|
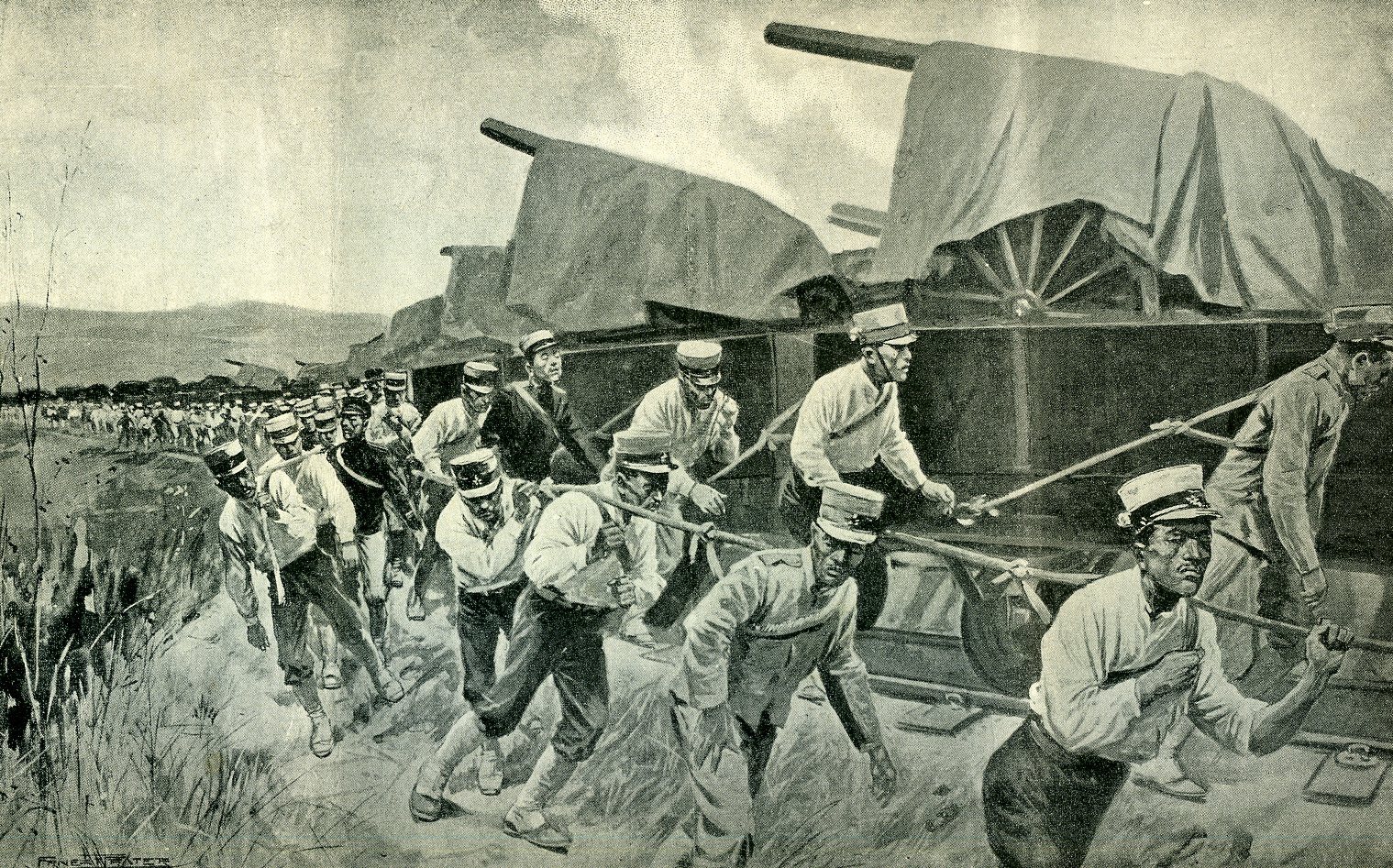
Battle Of Tashihchiao
The was a land engagement fought on 24–25 July 1904, during the Imperial Japanese Army's advance toward Liaoyang in first stage of the Russo-Japanese War. Tashihchiao (modern Dashiqiao) is located about southwest of the city of Haicheng, in present-day Liaoning Province, China. The town of Tashihchiao was of strategic importance in the Russo-Japanese War, as it was a railroad junction between the main line on the Russian South Manchurian Railway and a spur which led to the old treaty port of Yingkou (Newchwang). Control of both was essential for further advances by Japanese forces towards Liaoyang and Mukden. Preparations by the Japanese On the Japanese side were the 3rd, 4th, 5th and 6th Divisions of the Japanese Second Army under General Oku Yasukata. The combined force had over 64,000 men, including 46,000 infantry, and 252 guns. After the victory at the Battle of Telissu, General Oku rested for four days for re-supply, which was delayed due to heavy rains, and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1905 over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major theatres of military operations were located in Liaodong Peninsula and Mukden in Southern Manchuria, and the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. Russia sought a warm-water port on the Pacific Ocean both for its navy and for maritime trade. Vladivostok remained ice-free and operational only during the summer; Port Arthur, a naval base in Liaodong Province leased to Russia by the Qing dynasty of China from 1897, was operational year round. Russia had pursued an expansionist policy east of the Urals, in Siberia and the Far East, since the reign of Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century. Since the end of the First Sino-Japanese War in 1895, Japan had feared Russian en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd Division (Imperial Japanese Army)
The was an infantry division in the Imperial Japanese Army. Its call sign was the . History The 3rd Division was formed in Nagoya in January 1871 as the , one of six regional commands created in the fledgling Imperial Japanese Army. The Nagoya Garrison had responsibility for the central region of Japan. This region was known as the Chūbu district, and stretched from Aichi Prefecture to Ishikawa Prefecture. Upon the recommendations of the Prussian military advisor Jakob Meckel to the Japanese government, the six regional commands were transformed into divisions under the army reorganization of 14 May 1888. As one of the oldest divisions in the Imperial Japanese Army, the 3rd Division participated in combat operations during the First Sino-Japanese War, the Russo-Japanese War, the Siberian Intervention, and the Shandong Incident. Some of its more noteworthy commanders included Katsura Taro, Hasegawa Yoshimichi, Uehara Yusaku and Nobuyoshi Muto. 9 December 1938, the 3rd Divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Of Fire (weaponry)
The field of fire of a weapon (or group of weapons) is the area around it that can easily and effectively be reached by gunfire. The term 'field of fire' is mostly used in reference to machine guns. Their fields of fire incorporate the beaten zone. The term originally came from the 'field of fire' in front of forts (and similar defensive positions), cleared so there was no shelter for an approaching enemy. Beaten zone is a concept in indirect infantry small arms fire, specifically machine guns. It describes the area between the "first catch" and the "last graze" of a bullet's trajectory. At the first of these points, a bullet will hit a standing man in the head, at the last of these points, as the bullet drops, it will hit a standing man in the feet. Anyone standing within a given gun's beaten zone will be hit somewhere from head to foot. Given that there is variance in the path of each bullet, and differences in mechanisms as designed, all machine guns have beaten zones wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexei Kuropatkin
Aleksey Nikolayevich Kuropatkin (russian: Алексе́й Никола́евич Куропа́ткин; March 29, 1848January 16, 1925) served as the Russian Imperial Minister of War from January 1898 to February 1904 and as a field commander subsequently. Historians often hold him responsible for major Russian defeats in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904 to 1905, most notably at the Battle of Mukden (1905) and at the Battle of Liaoyang (August-September 1904). Biography Early years Kuropatkin was born in 1848 in Kholmsky Uyezd, Pskov Governorate, in the Russian Empire. His father, a retired army captain, came from landed gentry. Educated in the Cadet Corps and Pavlovsky Military School, Kuropatkin entered the Imperial Russian Army in 1864. On August 8, 1866, he was promoted to lieutenant in the 1st Turkestan Infantry Battalion, and took part in the conquest of Bukhara, the storming of Samarkand and other battles in the Russian conquest of Turkestan. He was promoted to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st Siberian Army Corps
The 1st Siberian Army Corps was an elite unit of the Imperial Russian Army. It was raised in May 1900 and disbanded in August 1918. History The 1st Siberian Army Corps was raised in May 1900 under the command of Lieutenant General Nikolai Linevich and was one of the two most engaged Russian corps during the Russo-Japanese War. It took part in the battle of Telissu, the battle of Tashihchiao, the battle of Liaoyang, the battle of Sandepu and the battle of Mukden.Kowner, p. 93 It also took part in World War I. Its last major action was at the Battle of Galați. Organization 1904 * 1st Siberian Rifle Division (Lieutenant General Gerngross) **1st Brigade (Major General Rutowski) *** 1st Infantry Regiment (3 battalions) ***2nd Infantry Regiment (3 battalions) **2nd Brigade (Major General Maximovich) ***3rd Infantry Regiment (3 battalions) ***4th Infantry Regiment (3 battalions) ** 1st East Siberian Rifle Artillery Brigade (Major General Lutshkovski) ***4 Field Artillery Batteries (6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Non-Commissioned Officers In A Millet Field
Japanese may refer to: * Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia * Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan * Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture ** Japanese diaspora, Japanese emigrants and their descendants around the world * Japanese citizens, nationals of Japan under Japanese nationality law ** Foreign-born Japanese, naturalized citizens of Japan * Japanese writing system, consisting of kanji and kana * Japanese cuisine, the food and food culture of Japan See also * List of Japanese people * * Japonica (other) * Japonicum * Japonicus * Japanese studies Japanese studies (Japanese: ) or Japan studies (sometimes Japanology in Europe), is a sub-field of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on Japan. It incorporates fields such as the study of Japanese ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
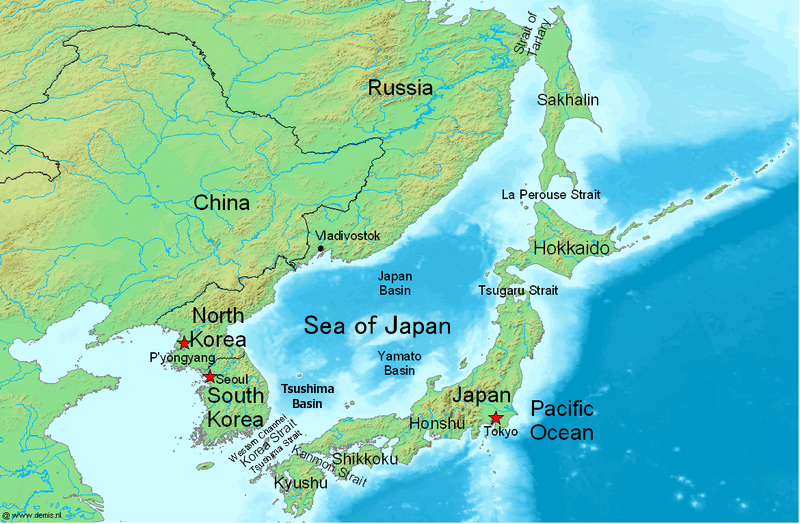
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commerce Raiding
Commerce raiding (french: guerre de course, "war of the chase"; german: Handelskrieg, "trade war") is a form of naval warfare used to destroy or disrupt logistics of the enemy on the open sea by attacking its merchant shipping, rather than engaging its combatants or enforcing a blockade against them. Privateering The first sort of commerce raiding was for nations to commission privateers. Early instances of this type of warfare were by the English and Dutch against the Spanish treasure fleets of the 16th century, which resulted in financial gain for both captain and crew upon capture of enemy vessels ("Prize (law), prizes"). 17th and 18th centuries Privateers formed a large part of the total military force at sea during the 17th and 18th centuries. In the First Anglo-Dutch War, English privateers attacked the trade on which the United Provinces of the Netherlands, United Provinces entirely depended, capturing over 1,000 Dutch merchant ships. During the subsequent Anglo-Spanish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Gauge
In rail transport, track gauge (in American English, alternatively track gage) is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge differences often present a barrier to wider operation on railway networks. The term derives from the metal bar, or gauge, that is used to ensure the distance between the rails is correct. Railways also deploy two other gauges to ensure compliance with a required standard. A ''loading gauge'' is a two-dimensional profile that encompasses a cross-section of the track, a rail vehicle and a maximum-sized load: all rail vehicles and their loads must be contained in the corresponding envelope. A ''structure gauge'' specifies the outline into which structures (bridges, platforms, lineside equipment etc.) must not encroach. Uses of the term The most common use of the term "track gauge" refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalian
Dalian () is a major sub-provincial port city in Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, and is Liaoning's second largest city (after the provincial capital Shenyang) and the third-most populous city of Northeast China. Located on the southern tip of Liaodong peninsula, it is the southernmost city in both Liaoning and the entire Northeast. Dalian borders the prefectural cities of Yingkou and Anshan to the north and Dandong to the northeast, and also shares maritime boundaries with Qinhuangdao and Huludao across the Liaodong Bay to west and northwest, Yantai and Weihai on the Shandong peninsula across the Bohai Strait to the south, and North Korea across the Korea Bay to the east. As of the 2020 census, its total population was 7,450,785 inhabitants whom 5,106,719 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made of 6 out of 7 urban districts, Pulandian District not being conurbated yet. Today a financial, shipping, and logistics center for East Asia, Dalian has a signific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Telissu
The Battle of Te-li-ssu ( '), also called Battle of Wafangou (russian: Бой у Вафангоу) after the nearby railway station, was a land battle of the Russo-Japanese War. It was fought at a hamlet some north of Port Arthur, Manchuria. The hamlet is known today as ''Délì-sì'', and is located just north of Wafangdian, Liaoning Province, China. It was fought on 14–15 June 1904 between the Japanese Second Army under General Oku Yasukata and the Russian First Siberian Army Corps under Lieutenant General Georgii Stackelberg. Background After the loss to the Japanese at the Battle of Nanshan, the Russian Viceroy Yevgeni Alekseyev came under extreme political pressure to make a military advance to prevent the complete encirclement of Port Arthur. The Commander-in-Chief of the Imperial Russian Army in Manchuria, General Alexei Kuropatkin, disagreed vehemently to this plan, which he felt to be both foolhardy and dangerous, and he preferred to wait in Mukden for the Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Army (Japan)
The was an army of the Imperial Japanese Army. It was raised and demobilized on four occasions. History The Japanese 2nd Army was initially raised during the First Sino-Japanese War from September 27, 1894, to May 14, 1895, under the command of General Ōyama Iwao. It was revived for the Russo-Japanese War from March 6, 1904, to January 2, 1906, under the command of General Oku Yasukata. It fought in most of the major campaigns of the war, including the Battle of Nanshan, Battle of Te-li-Ssu, Battle of Tashihchiao, Battle of Shaho, Battle of Liaoyang, Battle of Sandepu, and Battle of Mukden. The Japanese 2nd Army was raised again on August 23, 1937, and placed under the command of the Japanese Northern China Area Army as reinforcement to Japanese forces in China following the Marco Polo Bridge Incident. The 2nd Army participated in the North China Incident, Tianjin–Pukou Railway Operation, Battle of Xuzhou and Battle of Taierzhuang before being demobilized on Decembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |