|
Bathocyroe Paragaster
''Bathocyroe'' is a genus of ctenophore Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and ...s, the only genus in the family Bathocyroidae. References Lobata Ctenophore genera {{Ctenophore-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
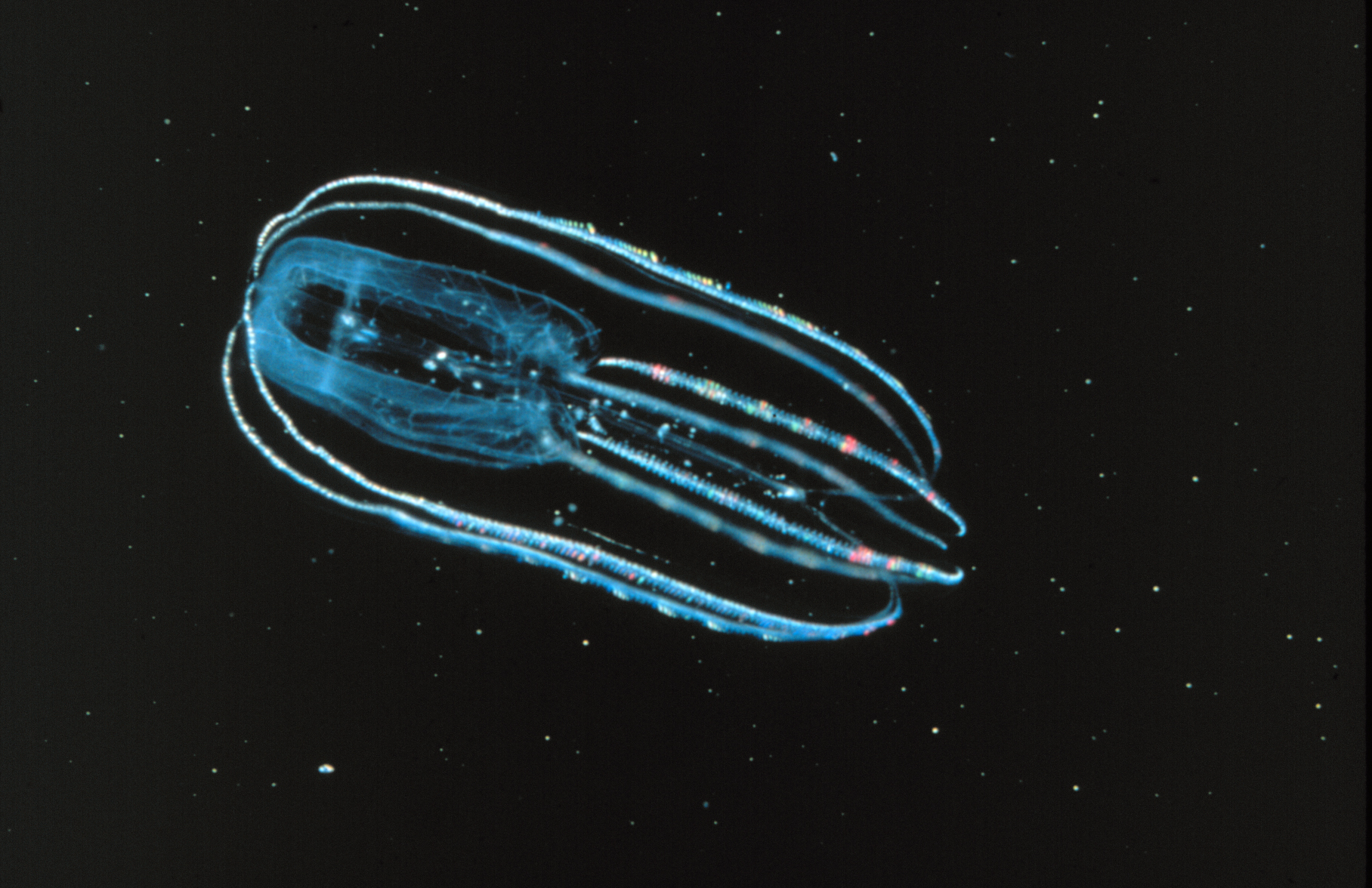
Bathocyroe Fosteri
''Bathocyroe fosteri'' is a species of lobate ctenophore found at intermediate depths in all the world's oceans. The species is very common and abundant near the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. It is bioluminescent, and is typically observed hanging motionlessly in an upright or inverted posture although it can flap its oral lobes to swim. This deep-sea comb jelly is named for Alvin (DSV-2) ''Alvin'' (DSV-2) is a crewed deep-ocean research submersible owned by the United States Navy and operated by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) in Woods Hole, Massachusetts. The vehicle was built by General Mills' Electronics Grou ... pilot Dudley Foster, who collected the first specimens. Description ''Bathocyroe fosteri'' is mostly transparent with red pigmented inner gut walls. It has short comb rows and measures 2–4 cm across the oral lobes. These oral lobes are used to contain prey until they are drawn into the gut with its tentacles. References External links OurAm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathocyroe Longigula
''Bathocyroe'' is a genus of ctenophore Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and ...s, the only genus in the family Bathocyroidae. References Lobata Ctenophore genera {{Ctenophore-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bathocyroe Paragaster
''Bathocyroe'' is a genus of ctenophore Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and ...s, the only genus in the family Bathocyroidae. References Lobata Ctenophore genera {{Ctenophore-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenophore
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles") that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless platyct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobata
Lobata is an order of Ctenophora in the class Tentaculata with smaller tentacles than other ctenophores, and distinctive flattened lobes extending outwards from their bodies. They grow up to about long. Anatomy The lobates have a pair of lobes, which are muscular, cuplike extensions of the body that project beyond the mouth. Their inconspicuous tentacles originate from the corners of the mouth, running in convoluted grooves and spreading out over the inner surface of the lobes (rather than trailing far behind, as in the Cydippida). Between the lobes on either side of the mouth, many species of lobates have four auricles, gelatinous projections edged with cilia that produce water currents that help direct microscopic prey toward the mouth. This combination of structures enables lobates to feed continuously on suspended planktonic prey. Lobates have eight comb-rows, originating at the aboral pole and usually not extending beyond the body to the lobes; in species with (four) au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |