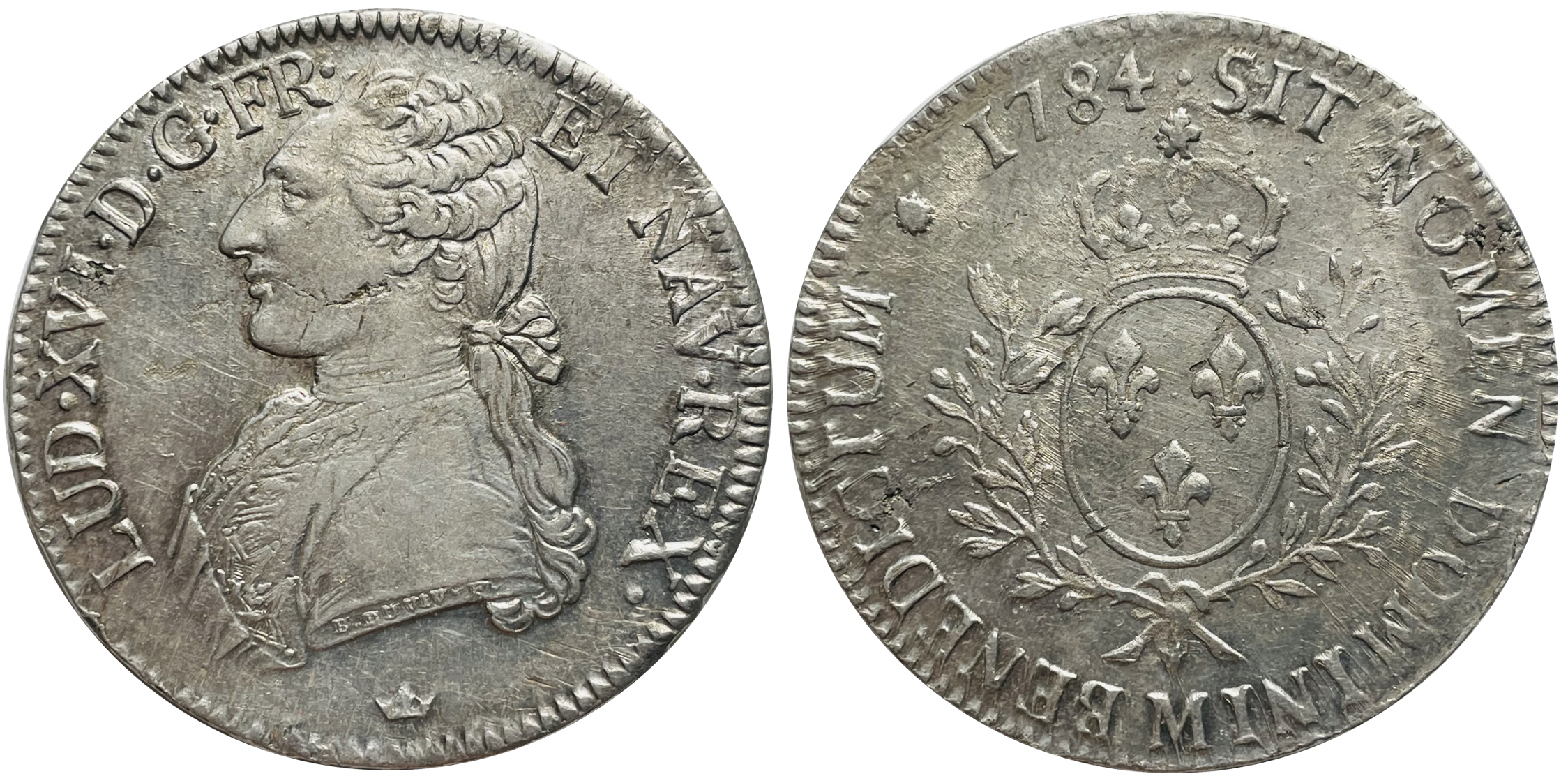
|
Basilikon
The ''basilikon'' ( el, ฮฒฮฑฯฮนฮปฮนฮบฯฮฝ ๏ฟฝฯฮผฮนฯฮผฮฑ}, "imperial oin), commonly also referred to as the (Greek: ฮดฮฟฯ ฮบฮฌฯฮฟฮฝ), was a widely circulated Byzantine silver coin of the first half of the 14th century. Its introduction marked the return to a wide-scale use of silver coinage in the Byzantine Empire, and presaged the total abandonment of the gold coins around the middle of the century. History The ''basilikon'' was introduced shortly before 1304 by Emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos (r. 1282โ1328), in direct imitation of the Venetian silver ducat or '' grosso'', chiefly to pay the mercenaries of the Catalan Company... The Byzantine coin closely followed the iconography of the Venetian model, with a seated Christ on the obverse and the two standing figures of Andronikos II and his son and co-emperor Michael IX Palaiologos (r. 1294โ1320) replacing St. Mark and the Doge of Venice on the reverse. The similarity was reinforced by the name of the new coin: the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos II Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos II Palaiologos2.jpg , caption = Miniature from the manuscript of George Pachymeres' ''Historia'' , succession = Byzantine emperor , reign = 11 December 1282 โ24 May 1328 , coronation = 8 November 1272 , cor-type1 = Coronation , regent = Michael IX Palaiologos , reg-type = Co-emperor , predecessor = Michael VIII Palaiologos (alone) , successor = Andronikos III Palaiologos , spouse = Anna of Hungary Yolande of Montferrat , issue = Michael IX Palaiologos Constantine Palaiologos John Palaiologos Theodore I, Marquis of Montferrat Demetrios Palaiologos Simonis (Simonida Nemanjiฤ), Queen of SerbiaIrene Palaiologina (wife of John II Doukas), Sebastokratorissa of Thessaly , issue-link = #Family , issue-pipe = more... , dynasty = Palaiologos , father = Michael VIII Palaiologos , mother = Theodora Palaiologina , birth_date = 25 March 1259 , birth_place = Nicaea, Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael IX Palaiologos
, image = 154 - Michael IX Palaiologos (Mutinensis - color).png , caption = 15th-century portrait of Michael IX (from a 15th-century codex containing a copy of the ''Extracts of History'' by Joannes Zonaras) , succession = Byzantine emperor , reign = 21 May 1294 โ12 October 1320 , coronation = 21 May 1294, Hagia Sophia , regent = Andronikos II Palaiologos , reg-type = Co-emperor , predecessor = Andronikos II (alone) , successor = Andronikos II (alone), Andronikos III ( in Macedonia) , spouse = , issue = , dynasty = Palaiologos , father = Andronikos II Palaiologos , mother = Anna of Hungary , birth_date = 17 April 1277 , birth_place = Constantinople(now Istanbul, Turkey) , death_date = , death_place = Thessaloniki, Greece , place of burial = , , title= Emperor and Autocrat of the Romans Michael IX Palaiologos or Palaeologus ( el, ฮฮนฯฮฑฮฎฮป ฮฮฟฯ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ducat
The ducat () coin was used as a trade coin in Europe from the later Middle Ages from the 13th to 19th centuries. Its most familiar version, the gold ducat or sequin containing around of 98.6% fine gold, originated in Venice in 1284 and gained wide international acceptance over the centuries. Similarly named silver ducatons also existed. The gold ducat circulated along with the Florentine florin and preceded the modern British pound sterling and the United States dollar. Predecessors The word ''ducat'' is from Medieval Latin ''ducalis'' = "relating to a duke (or dukedom)", and initially meant "duke's coin" or a "duchy's coin". The first issue of scyphate billon coins modelled on Byzantine ''trachea'' was made by King Roger II of Sicily as part of the Assizes of Ariano (1140). It was to be a valid issue for the whole kingdom. The first issue bears the figure of Christ and the Latin inscription ''Sit tibi, Christe, datus, quem tu regis iste ducatus'' (meaning "O Christ, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miliaresion
The ''miliaresion'' ( el, ฮผฮนฮปฮนฮฑฯฮฎฯฮนฮฟฮฝ, from la, miliarensis), is a name used for two types of Byzantine silver coins. In its most usual sense, it refers to the themed flat silver coin struck between the 8th and 11th Century. History Originally, the name was given to a series of silver coins issued in the 4th century that were struck 72 to the pound and were the equivalent of 1,000 '' nummi''. Thereafter and until the 7th century, the Byzantines did not get regularly circulate silver coins, although there were a very small number of commemorative issues struck. In the 7th century, a ''miliaresion'' was an alternative name possibly given to a variation on the short-lived hexagram coin minted during the time of Heraclius and Constans II. From , this variant coin, broader and thinner than the hexagram, was instituted by Leo III the Isaurian ().. The new coin, for which the term ''miliaresion'' is usually preserved among numismatists, was apparently struck 144 to the pou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperpyron
The ''hyperpyron'' ( ''nรณmisma hypรฉrpyron'') was a Byzantine coin in use during the late Middle Ages, replacing the '' solidus'' as the Byzantine Empire's gold coinage. History The traditional gold currency of the Byzantine Empire had been the '' solidus'' or '' nomisma'', whose gold content had remained steady at 24 carats for seven centuries and was consequently highly prized. From the 1030s, however, the coin was increasingly debased, until in the 1080s, following the military disasters and civil wars of the previous decade, its gold content was reduced to almost zero. Consequently, in 1092, Emperor Alexios I Komnenos ( 1081โ1118) undertook a drastic overhaul of the Byzantine coinage system and introduced a new gold coin, the ''hyperpyron'' (meaning "super-refined"). This was of the same standard weight (4.45 grams) as the ''solidus'', but only 20.5 carat purity instead of 24, resulting in a reduced gold content of only 4.1 grams instead of 4.8 grams. The lower purity was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basileus
''Basileus'' ( el, ) is a Greek term and title that has signified various types of monarchs in history. In the English-speaking world it is perhaps most widely understood to mean " monarch", referring to either a " king" or an " emperor" and also by bishops of the Eastern orthodox church and Eastern Catholic Churches. The title was used by sovereigns and other persons of authority in ancient Greece, the Byzantine emperors, and the kings of modern Greece. The feminine forms are ''basileia'' (), ''basilis'' (), ''basilissa'' (), or the archaic ''basilinna'' (), meaning "queen" or "empress". Etymology The etymology of ''basileus'' is uncertain. The Mycenaean form was *''gสทasileus'' (Linear B: , ''qa-si-re-u''), denoting some sort of court official or local chieftain, but not an actual king. Its hypothetical earlier Proto-Greek form would be *''gสทatileus''. Some linguists assume that it is a non-Greek word that was adopted by Bronze Age Greeks from a pre-existing lingu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Coins
Silver coins are considered the oldest mass-produced form of coinage. Silver has been used as a coinage metal since the times of the Greeks; their silver drachmas were popular trade coins. The ancient Persians used silver coins between 612โ330 BC. Before 1797, British pennies were made of silver. As with all collectible coins, many factors determine the value of a silver coin, such as its rarity, demand, condition and the number originally minted. Ancient silver coins coveted by collectors include the Denarius and Miliarense, while more recent collectible silver coins include the Morgan Dollar and the Spanish Milled Dollar. Other than collector's silver coins, silver bullion coins are popular among people who desire a "hedge" against currency inflation or store of value. Silver has an international currency symbol of XAG under ISO 4217. Origins and early development of silver coins The earliest coins in the world were minted in the kingdom of Lydia in Asia Minor aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Oxford Dictionary Of Byzantium
The ''Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium'' (ODB) is a three-volume historical dictionary published by the English Oxford University Press. With more than 5,000 entries, it contains comprehensive information in English on topics relating to the Byzantine Empire. It was edited by Alexander Kazhdan, and was first published in 1991.''The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium'', Oxford University Press, New York and Oxford, 1991. Kazhdan was a professor at Princeton University who became a Senior Research Associate at Dumbarton Oaks, Washington, DC, before his death. He contributed to many of the articles in the Dictionary and always signed his initials ''A.K.'' at the end of the article to indicate his contribution. Description The dictionary is available in printed and e-reference text versions from Oxford Reference Online. It covers the main historical events of Byzantium, as well as important social and religious events. It also includes biographies of eminent political and literary person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stavraton
The ''stavraton'' or ''stauraton'' ( el, ฯฯฮฑฯ ฯฮฌฯฮฟฮฝ) was a type of silver coin used during the last century of the Byzantine Empire. History The name ''stavraton'' first appears in the mid-11th century for a gold '' histamenon'' showing the Byzantine emperor holding a cross-shaped scepter, but in its more specific sense, it denotes the large silver coins introduced by Emperor John V Palaiologos (r. 1341โ1376, 1379โ1391) in circa 1367 and used for the last century of Byzantine history.. The late Byzantine coin was probably named after the cross (Greek: ฯฯฮฑฯ ฯฯฯ, ''stavros''/''stauros'') that featured in its presumed model, the double '' gigliato'' of Naples and the Provence; alternatively, the name may have derived from the small crosses at the beginning of the coins' inscriptions, an unusual feature for Byzantine currency, although these are not very conspicuous.. The coin was designed to replace the defunct gold ''hyperpyron'' as the highest-denomination coin in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The Sea has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltarโthe narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africaโis only wide. The Mediterr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68โ69); "Asia" (pp. 90โ91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexagram (currency)
The hexagram ( el, , ''hexagramma'') was a large silver coin of the Byzantine Empire issued primarily during the 7th century AD. With the exception of a few 6th-century ceremonial issues, silver coins were not used in the late Roman/early Byzantine monetary system (see Byzantine coinage), chiefly because of the great fluctuation of its price relative to gold. Only under Emperor Heraclius (r. 610โ641), in 615, were new silver coins minted to cover the needs of the war with Sassanid Persia. The material for these coins came chiefly from the confiscation of church plate. They were named after their weight of six '' grammata'' (6.84 grams), and probably valued at 12 to the gold ''solidus''... The Hexagrams uniquely carried the inscription of ''Deus adiuta Romanis'' or "May God help the Romans"; It is believed that this shows the desperation of the empire at this time. The coin remained in regular issue under Heraclius's successor Constans II (r. 641โ668), from whose reign many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |