|
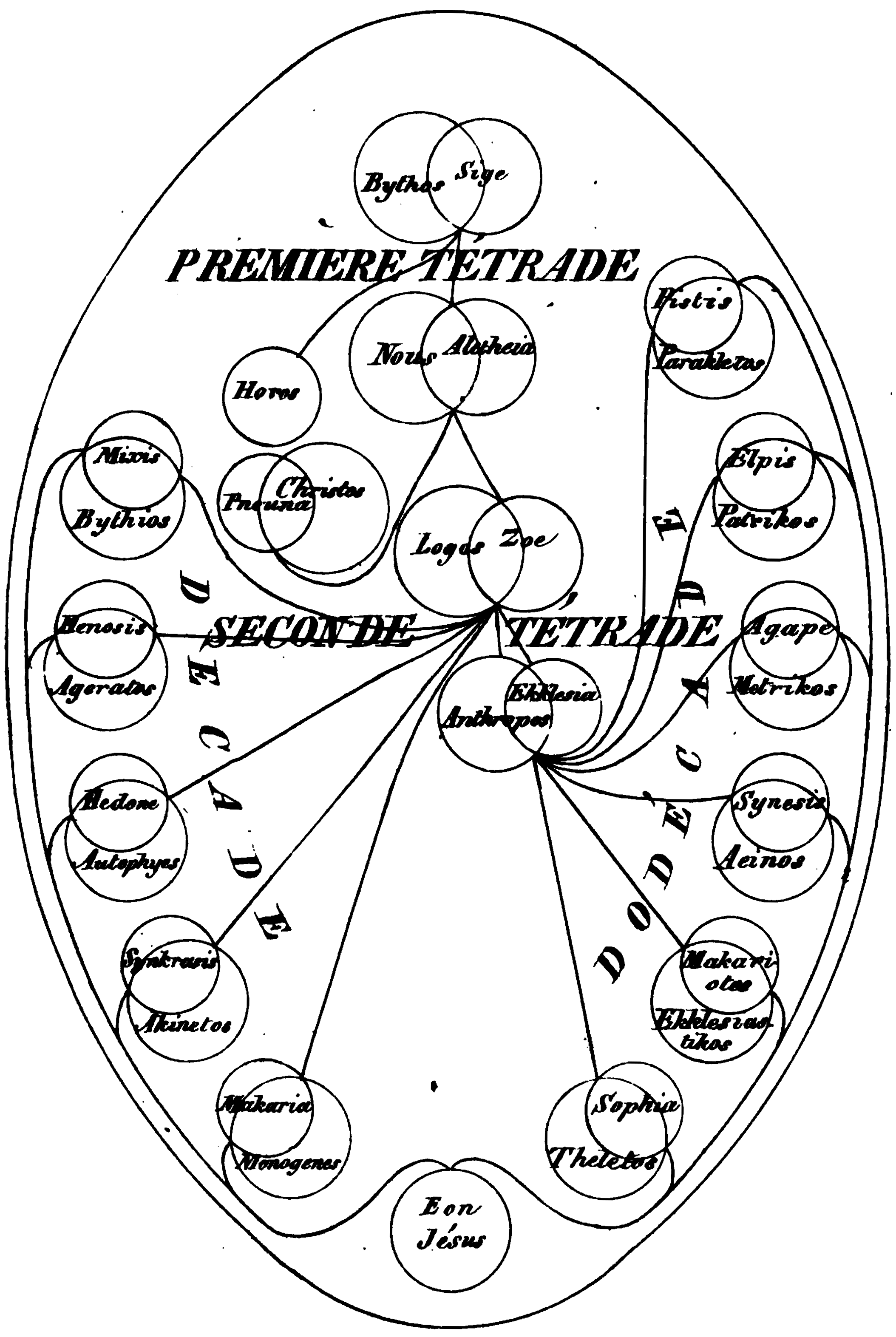
Barbelo
Barbēlō (Greek: Βαρβηλώ)Iren., Epiph., Philast., ''Pist. Soph''., Hier.; -ρώ Epiph. as an alternative, 92 A, and similarly the Epitome, p. 354 Dind.; -λ, Epit. ''l. c. bis;'' -λώθ Theodoret. refers to the first emanation of God in several forms of Gnostic cosmogony. Barbēlō is often depicted as a supreme female principle, the single passive antecedent of creation in its manifoldness. This figure is also variously referred to as 'Mother-Father' (hinting at her apparent androgyny), 'First Human Being', 'The Triple Androgynous Name', or 'Eternal Aeon'. So prominent was her place amongst some Gnostics that some schools were designated as ''Barbeliotae'', Barbēlō worshippers or Barbēlō gnostics. The nature of Barbēlō Nag Hammadi Library In the ''Apocryphon of John'', a tractate in the Nag Hammadi Library containing the most extensive recounting of the Sethian creation myth, the Barbēlō is described as "the first power, the glory, Barbēlō, the perfect g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Three Steles Of Seth
The Three Steles of Seth is a 3rd-century Sethian Gnostic text from the New Testament apocrypha. History The main surviving copies come from the Nag Hammadi library, and were translated and explained by Paul Claude, member of the Nag Hammadi Research Group of the Faculty of Theology and Religious Studies, Université Laval (Quebec). The text concerns a revelation to Dositheos about three steles (text written into specially created stones). Many scholars think that they are designed as liturgy. The text is thought to be from the Sethian sect of Gnostics (the sect that viewed the biblical Seth as their hero, who was reincarnated as Jesus). Their other texts include the Apocalypse of Adam, Apocryphon of John, the Trimorphic Protennoia, and the Coptic Gospel of the Egyptians. The text is thought to be a 3rd-century development of the Sethian Gnostics, as they became more separated from Christianity, and closer to Platonism. The Three Steles (or Tablets) of Seth are in essence, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zostrianos
Zostrianos is a 3rd-century Sethian Gnostic text from the New Testament apocrypha. The main surviving copies come from the Nag Hammadi library, but it is heavily damaged.John D. Turner of the University of Nebraska writes concerning its date: "... one may date Allogenes around 200 C.E., with Zostrianos coming a bit later around 225 C.E. (Porphyry certainly recognized it as a spurious and recent work)." Porphyry's biography of Plotinus mentions ''Zostrianos''. The ''Enneads'' of Plotinus also criticize many Gnostic ideas that are given in ''Zostrianos''. Overview Like Marsanes and Allogenes, the text concerns a vision received by a man named Zostrianos and explains and enumerates, in great detail, the emanations that the Gnostics said are produced by God (the true, highest God as opposed to the demiurge), in the Gnostics' esoteric cosmology. Similarly to other gnostic literature, Zostrianos says, "Flee from the madness and the bondage of femaleness and choose for yourselves the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borborites
According to the ''Panarion'' of Epiphanius of Salamis (ch. 26), and Theodoret's ''Haereticarum Fabularum Compendium'', the Borborites or Borborians ( el, Βορβοριανοί; in Egypt, Phibionites; in other countries, Koddians, Barbelites, Secundians, Socratites, Zacchaeans, Stratiotics) were a Christian Gnostic sect, said to be descended from the Nicolaitans. It is difficult to know for sure the practices of the group, as both Epiphanius and Theodoret were opponents of the group. According to Epiphanius, the sect were libertines who embraced the pleasures of the earthly world. Etymology The word ''Borborite'' comes from the Greek word , meaning "mud"; the name ''Borborites'' can therefore be translated as "filthy ones", and is unlikely to be the term the sect used for themselves. The name ''Koddian'' is claimed by Epiphanius to derive from an Aramaic term for a dish or bowl; J. J. Buckley writes that the likely root, ''kuda'', refers in both Syriac Aramaic and Mandai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnostic
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Jewish and early Christian sects. These various groups emphasized personal spiritual knowledge (''gnosis'') above the orthodox teachings, traditions, and authority of religious institutions. Gnostic cosmogony generally presents a distinction between a supreme, hidden God and a malevolent lesser divinity (sometimes associated with the Yahweh of the Old Testament) who is responsible for creating the material universe. Consequently, Gnostics considered material existence flawed or evil, and held the principal element of salvation to be direct knowledge of the hidden divinity, attained via mystical or esoteric insight. Many Gnostic texts deal not in concepts of sin and repentance, but with illusion and enlightenment. Gnostic writings flourished among certain Christian groups in the Mediterranean world aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apocryphon Of John
The ''Apocryphon of John'', also called the ''Secret Book of John'' or the ''Secret Revelation of John'', is a 2nd-century Sethianism, Sethian gnosticism, Gnostic Christian pseudepigrapha, pseudographical text attributed to John the Apostle. It is one of the texts addressed by Irenaeus in his ''Against Heresies (Irenaeus), Against Heresies,'' placing its composition before 180 CE. It is presented as describing Jesus appearing and giving secret knowledge (gnosis) to his disciple John. The author describes it as having occurred after Jesus had "gone back to the place from which he came". Overview Many second-century Christians, both Gnostic and orthodox, hoped to receive a transcendent personal revelation such as Paul the Apostle reported to the church at Corinth () or that John experienced on the isle of Patmos, which inspired the ''Book of Revelation''. As ''Acts'' narrates what happened after the time Jesus ascended to heaven, so the ''Apocryphon of John'' begins at the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophia (Gnosticism)
Sophia ( grc-koi, Σοφíα "Wisdom", cop, ⲧⲥⲟⲫⲓⲁ "the Sophia") is a major theme, along with Knowledge ( ''gnosis'', Coptic ), among many of the early Christian knowledge-theologies grouped by the heresiologist Irenaeus as (), ‘knowing’ or ‘men that claimed to have deeper wisdom’. Gnosticism is a 17th-century term expanding the definition of Irenaeus' groups to include other syncretic and mystery religions. In Gnosticism, Sophia is a feminine figure, analogous to the human soul but also simultaneously one of the feminine aspects of God. Gnostics held that she was the ''syzygy'' (female twin Aeon (Gnosticism), divine Aeon) of Jesus (i.e. the Bride of Christ), and Holy Spirit of the Trinity. She is occasionally referred to by the Hebrew language, Hebrew equivalent of (, he, חכמה ) and as (). In the Nag Hammadi library, Nag Hammadi texts, Sophia is the lowest Aeon, or anthropic expression of the emanation of the light of God. She is considered to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autogenes
In Sethian Gnosticism, Autogenes (Meaning "Self-Born One" in Greek) is an emanation or son of Barbelo (along with Kalyptos and Protophanes according to ''Zostrianos''). Autogenes is mentioned in Nag Hammadi texts such as ''Zostrianos'', ''The Three Steles of Seth'', ''Allogenes the Stranger'', and ''Marsanes''. Autogenes in Gnosticism is roughly parallel to the Platonic soul. See also *Aeon (Gnosticism) *Plato's theory of soul Plato's theory of soul, which was inspired by the teachings of Socrates, considered the psyche ( ψυχή) to be the essence of a person, being that which decides how people behave. Plato considered this essence to be an incorporeal, eternal occu ... References Gnostic deities {{Gnosticism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protophanes
In Sethian Gnosticism, Protophanes ("the First-Appearing One") is one of the three emanations of Barbelo (along with Kalyptos and Autogenes according to ''Zostrianos''). Protophanes is mentioned in Nag Hammadi texts such as ''Zostrianos'', ''The Three Steles of Seth'', Allogenes the Stranger'', and ''Marsanes''. See also *Aeon (Gnosticism) In many Gnostic systems, various emanations of God are known by such names as One, Monad, ''Aion teleos'' (αἰών τέλεος "The Broadest Aeon"), Bythos (, "depth" or "profundity"), ''Proarkhe'' ("before the beginning", ), ''Arkhe'' ("the ... References Gnostic deities {{Gnosticism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalyptos
In Sethian Gnosticism, Kalyptos ("the Hidden One") is one of the three emanations of Barbelo (along with Protophanes and Autogenes according to ''Zostrianos''). Kalyptos is mentioned in Nag Hammadi texts such as ''Zostrianos'', ''The Three Steles of Seth'', ''Allogenes the Stranger'', and ''Marsanes''. See also *Aeon (Gnosticism) *Hypostasis (philosophy and religion) Hypostasis (Greek: ὑπόστασις, ''hypóstasis'') is the underlying state or underlying substance and is the fundamental reality that supports all else. In Neoplatonism the hypostasis of the soul, the intellect (''nous'') and "the one" was ... References Gnostic deities {{Gnosticism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coptic Gospel Of The Egyptians
Two versions of the formerly lost ''Holy Book of the Great Invisible Spirit,'' also informally called the ''Coptic Gospel of the Egyptians''John D. Turner: "Since the late 1940s it has become customary to refer to it inappropriately as the Gospel of the Egyptians." (which is quite distinct from the Greek Gospel of the Egyptians) or the ''Gospel of the Egyptians'', were among the codices in the Nag Hammadi library, discovered in 1945. It received the name because towards the end of the text it is also expressed as the “Egyptian Gospel.” Although it is possible that it was written in Egypt, it is far more likely that the name is based on connections made between Seth of the Old Testament and Set, the ancient Egyptian god of violence, chaos, and storms. This Gospel differs from the Gospel of Philip and the Gospel of Truth in that it is not from a Valentinian perspective and instead focuses on a viewpoint rooted in Sethianism. Overview The main contents concern the Sethian Gnostic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsanes
Marsanes is a Sethian Gnostic text from the New Testament apocrypha. The only surviving copy comes from the Nag Hammadi library, albeit with four pages missing, and several lines damaged beyond recovery, including the first ten of the fifth page. Scholars speculate that the text was originally written by a Syrian in Greek during the third century. Overview Like Zostrianos, and Allogenes, the text describes a very elaborate esoteric cosmogony of successive emanations from an original God, as revealed by Marsanes, who is recognized as a Gnostic prophet. Within the text there are indications that the Sethians had developed ideas of monism, an idea comparable to Heracleon's notion of universal perfection and permanence as expressed through the constancy of the total mass of things within it (that is, ''all'' matter in the universe may only change form, and may not be created or destroyed), and the later Stoic Stoic may refer to: * An adherent of Stoicism; one whose moral quality is as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimorphic Protennoia
The ''Trimorphic Protennoia'' is a Sethian (gnostic), Sethian Gnostic text from the New Testament apocrypha. The only surviving copy comes from the Nag Hammadi library (Nag Hammadi Codex XIII, Codex XIII). I [am] the Thought of the Father, Protennoia, that is, Barbelo, the perfect Glory, and the immeasurable Invisible One who is hidden. I am the Image of the Invisible Spirit, and it is through me that the All took shape, and (I am) the Mother (as well as) the Light which she appointed as Virgin, she who is called 'Meirothea', the incomprehensible Womb, the unrestrainable and immeasurable Voice. Similarities with other texts Like the ''Apocryphon of John'', to which it is similar, it is thought to be from the mid-second century, and similar in style to the ''Gospel of John''. In particular, there is great similarity with the prologue. Mysticism The name of the text means ''The First Thought which is in Three Forms'' (or ''The Three Forms of the First Thought''), and appears to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |