of approximately 20,000 troops from the following countries: United States, 2,000; Japan, 10,000; Russia, 4,000; Britain, 3,000; France, 800; Germany, 200; Austria and Italy, 100. The Alliance defeated the Chinese army at Beicang on August 5. The Chinese retreated approximately 12 miles to Yangcun, where they took up prepared positions between the east bank of the Hai River and a railroad embankment. Yangcun was the strongpoint at which the Chinese army hoped to stop the advance of the Alliance army. The country was flat, with little cover for the attackers except for fields o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by the Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists (), known as the "Boxers" in English because many of its members had practised Chinese martial arts, which at the time were referred to as "Chinese boxing". After the Sino-Japanese War of 1895, villagers in North China feared the expansion of foreign spheres of influence and resented the extension of privileges to Christian missionaries, who used them to shield their followers. In 1898 Northern China experienced several natural disasters, including the Yellow River flooding and droughts, which Boxers blamed on foreign and Christian influence. Beginning in 1899, Boxers spread violence across Shandong and the North China Plain, destroying foreign property such as railroads and attacking or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Beijing Legation Quarter
The siege of the International Legations occurred in 1900 in Peking, the capital of the Qing Empire, during the Boxer Rebellion. Menaced by the Boxers; an anti-Christian anti-foreign peasant movement, 900 soldiers, sailors, marines, and civilians, largely from Europe, Japan, and the United States, and about 2,800 Chinese Christians took refuge in the Peking Legation Quarter. The Qing government took the side of the Boxers after the Eight-Nation Alliance invaded Tianjin at the Battle of the Taku Forts (1900), without a formal declaration of war. The foreigners and Chinese Christians in the Legation Quarter survived a 55-day siege by the Qing Army and Boxers. The siege was broken by an international military force, which marched from the coast of China, defeated the Qing Army, and occupied Peking (now known as Beijing). The siege was called by the ''New York Sun'' "the most exciting episode ever known to civilization." Legation Quarter The Legation Quarter was approximately l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1900 In China
Events in the year 1900 in China. Incumbents *Guangxu Emperor (27th year) Events January * January 15, Li Hongzhang, Viceroy of Liangguang, visited Hong Kong and met with Governor of Hong Kong, Governor Henry Arthur Blake. March * March 27, Li Hongzhang, Viceroy of Liangguang, provinces reported to the central government that some of the gangsters in Hong Kong wanted to attack the provincial capital, and secretly demanded that the Governor of Hong Kong to ban. June *June 10–28 - Seymour Expedition *June 16–17 - Battle of Dagu Forts (1900) * June — Zhang Decheng went to see the Viceroy of Zhili, Yu Lu. He presented himself to him as the founder of the Boxer movement, and the viceroy promised to provide the Boxers with money and equipment.[2] *June 20 – August 14 - Siege of the International Legations * June Taiyuan massacre, Taiyuan Nationalist reaction in China against Christian missionaries and churches claimed more than thirty-two thousand lives. The worst massacre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battles Of The Boxer Rebellion
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, wherea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Kerr
Douglas Kerr is a British writer and academic who is best known for his work on Arthur Conan Doyle and George Orwell. Life and works Kerr was born in 1951 in Broughty Ferry, Dundee. Kerr went to school in Scotland, where he started reading Conan Doyle and never stopped. He went on to read English at Trinity College, Cambridge in 1969 before completing his PhD in comparative literature at Warwick University in 1978. In 1979, Kerr travelled to Hong Kong, where he had obtained an appointment as a lecturer in the Department of English Studies and Comparative Literature at the University of Hong Kong. Over the next 38 years, he advanced his academic career in Hong Kong, appointed associate professor and head of the English Department in 1996, associate Dean of the Faculty of Arts in 2002, Professor of English in 2006 and Dean of the Faculty of Arts in 2014. Apart from his usual academic responsibilities, Kerr's publication record was prolific, and includes around 110 papers, artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seymour Expedition
The Seymour Expedition was an attempt by a multi-national military force to march to Beijing and relieve the Siege of the Legations and foreign nationals from attacks by government troops and Boxers in 1900. The Chinese army and Boxer fighters defeated the Seymour armies and forced them to return to Tianjin (Tientsin). It was followed later in the summer by the successful Gaselee Expedition. Historical background Boxer bands advanced on Beijing in May and June 1900. The Qing court was ambivalent about the Boxers, fearing that they might become anti-Qing. The Boxers became a serious threat to Western and Japanese citizens, murdering missionaries and Chinese Christians living northern China. The diplomatic legations in Beijing requested that guards be sent to protect them. As such, more than 400 marines and naval troops from eight countries arrived in Beijing on 31 May. However, as the Boxers began posing a more significant threat, it became apparent that additional troops we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuomintang
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a major political party in the Republic of China, initially on the Chinese mainland and in Taiwan after 1949. It was the sole party in China during the Republican Era from 1928 to 1949, when most of the Chinese mainland was under its control. The party retreated from the mainland to Taiwan on 7 December 1949, following its defeat in the Chinese Civil War. Chiang Kai-shek declared martial law and retained its authoritarian rule over Taiwan under the ''Dang Guo'' system until democratic reforms were enacted in the 1980s and full democratization in the 1990s. In Taiwanese politics, the KMT is the dominant party in the Pan-Blue Coalition and primarily competes with the rival Democratic Progressive Party (DPP). It is currently the largest opposition party in the Legislative Yuan. The current chairman is Eric Chu. The party originate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The territories controlled by the ROC consist of 168 islands, with a combined area of . The main island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', has an area of , with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. The capital, Taipei, forms along with New Taipei City and Keelung the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include Taoyuan, Taichung, Tainan, and Kaohsiung. With around 23.9 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries in the world. Taiwan has been settled for at least 25,000 years. Ancestors of Taiwanese indigenous peoples settled the island around 6,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Yat-sen
Sun Yat-sen (; also known by several other names; 12 November 1866 – 12 March 1925)Singtao daily. Saturday edition. 23 October 2010. section A18. Sun Yat-sen Xinhai revolution 100th anniversary edition . was a Chinese politician who served as the first provisional president of the Republic of China and the first leader of the Kuomintang (Nationalist Party of China). He is called the "Father of the Nation" in the Republic of China, and the "Forerunner of the Revolution" in the People's Republic of China for his instrumental role in the overthrow of the Qing dynasty during the Xinhai Revolution. Sun is unique among 20th-century Chinese leaders for being widely revered in both Mainland China and Taiwan. Sun is considered to be one of the greatest leaders of modern China, but his political life was one of constant struggle and frequent exile. After the success of the revolution in 1911, he quickly resigned as president of the newly founded Republic of China and relinquished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captured Foreign Officers General Dong
{{disambiguation ...
Captured may refer to: * ''Captured'' (Journey album), 1981 * ''Captured'' (Rockwell album), 1985 * ''Captured'', a 1995 album by The Albion Band * ''Captured'' (Caroline's Spine album), 2007 * ''Captured'' (Christian Bautista album), 2008 * ''Captured'' (mixtape), a 2018 mixtape by Spice * ''Captured!'', a 1933 war film * ''Captured'' (1998 film), a 1998 thriller film * ''Captured'' (video game), a video game released in 1986 for the Commodore 64 * "Captured", a song by Heaven 17 See also *Capture (other) Capture may refer to: *Asteroid capture, a phenomenon in which an asteroid enters a stable orbit around another body *Capture, a software for lighting design, documentation and visualisation *"Capture" a song by Simon Townshend *Capture (band), an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th Infantry Regiment (United States)
The 9th Infantry Regiment ("Manchu") is a parent infantry regiment of the United States Army. Unrelated units designated the 9th Infantry Regiment were organized in the United States Army in 1798 during the Quasi-War, in 1812 during the war of 1812, and in 1847 during the Mexican–American War. The 1812 regiment fought in the Battle of Lundy's Lane, and the 1847 regiment in the Battle for Mexico City. The lineage of the current regiment begins with the 1855 organization of the 9th Infantry Regiment, which was dispatched to the Pacific Northwest, where it served in the American Indian Wars. The regiment remained in the west during the American Civil War, garrisoning posts near San Francisco. After the end of the American Civil War the regiment continued its service through the final Indian Wars, then fought at the Battle of San Juan Hill during the Spanish–American War. During the Boxer Rebellion, the 9th Infantry was sent to China, where it earned the nickname Manchu. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th Infantry Regiment (United States)
The 14th Infantry Regiment ("Golden Dragons" ) is a United States Army light infantry regiment. It has served in the American Civil War, Boxer Rebellion, World War II, Korean War, Vietnam War, Operation Restore Hope, Operation Uphold Democracy, Operation Joint Guard, Operation Desert Storm, Operation Enduring Freedom, Operation Gothic Serpent, Operation New Dawn, Operation Resolute Support, and Operation Iraqi Freedom. The 14th Infantry Regiment did not take part in combat during World War I. It has also conducted peacekeeping and humanitarian missions in the Sinai Peninsula, Guantánamo Bay in Cuba, Bosnia, and Kosovo. Only the 2nd Battalion of the 14th Infantry Regiment is currently active, assigned to 2nd Brigade, 10th Mountain Division at Fort Drum, New York. History Civil War, 1861–66 In May 1861, President Abraham Lincoln called for the creation of nine additional Regular Army infantry regiments in preparation for the looming civil war. These regiments were desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |