|
Battle Of Wolf Mountain
The Battle of Wolf Mountain (also known as the Battle of the Wolf Mountains, Miles's Battle on the Tongue River, the Battle of the Butte, Where Big Crow Walked Back and Forth, and called the Battle of Belly Butte by the Northern Cheyenne) was a battle fought on January 8, 1877, by soldiers of the United States Army against Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne warriors during the Great Sioux War of 1876. The battle was fought in southern Montana Territory, about four miles southwest of modern-day Birney, Montana, along the Tongue River. and In 2001, the Wolf Mountains Battlefield was listed on the National Register of Historic Places, and was raised to the status of National Historic Landmark in 2008. Background Following the defeat of Lieutenant Colonel George A. Custer on June 25, 1876, in the Battle of Little Bighorn, the United States government sent a large number of reinforcements into Montana Territory. By autumn, a few bands of the Sioux and Cheyenne tribes had beg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Sioux War Of 1876
The Great Sioux War of 1876, also known as the Black Hills War, was a series of battles and negotiations that occurred in 1876 and 1877 in an alliance of Lakota Sioux and Northern Cheyenne against the United States. The cause of the war was the desire of the US government to obtain ownership of the Black Hills. Gold had been discovered in the Black Hills, settlers began to encroach onto Native American lands, and the Sioux and the Cheyenne refused to cede ownership. Traditionally, American military and historians place the Lakota at the center of the story, especially because of their numbers, but some Native Americans believe the Cheyenne were the primary target of the American campaign. Among the many battles and skirmishes of the war was the Battle of the Little Bighorn; often known as Custer's Last Stand, it is the most storied of the many encounters between the US Army and mounted Plains Indians. Despite the Indian victory, the Americans leveraged national resources to fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
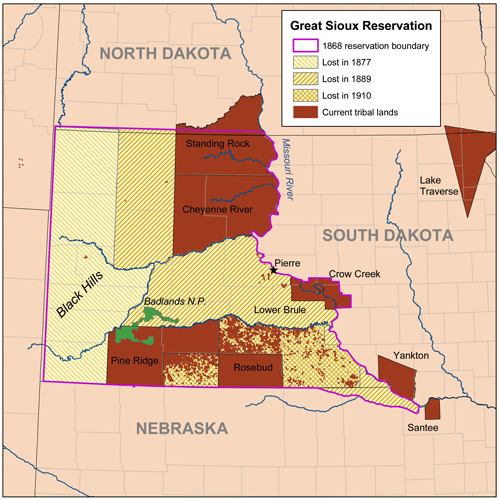
Indian Reservation
An Indian reservation is an area of land held and governed by a federally recognized Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs and not to the state government in which it is located. Some of the country's 574 federally recognized tribes govern more than one of the 326 Indian reservations in the United States, while some share reservations, and others have no reservation at all. Historical piecemeal land allocations under the Dawes Act facilitated sales to non–Native Americans, resulting in some reservations becoming severely fragmented, with pieces of tribal and privately held land being treated as separate enclaves. This jumble of private and public real estate creates significant administrative, political and legal difficulties. The total area of all reservations is , approximately 2.3% of the total area of the United States and about the size of the state of Idaho. While most reservations are small c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th Infantry Regiment (United States)
The 5th Infantry Regiment (nicknamed the "Bobcats") is an infantry regiment of the United States Army that traces its origins to 1808. Origins: War of 1812 The 5th Infantry Regiment was created by an Act of Congress of 3 March 1815,The Fifth Regiment of Infantry p. 466 which reduced the Regular Army from the 46 infantry and 4 rifle regiments it fielded in the to a peacetime establishment of 8 infantry regiments (reduced to 7 in 1821). The Army's current regimental numbering system dates from this act. Six of the old regiments (4th, 9th, 13th, 21st, 40th and 46th) were consolidated into the new 5th Regiment, which was organized on 15 May 1815 under the comman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Robinson
Fort Robinson is a former U.S. Army fort and now a major feature of Fort Robinson State Park, a public recreation and historic preservation area located west of Crawford on U.S. Route 20 in the Pine Ridge region of northwest Nebraska. The fort was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1960 and is part of the Fort Robinson and Red Cloud Agency historic district. This includes Fort Robinson and the site of the second Red Cloud Agency (about to the east). The district also includes the Camp Camby site and the 1886 Percy Homestead. The fort is managed by the Nebraska Game and Parks Commission, with some individual buildings operated by the History Nebraska and the University of Nebraska. History In August 1873, the Red Cloud Agency was moved from the North Platte River to the White River, near what is now Crawford, Nebraska, in the northwest corner of the state. The following March, the U. S. Government authorized the establishment of a military camp at the agency site. Som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
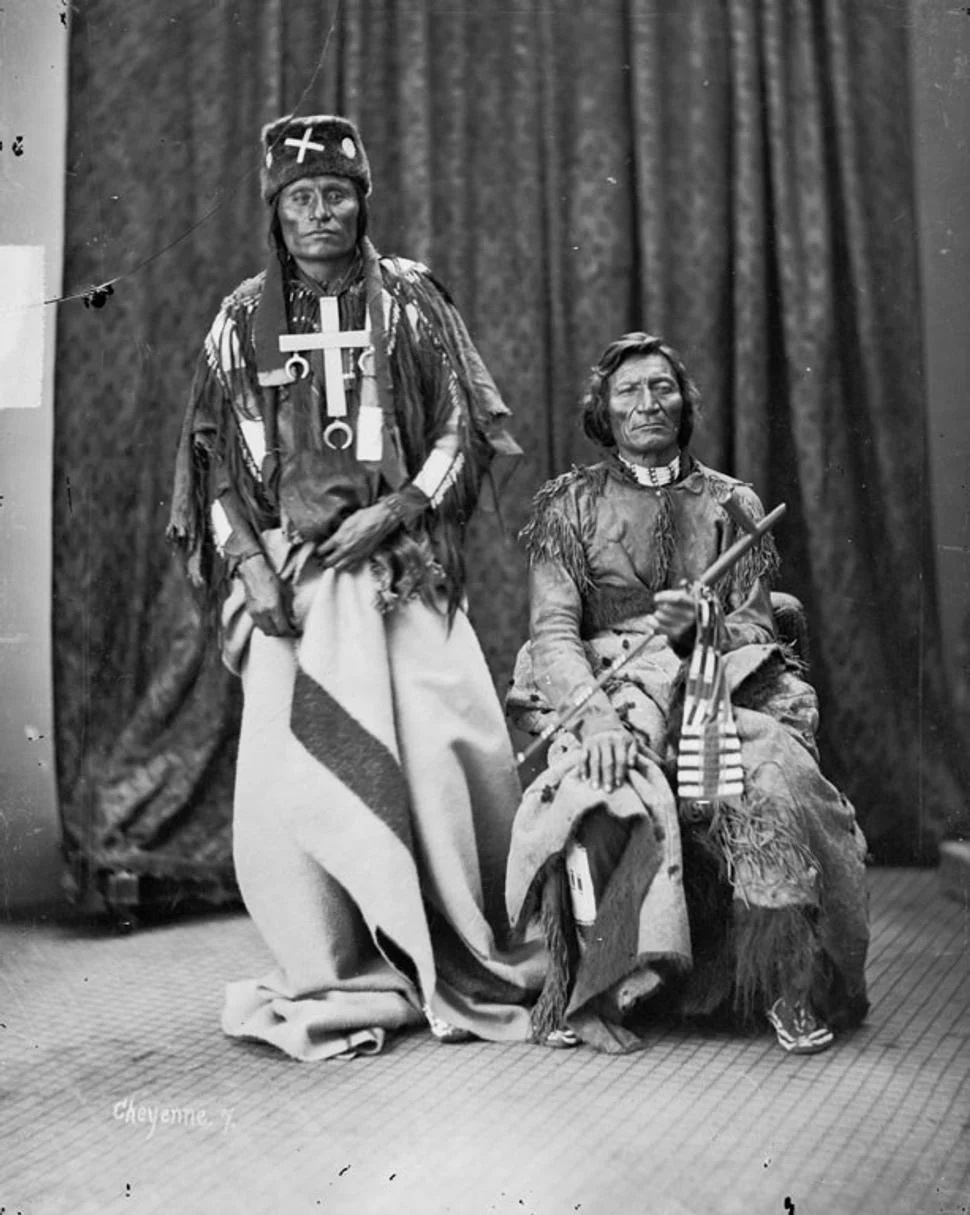
Two Moons
Two Moons (1847–1917), or ''Ishaynishus'' (Cheyenne language, Cheyenne: ''Éše'he Ôhnéšesêstse''), was one of the Cheyenne chiefs who took part in the Battle of the Little Bighorn and other battles against the United States Army. Life Two Moons was the son of Carries the Otter, an Arikara captive who married into the Cheyenne tribe. Perhaps known best for his participation in battles such as the Battle of the Rosebud against George Crook, General Crook on June 17, 1876, in the Montana Territory, the Battle of Little Big Horn on June 25, 1876 and what would prove to be his last battle, the Battle of Wolf Mountain on January 8, 1877. Two Moons' defeat at Wolf Mountain by General Nelson A. Miles led inevitably to the surrender of his Cheyenne band to Miles at Fort Keogh in April 1877. After the surrender of his Cheyenne band, Two Moons enlisted as an United States Army Indian Scouts, Indian Scout under General Miles. As a result of Two Moons' pleasant personality, the friendli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Keogh
Fort Keogh is a former United States Army post located at the western edge of modern Miles City, Montana, Miles City, in the U.S. state of Montana. It is situated on the south bank of the Yellowstone River, at the mouth of the Tongue River (Montana), Tongue River. Colonel Nelson A. Miles, commanding the 5th Infantry Regiment (United States), 5th Infantry Regiment, founded the post in August 1876, in the wake of the Battle of the Little Bighorn, as a base for patrols to prevent the Cheyenne and Sioux involved in the battle from escaping to Canada. The fort was originally known as the Tongue River Cantonment for two years. When relocated one mile west in 1878, it was renamed Fort Keogh in honor of Captain Myles Keogh, who was killed at the Little Bighorn. In 1877, the fort became the headquarters for the newly created District of the Yellowstone (a sub-unit of the Department of Dakota), which was commanded by Miles. The development of Fort Keogh as a military installation soon stimu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dull Knife
Morning Star ( Cheyenne: ''Vóóhéhéve''; also known by his Lakota Sioux name ''Tȟamílapȟéšni'' or its translation, Dull Knife) (1810–1883) was a great chief of the Northern Cheyenne people and headchief of the ''Notameohmésêhese'' ("Northern Eaters"; also simply known as ''Ȯhmésėhese'' or "Eaters") band on the northern Great Plains during the 19th century. He was noted for his active resistance to westward expansion and the United States federal government. It is due to the courage and determination of Morning Star and other leaders that the Northern Cheyenne still possess a homeland in their traditional country in present-day Montana. Although he was known as "Dull Knife" (or ''Motšêške Ôhnêxahpo'' in Cheyenne, a translation of his Lakota name) to local settlers, U.S. military leaders, and other American Indians, his Cheyenne name is translated as "Morning Star". A Cheyenne warrior in every sense of the word, Morning Star was described by many writers of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranald S
Ranald is an English Hanks; Hodges 2006 pp. 407–408; Hanks; Hodges 2003; Hanks; Hodges 1997 pp. 204, 205. and Scots masculine given name. It is an Anglicised form of the Scottish Gaelic name ''Raghnall''. A short form of ''Ranald'' is ''Ran''. Hanks; Hodges 2003; Hanks; Hodges 1997 p. 205. Notable persons *Ranald Graham (1941–2010), Scottish writer, television director and producer *Ranald Leask, British journalist *Ranald MacDonald (bishop) (1756–1832), Scottish Roman Catholic bishop *Ranald George Macdonald (1788–1873), Scottish clan chief and Member of British Parliament *Ranald MacDonald (1824–1894), English language teacher in Japan *Ranald Roderick Macdonald (1945–2007), British mathematician and psychologist *Ranald MacDougall (1915–1973), American screenwriter *Ranald S. Mackenzie (1840–1889), United States Army officer and general during the Civil War *Ranald Sutherland, Lord Sutherland (born 1932), Scottish judge Fictional characters *R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitting Bull
Sitting Bull ( lkt, Tȟatȟáŋka Íyotake ; December 15, 1890) was a Hunkpapa Lakota leader who led his people during years of resistance against United States government policies. He was killed by Indian agency police on the Standing Rock Indian Reservation during an attempt to arrest him, at a time when authorities feared that he would join the Ghost Dance movement. Before the Battle of the Little Bighorn, Sitting Bull had a vision in which he saw many soldiers, "as thick as grasshoppers", falling upside down into the Lakota camp, which his people took as a foreshadowing of a major victory in which many soldiers would be killed. About three weeks later, the confederated Lakota tribes with the Northern Cheyenne defeated the 7th Cavalry under Lt. Col. George Armstrong Custer on June 25, 1876, annihilating Custer's battalion and seeming to bear out Sitting Bull's prophetic vision. Sitting Bull's leadership inspired his people to a major victory. In response, the U.S. governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in the roles of reconnaissance, screening, and skirmishing in many armies, or as heavy cavalry for decisive shock attacks in other armies. An individual soldier in the cavalry is known by a number of designations depending on era and tactics, such as cavalryman, horseman, trooper, cataphract, knight, hussar, uhlan, mamluk, cuirassier, lancer, dragoon, or horse archer. The designation of ''cavalry'' was not usually given to any military forces that used other animals for mounts, such as camels or elephants. Infantry who moved on horseback, but dismounted to fight on foot, were known in the early 17th to the early 18th century as '' dragoons'', a class of mounted infantry which in most armies later evolved into standard cavalry while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy, fairly immobile siege engines. As technology improved, lighter, more mobile field artillery cannons developed for battlefield use. This development continues today; modern self-propelled artillery vehicles are highly mobile weapons of great versatility generally providing the largest share of an army's total firepower. Originally, the word "artillery" referred to any group of soldiers primarily armed with some form of manufactured weapon or armor. Since the introduction of gunpowder and cannon, "artillery" has largely meant cannons, and in contemporary usage, usually refers to shell-firing guns, howitzers, and mortars (collectively called ''barrel artillery'', ''cannon artillery'', ''gun artillery'', or - a layman t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets '' infant''. The individual-soldier term ''infantry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |