|
Lobata
Lobata is an order of Ctenophora in the class Tentaculata with smaller tentacles than other ctenophores, and distinctive flattened lobes extending outwards from their bodies. They grow up to about long. Anatomy The lobates have a pair of lobes, which are muscular, cuplike extensions of the body that project beyond the mouth. Their inconspicuous tentacles originate from the corners of the mouth, running in convoluted grooves and spreading out over the inner surface of the lobes (rather than trailing far behind, as in the Cydippida). Between the lobes on either side of the mouth, many species of lobates have four auricles, gelatinous projections edged with cilia that produce water currents that help direct microscopic prey toward the mouth. This combination of structures enables lobates to feed continuously on suspended planktonic prey. Lobates have eight comb-rows, originating at the aboral pole and usually not extending beyond the body to the lobes; in species with (four) au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobata Incertae Sedis
Lobata is an order of Ctenophora in the class Tentaculata with smaller tentacles than other ctenophores, and distinctive flattened lobes extending outwards from their bodies. They grow up to about long. Anatomy The lobates have a pair of lobes, which are muscular, cuplike extensions of the body that project beyond the mouth. Their inconspicuous tentacles originate from the corners of the mouth, running in convoluted grooves and spreading out over the inner surface of the lobes (rather than trailing far behind, as in the Cydippida). Between the lobes on either side of the mouth, many species of lobates have four auricles, gelatinous projections edged with cilia that produce water currents that help direct microscopic prey toward the mouth. This combination of structures enables lobates to feed continuously on suspended planktonic prey. Lobates have eight comb-rows, originating at the aboral pole and usually not extending beyond the body to the lobes; in species with (four) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
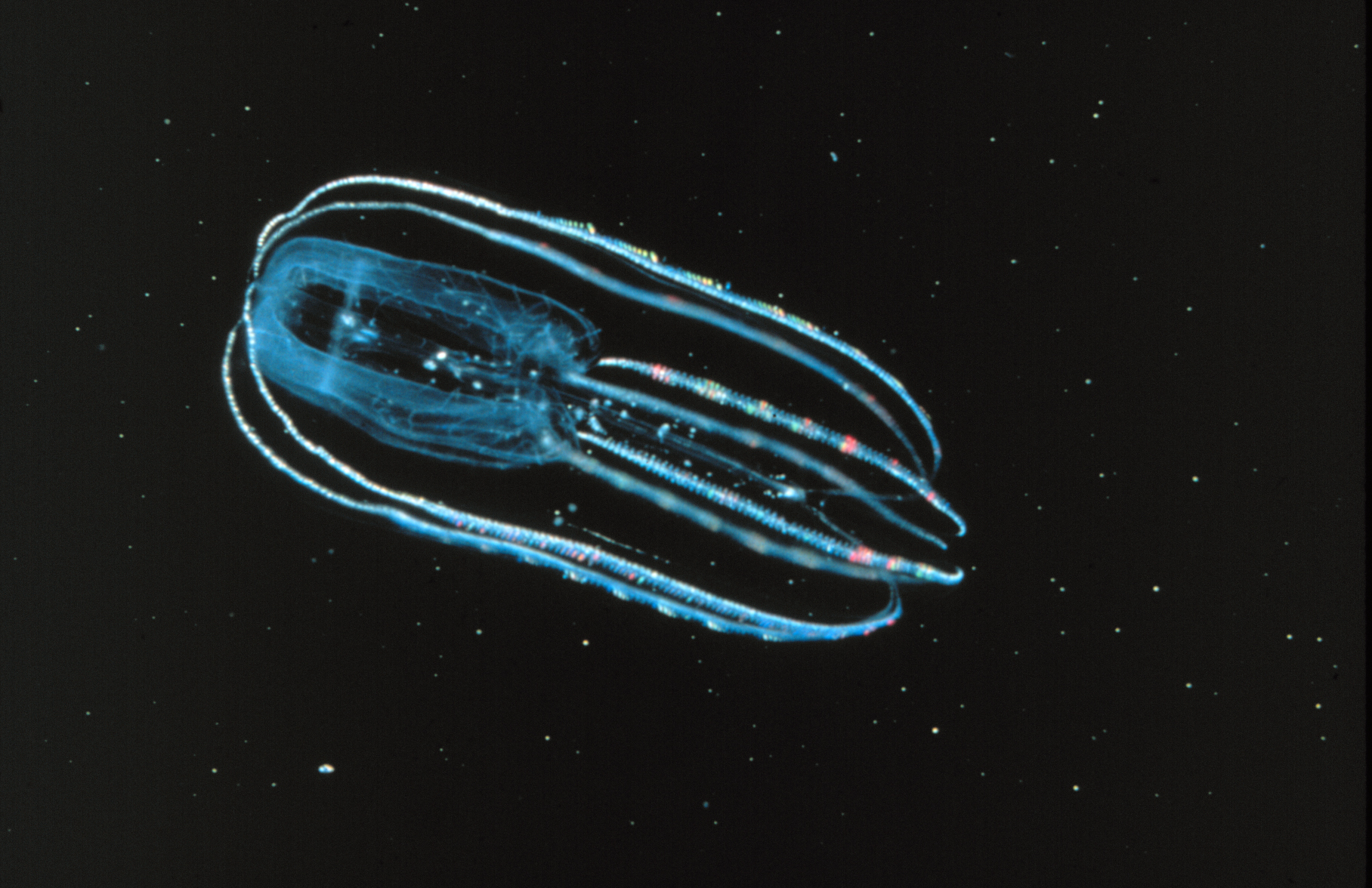
Ctenophore - Bolinopsis Infundibulum
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles") that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless platyct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenophora
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles") that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless plat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
São Tomé And Príncipe
São Tomé and Príncipe (; pt, São Tomé e Príncipe (); English: " Saint Thomas and Prince"), officially the Democratic Republic of São Tomé and Príncipe ( pt, República Democrática de São Tomé e Príncipe), is a Portuguese-speaking island country in the Gulf of Guinea, off the western equatorial coast of Central Africa. It consists of two archipelagos around the two main islands of São Tomé and Príncipe, about apart and about off the north-western coast of Gabon. With a population of 201,800 (2018 official estimate),Instituto Nacional de Estadística de São Tomé e Príncipe, as at 13 May 2018. São Tomé and Príncipe is the second-smallest and second-least populous African sovereign state after Seychelles. The islands were uninhabited until their discovery by Portuguese explorers in the 15th century. Gradually colonized and settled throughout the 16th century, they collectively served as a vital commercial and trade centre for the Atlantic slave trade. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobatolampea Tetragona
Lobatolampeidae is a family of ctenophores belonging to the order Lobata Lobata is an order of Ctenophora in the class Tentaculata with smaller tentacles than other ctenophores, and distinctive flattened lobes extending outwards from their bodies. They grow up to about long. Anatomy The lobates have a pair of lo .... The family consists of only one genus: ''Lobatolampea'' Horita, 2000. References Lobata {{ctenophore-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lampoctenidae
''Lampocteis'' is a monotypic genus of comb jellies, the only genus in family Lampoctenidae. The sole species in this new genus is ''Lampocteis cruentiventer'', the bloodybelly comb jelly. This ctenophore was first collected in the Pacific Ocean off the coast of San Diego, California, in 1979. It was described to science in 2001. Two morphological differences separating it from previously known comb jellies warranted the naming of a new family for this animal.Harbison, G. R., G. I. Matsumoto, and B. H. Robison. (2001)''Lampocteis cruentiventer'' gen. nov., sp. nov.: A new mesopelagic lobate ctenophore, representing the type of a new family (Class Tentaculata, Order Lobata, Family Lampoctenidae, fam. nov.).''Bulletin of Marine Science'' 68:2 299-311. This ctenophore differs from all previously described lobate ctenophores in two major ways: (1) all of the meridional canals have blind aboral endings, and (2) the body is penetrated by a deep notch located between the adjacent subten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tentaculata
Tentaculata is a class of comb jellies. The common feature of this class is a pair of long, feathery, contractile tentacles, which can be retracted into specialised ciliated sheaths. In some species, the primary tentacles are reduced and they have smaller, secondary tentacles. The tentacles have colloblasts, which are sticky-tipped cells that trap small prey. Body size and shape varies widely. The group includes the small, oval sea gooseberries found on both Atlantic and Pacific coasts. The more flattened species of the genus '' Mnemiopsis'', about long, are common on the upper Atlantic coast; it has a large mouth and mainly feeds on larval molluscs and copepods. This species is brilliantly luminescent. The similar, but larger, genus '' Leucothea'' is abundant on the Pacific coast. Venus girdle The Venus girdle (''Cestum veneris'') is a comb jelly in the family Cestidae. It is the only member of its genus, ''Cestum''. Description Venus girdles resemble transparent ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocyropsis
Ocyropsis is a genus of Ctenophores, which are commonly known as Comb Jellies. Ocyropsis belong to the family of Ocyropsidae. Ocyropsis possesses two large lateral muscular lobes and four auricles, and appear pale and translucent in color. Ocyropsis habitat is not precise as their gelatinous composition can make it difficult to study. They have been found in warm and cold waters. Unlike other, slow swimming Ctenophores, Ocyropsis are efficient in evading their predators. They use their oral lobes for additional propulsion and a secrete luminous mucous in efforts to evade predators. The muscular oral lobes of the Ocyropsis are used to grab its prey, and then moved to the prehensile mouth for absorption. Distribution Habitat There is lack of knowledge known about Ctenophores habitats. Ocyropsis have been found in both warm and cold waters. They were found and photographed specifically near South Africa near Southern Mozambique to False Bay. There have also been reports of Ocyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurhamphaeidae
Eurhamphaeidae is a family of ctenophores. Taxonomy The family Eurhamphaeidae contains the following species: * Genus '' Deiopea'' **''Deiopea kaloktenota'' Chun, 1879 * Genus ''Eurhamphaea'' **''Eurhamphaea vexilligera'' Gegenbaur, 1856 * Genus ''Kiyohimea'' **''Kiyohimea aurita'' Komai and Tokioka, 1940 ** ''Kiyohimea usagi Eurhamphaeidae is a family of ctenophores. Taxonomy The family Eurhamphaeidae contains the following species: * Genus '' Deiopea'' **'' Deiopea kaloktenota'' Chun, 1879 * Genus ''Eurhamphaea'' **''Eurhamphaea vexilligera'' Gegenbaur, 1856 ...'' Matsumoto and Robison, 1992 References Lobata {{Ctenophore-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |