|
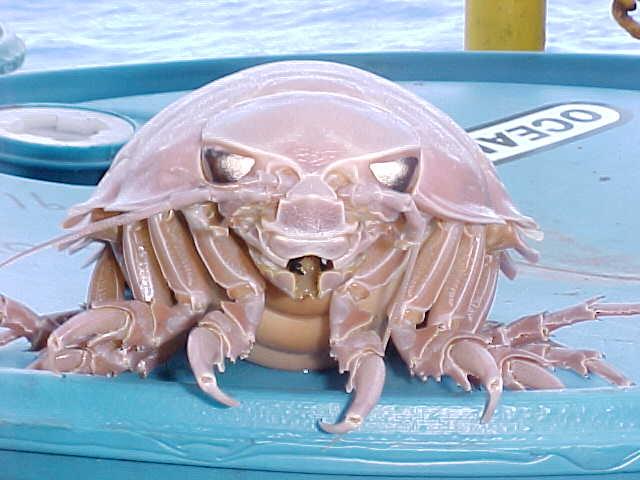
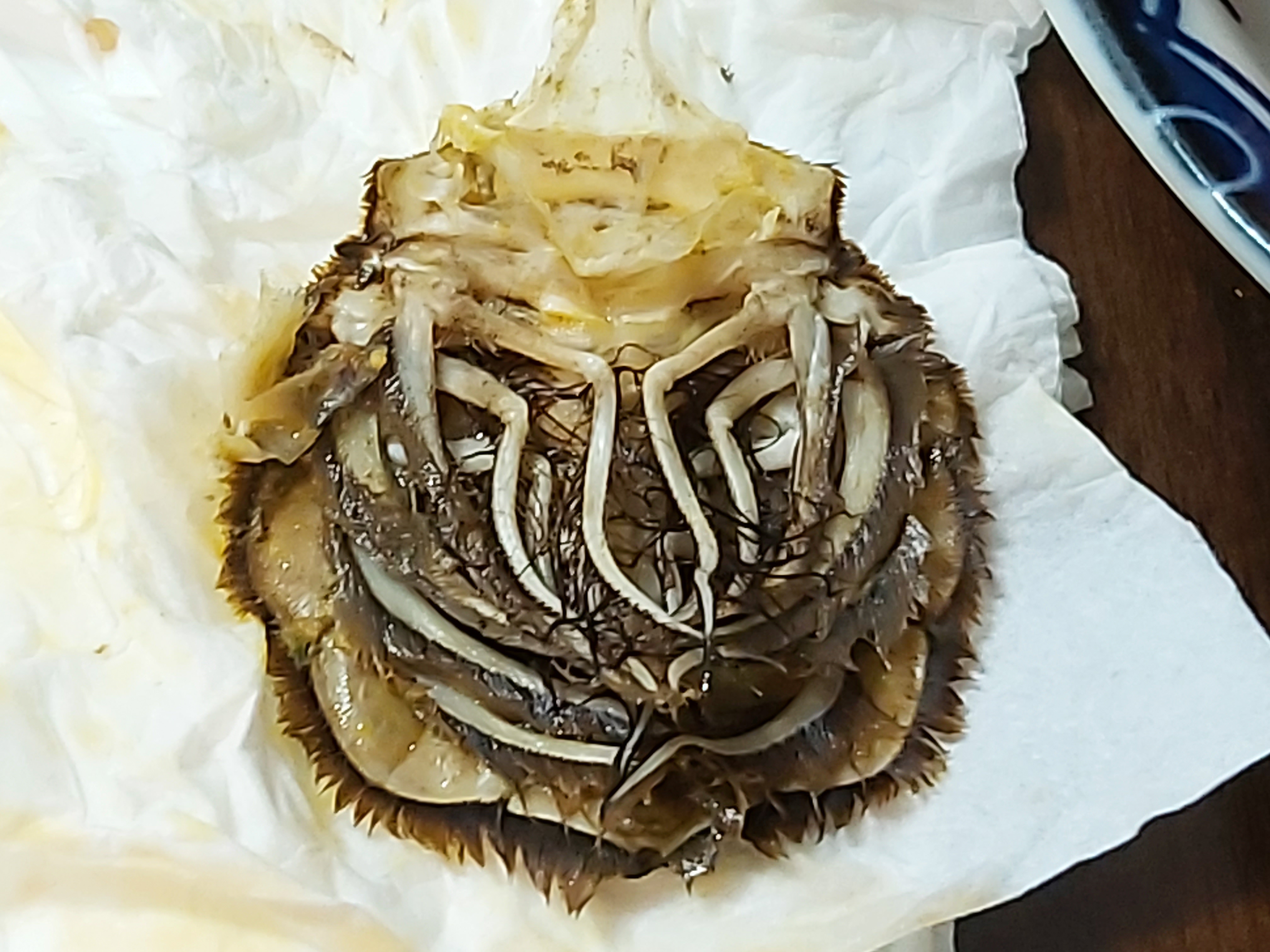
Bathynomus Giganteus
''Bathynomus giganteus'' is a species of aquatic crustacean, of the order Isopoda. It is a member of the giant isopods (''Bathynomus''), and as such it is related—albeit distantly—to shrimps and crabs. It was the first ''Giant isopod, Bathynomus'' species ever documented, and was described in 1879 by French zoologist Alphonse Milne-Edwards, Alphonse Milne Edwards after the isopod was found in fishermen's nets off the coast of the Dry Tortugas in the Gulf of Mexico. The ''Bathynomus'' is benthic and abundant in cold waters with a depth of in the West Atlantic, including the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea, Caribbean. It was the first species of ''Bathynomus'' to be Species description, described and historically it was reported from other oceans, but these are now recognized as other closely related species. The unusually large size of ''Bathynomus'' has been attributed to an effect called deep-sea gigantism, where invertebrates living in cold deep waters tend to grow larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalon (arthropod Head)
The cephalon is the head section of an arthropod. It is a tagma, i.e., a specialized grouping of arthropod segments. The word cephalon derives from the Greek κεφαλή (kephalē), meaning "head". Insects In insects, ''head'' is a preferred term. The insect head consists of five segments, including three (the labial, maxillary and mandibular) necessary for food uptake, which are altogether known as the gnathocephalon and house the suboesophageal ganglion of the brain, as well as the antennal segment, and an ocular segment, as well as a non segmented fused section of the head where the archicerebrum is housed known as the acron. See also arthropod head problem. Chelicerates and crustaceans In chelicerates and crustaceans, the cephalothorax is derived from the fusion of the cephalon and the thorax, and is usually covered by a single unsegmented carapace. In relation with the arthropod head problem, phylogeny studies show that members of the Malacostraca class of cru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustaceans Of The Atlantic Ocean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cymothoida
Cymothoida is the name of a suborder of isopod crustaceans with a mostly carnivorous or parasitic lifestyle. It contains more than 2,700 described species in four superfamilies. Members of the suborder are characterised by their specialised mouthparts which include a mandible with a tooth-like process which is adapted for cutting or slicing. Classification Cymothoida contains these superfamilies and families: *Superfamily Anthuroidea Leach, 1814 ** Antheluridae Poore & Lew Ton, 1988 ** Anthuridae Leach, 1814 ** Expanathuridae Poore, 2001 ** Hyssuridae Wägele, 1981 ** Leptanthuridae Poore, 2001 ** Paranthuridae Menzies & Glynn, 1968 *Superfamily Cymothooidea Leach, 1814 **Aegidae White, 1850 **Anuropidae Stebbing, 1893 ** Barybrotidae Hansen, 1890 **Cirolanidae Dana, 1852 ** Corallanidae Hansen, 1890 ** Cymothoidae Leach, 1818 **Gnathiidae Leach, 1814 ** Protognathiidae Wägele & Brandt, 1988 ** Tridentellidae Bruce, 1984 *Superfamily Cryptoniscoidea Kossmann, 1880 **Asconisc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathynomus Giganteus
''Bathynomus giganteus'' is a species of aquatic crustacean, of the order Isopoda. It is a member of the giant isopods (''Bathynomus''), and as such it is related—albeit distantly—to shrimps and crabs. It was the first ''Giant isopod, Bathynomus'' species ever documented, and was described in 1879 by French zoologist Alphonse Milne-Edwards, Alphonse Milne Edwards after the isopod was found in fishermen's nets off the coast of the Dry Tortugas in the Gulf of Mexico. The ''Bathynomus'' is benthic and abundant in cold waters with a depth of in the West Atlantic, including the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea, Caribbean. It was the first species of ''Bathynomus'' to be Species description, described and historically it was reported from other oceans, but these are now recognized as other closely related species. The unusually large size of ''Bathynomus'' has been attributed to an effect called deep-sea gigantism, where invertebrates living in cold deep waters tend to grow larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Fishing
Commercial fishing is the activity of catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit, mostly from wild fisheries. It provides a large quantity of food to many countries around the world, but those who practice it as an industry must often pursue fish far into the ocean under adverse conditions. Large-scale commercial fishing is also known as industrial fishing. The major fishing industries are not only owned by major corporations but by small families as well. In order to adapt to declining fish populations and increased demand, many commercial fishing operations have reduced the sustainability of their harvest by fishing further down the food chain. This raises concern for fishery managers and researchers, who highlight how further they say that for those reasons, the sustainability of the marine ecosystems could be in danger of collapsing. Commercial fishermen harvest a wide variety of animals. However, a very small number of species support the majority of the world ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pereiopod
The decapod (crustaceans such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment may possess one pair of appendages, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. They are, from head to tail: Cephalothorax Head # antennules # antennae #mandibles # first maxillae # second maxillae The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eyes. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp. Thorax / pereon #first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walking legs and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manca
The manca (plural: ''mancae'') is the post- larval juvenile in some crustaceans. The manca stage is the defining characteristic of a clade called Mancoida which comprises all the member of the Peracarida except the Amphipoda. Mancae closely resemble the adult form, but for the absence of the last pair of pereiopods. In some isopods, specifically the family Gnathiidae, the manca stage is a parasite Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ... of fish, and is also known as the praniza. References Crustaceans Developmental biology Larvae {{crustacean-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brood Pouch (Peracarida)
The marsupium or brood pouch, is a characteristic feature of Peracarida, including the orders Amphipoda, Isopoda, Cladocera, and Cumacea. It is an egg chamber formed by oostegites, which are appendages that are attached to the coxae (first segment) of the first pereiopods. Females lay their eggs directly into the brood chamber, and the young will develop there, undergoing several moults before emerging as miniature adults referred to as mancae. Males have no marsupium. References {{malacostraca-stub Crustacean anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
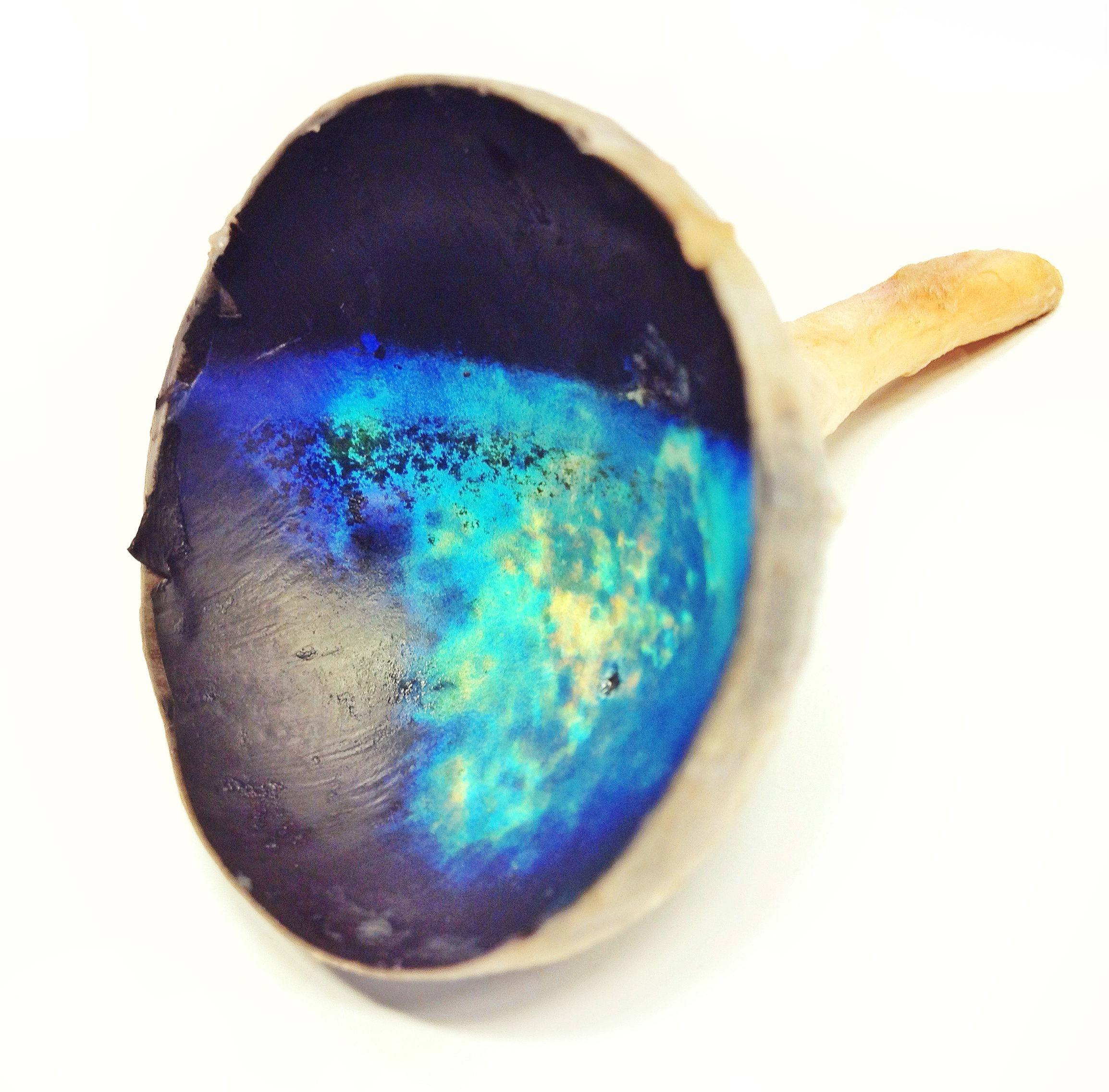
Tapetum Lucidum
The ''tapetum lucidum'' ( ; ; ) is a layer of tissue in the eye of many vertebrates and some other animals. Lying immediately behind the retina, it is a retroreflector. It reflects visible light back through the retina, increasing the light available to the photoreceptors (although slightly blurring the image). The tapetum lucidum contributes to the superior night vision of some animals. Many of these animals are nocturnal, especially carnivores, while others are deep sea animals. Similar adaptations occur in some species of spiders. Haplorhine primates, including humans, are diurnal and lack a ''tapetum lucidum''. Function and mechanism Presence of a ''tapetum lucidum'' enables animals to see in dimmer light than would otherwise be possible. The ''tapetum lucidum'', which is iridescent, reflects light roughly on the interference principles of thin-film optics, as seen in other iridescent tissues. However, the ''tapetum lucidum'' cells are leucophores, not iridophores. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Eye
A compound eye is a visual organ found in arthropods such as insects and crustaceans. It may consist of thousands of ommatidia, which are tiny independent photoreception units that consist of a cornea, lens, and photoreceptor cells which distinguish brightness and color. The image perceived by this arthropod eye is a combination of inputs from the numerous ommatidia, which are oriented to point in slightly different directions. Compared with single-aperture eyes, compound eyes have poor image resolution; however, they possess a very large view angle and the ability to detect fast movement and, in some cases, the polarization of light. Because a compound eye is made up of a collection of ommatidia, each with its own lens, light will enter each ommatidium instead of using a single entrance point. The individual light receptors behind each lens are then turned on and off due to a series of changes in the light intensity during movement or when an object in moving, creating a flic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleon
The decapod ( crustaceans such as a crab, lobster, shrimp or prawn) is made up of 20 body segments grouped into two main body parts: the cephalothorax and the pleon (abdomen). Each segment may possess one pair of appendages, although in various groups these may be reduced or missing. They are, from head to tail: Cephalothorax Head # antennules # antennae #mandibles # first maxillae # second maxillae The head also bears the (usually stalked) compound eyes. The distal portion of a mandible or maxilla which has a sensory function is known as a palp. Thorax / pereon #first maxillipeds #second maxillipeds #third maxillipeds #first pereiopods #second pereiopods #third pereiopods #fourth pereiopods #fifth pereiopods Maxillipeds are appendages modified to function as mouthparts. Particularly in the less advanced decapods, these can be very similar to the pereiopods. Pereiopods are primarily walking legs and are also used for gathering food. They are also the ten legs from which decapod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |