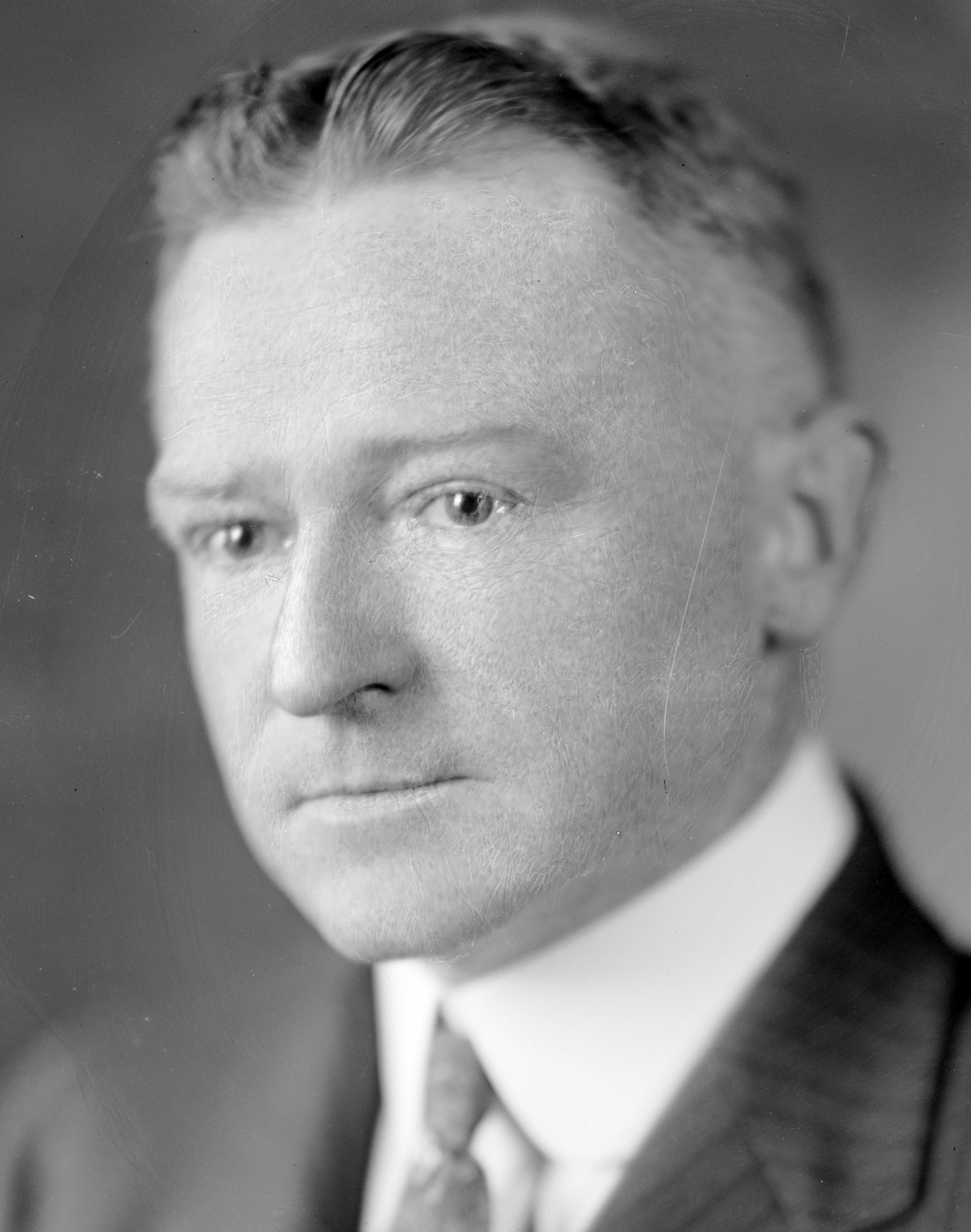|
Bathycrinus Australis
''Bathycrinus australis'' is a species of sea lily, a crinoid in the family Bathycrinidae. It is native to deep water in the Antarctic Ocean. It was initially identified as ''Bathycrinus aldrichianus'' by Philip Herbert Carpenter following the 1872-1876 HMS Challenger expedition. It was later distinguished as a new species by the American zoologist Austin Hobart Clark Austin Hobart Clark (December 17, 1880 – October 28, 1954) was an American zoologist. He was born in Wellesley, Massachusetts and died in Washington, D.C. His research covered a wide range of topics including oceanography, marine biolog .... References Bourgueticrinida Animals described in 1907 Taxa named by Austin Hobart Clark {{Crinoidea-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the sea lilies or "stone lilies". Adult echinoderms are found on the sea bed at every ocean depth, from the intertidal zone to the abyssal zone. The phylum contains about 7,000 living species, making it the second-largest grouping of deuterostomes, after the chordates. Echinoderms are the largest entirely marine phylum. The first definitive echinoderms appeared near the start of the Cambrian. The echinoderms are important both ecologically and geologically. Ecologically, there are few other groupings so abundant in the biotic desert of the deep sea, as well as shallower oceans. Most echinoderms are able to reproduce asexually and regenerate tissue, organs, and limbs; in some cases, they can undergo complete regeneration from a single limb. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crinoidea
Crinoids are marine animals that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that are attached to the sea bottom by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms are called feather stars or comatulids, which are members of the largest crinoid order, Comatulida. Crinoids are echinoderms in the phylum Echinodermata, which also includes the starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins and sea cucumbers. They live in both shallow water and in depths as great as . Adult crinoids are characterised by having the mouth located on the upper surface. This is surrounded by feeding arms, and is linked to a U-shaped gut, with the anus being located on the oral disc near the mouth. Although the basic echinoderm pattern of fivefold symmetry can be recognised, in most crinoids the five arms are subdivided into ten or more. These have feathery pinnules and are spread wide to gather planktonic particles from the water. At some stage in their lives, most crinoids have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articulata (Crinoidea)
Articulata are a subclass or superorder within the class Crinoidea, including the only living crinoid species. They are commonly known as sea lilies (stalked crinoids) or feather stars (unstalked crinoids). The Articulata are differentiated from the extinct subclasses by their lack of an anal plate in the adult stage and the presence of an entoneural system. Articulata first appeared in the fossil record during the Triassic period although other, now extinct crinoid groups, originated in the Ordovician. Characteristics Articulata exhibit pentamerous symmetry. The stalk, which consists of numerous disks held together by ligaments, supports a calyx or cup made of circlets of calcerous plates. In Comatulids, the stalk develops following the larval stage, but the juveniles shed all but the topmost disk to take up a free-living existence. Five often branched arms, which consist of articulated series of ossicles, extend from the oral plate and form the food-capture mechanism of Articula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comatulida
Comatulida is an order of crinoids. Members of this order are known as feather stars and mostly do not have a stalk as adults. The oral surface with the mouth is facing upwards and is surrounded by five, often divided rays with feathery pinnules. Comatulids live on the seabed and on reefs in tropical and temperate waters. Taxonomy Bourgueticrinida, the sea lilies, has traditionally been viewed as an order of Articulata and a sister taxon to Comatulida. A study published in 2011 suggested that it should be renamed Bourgueticrinina and viewed as a suborder of Comatulida. Characteristics Like other echinoderms, comatulids have pentamerous symmetry (five sided) as adults though the larvae have bilateral symmetry. Late in their development, the larvae are attached to the seabed by a stalk, but this is broken at metamorphosis and the juvenile crinoid is free living. The body has an endoskeleton made from a number of articulated calcareous plates known as ossicles covered by a thin e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathycrinidae
Bathycrinidae is a family of echinoderms in the class Crinoidea Crinoids are marine animals that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that are attached to the sea bottom by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms are called feather stars or comatulids, which are .... It contains the following genera and species: * '' Bathycrinus'' Wyville Thomson, 1872 ** '' Bathycrinus aldrichianus'' Wyville Thomson, 1877 ** '' Bathycrinus australis'' AH Clark, 1907 ** '' Bathycrinus australocrucis'' McKnight, 1973 ** '' Bathycrinus carpenterii'' (Danielssen & Koren, 1877) ** '' Bathycrinus gracilis'' Wyville Thomson, 1877 ** '' Bathycrinus mendeleevi'' Mironov, 2008 * '' Discolocrinus'' Mironov, 2008 ** '' Discolocrinus thieli'' Mironov, 2008 * '' Monachocrinus'' AH Clark, 1919 ** '' Monachocrinus aotearoa'' McKnight, 1973 ** '' Monachocrinus caribbeus'' (AH Clark, 1908) ** '' Monachocrinus mortenseni'' Gislén, 1938 ** '' Monachocrinus paradoxu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathycrinus
''Bathycrinus'' is a genus of crinoid Crinoids are marine animals that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that are attached to the sea bottom by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms are called feather stars or comatulids, which are ...s. References * Thuy B, Gale AS, Kroh A, Kucera M, Numberger-Thuy LD, Reich M, et al. (2012) Ancient Origin of the Modern Deep-Sea Fauna. PLoS ONE 7(10): e46913. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046913 {{Taxonbar, from=Q3456370 Crinoid genera Extant Early Cretaceous first appearances ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austin Hobart Clark
Austin Hobart Clark (December 17, 1880 – October 28, 1954) was an American zoologist. He was born in Wellesley, Massachusetts and died in Washington, D.C. His research covered a wide range of topics including oceanography, marine biology, ornithology, and entomology. Biography The son of Theodore Minot Clark and Jeannette French Clark, Clark obtained his Bachelor of Arts at Harvard University in 1903. He had five children with his first wife Mary Wendell Upham, whom he married on March 6, 1906. Mary died in December 1931 and Clark was remarried in 1933 to Leila Gay Forbes. In 1901, Clark organized a scientific expedition to Isla Margarita in Venezuela. From 1903 to 1905, he conducted research in the Antilles. From 1906 to 1907, he led a scientific team aboard the 1882 USS ''Albatross''. In 1908, he took a post at the National Museum of Natural History, which he held until his retirement in 1950. Clark had important and various roles in a number of learned societies: t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crinoid
Crinoids are marine animals that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that are attached to the sea bottom by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms are called feather stars or comatulids, which are members of the largest crinoid order, Comatulida. Crinoids are echinoderms in the phylum Echinodermata, which also includes the starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins and sea cucumbers. They live in both shallow water and in depths as great as . Adult crinoids are characterised by having the mouth located on the upper surface. This is surrounded by feeding arms, and is linked to a U-shaped gut, with the anus being located on the oral disc near the mouth. Although the basic echinoderm pattern of fivefold symmetry can be recognised, in most crinoids the five arms are subdivided into ten or more. These have feathery pinnules and are spread wide to gather planktonic particles from the water. At some stage in their lives, most crinoids have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Herbert Carpenter
Philip Herbert Carpenter (6 February 1852 – 21 October 1891), Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS, British naturalist and crinoid authority, was the fourth son of William Benjamin Carpenter. Education and research Carpenter was educated at University College School, then at University College London, University College, and afterwards became a Scholar of Trinity College, Cambridge, Trinity College, Cambridge, where he graduated in 1874. He was a member of the scientific staff of the deep-sea exploring expeditions of H.M.S. ''Lightning'' (1868) and ''Porcupine'' (1869–1870). In 1875, he was appointed assistant naturalist to HMS Valorous (1851), H.M.S. ''Valorous'' accompanying Admiral Sir George Strong Nares's Arctic expedition to Disco Island, and spent the summer sounding and dredging in Davis Strait and the North Atlantic. Career After the 1872–1876 HMS Challenger (1858), HMS Challenger expedition had returned, he was asked in January 1878 by Sir Wyville Thomson to describe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Description
A species description is a formal description of a newly discovered species, usually in the form of a scientific paper. Its purpose is to give a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differs from species that have been described previously or are related. In order for species to be validly described, they need to follow guidelines established over time. Zoological naming requires adherence to the ICZN code, plants, the ICN, viruses ICTV, and so on. The species description often contains photographs or other illustrations of type material along with a note on where they are deposited. The publication in which the species is described gives the new species a formal scientific name. Some 1.9 million species have been identified and described, out of some 8.7 million that may actually exist. Millions more have become extinct throughout the existence of life on Earth. Naming process A name of a new species becomes valid (available in zo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |