|
Baradostian
The Baradostian culture was an Upper Paleolithic flint industry culture found in the Zagros region in the border-country between Iraq and Iran. It was preceded by the Middle Paleolithic Mousterian culture, directly overlying it without an intervening bladelet industry. This culture is known for the high percentage of burins and some of these were similar to the distinctive nosed profile of the Aurignacian burins. Baradost is one of the mountains in the Zagros Mountains in Iraq. Characteristics Radiocarbon dates suggest that this was one of the earliest Upper Paleolithic complexes, beginning perhaps as early as 36,000 BC. Evidence found in the Yafteh cave assemblages, revealed that the early phase of this culture was not as sophisticated as the evolved middle phase, and it produced blades and bladelets using soft hammer from single platform prismatic cores with plain platforms. The Baradostian's relationship to neighbouring cultures remains unclear. This is also the case regard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
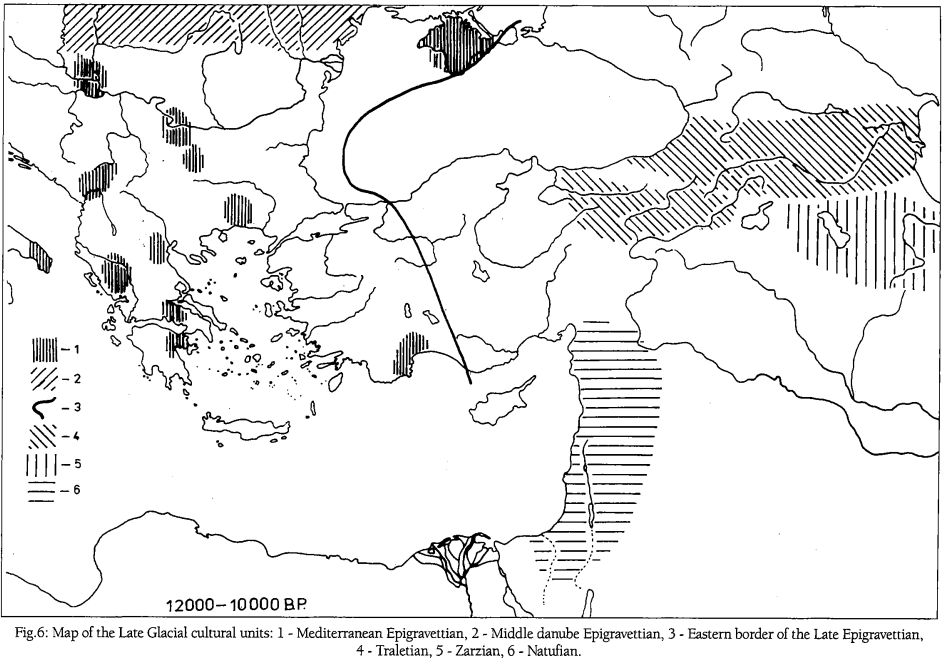
Zarzian Culture
Zarzian culture is an archaeological culture of late Paleolithic and Mesolithic in Southwest Asia. The period of the culture is estimated to have existed about 18,000–8,000 BCE. It was preceded by the Baradostian culture in the same region and was related to the Imereti culture of the Caucasus. The culture was named and recognised of the cave of Zarzi in Iraqi Kurdistan. Here were found plenty of microliths (up to 20% finds). Their forms are short and asymmetric trapezoids, and triangles with hollows. Andy Burns states "The Zarzian of the Zagros region of Iran is contemporary with the Natufian but different from it. The only dates for the entire Zarzian come from Palegawra Cave, and date to 17,300-17,000BP, but it is clear that it is broadly contemporary with the Levantine Kebaran, with which it shares features. It seems to have evolved from the Upper Palaeolithic Baradostian." There are only a few Zarzian sites and the area appears to have been quite sparsely populate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanidar Cave
Shanidar Cave ( ku, Zewî Çemî Şaneder ,ئەشکەوتی شانەدەر, ) is an archaeological site located on Bradost Mountain, within the Zagros Mountains, in the Erbil Governorate of Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq. It is known for the discovery of Neanderthal remains at the site, most notably Shanidar 1, who survived several injuries during his life, possibly due to care from others in his group, and Shanidar 4, the famed 'flower burial'."Shanidar Cave." ''Shanidar Cave , Unbelievable Kurdistan – Official Tourism Site of Kurdistan'', http://bot.gov.krd/erbil-province-mirgasor/history-and-heritage/shanidar-cave Until this discovery, Cro-Magnons, the earliest known ''H. sapiens'' in Europe, were the only individuals known for purposeful, ritualistic burials. Archaeology The site, 1/2 mile from the Great Zab river and near Rowanduz, lies at 2100 feet above sea level. The cave entrance is triangular, 82 feet wide by 26 high. Its dimensions are, at maximum, 175 feet wide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warwasi
Warwasi is a Paleolithic rockshelter site located at north of Kermanshah in western Iran. It was excavated by Bruce Howe under direction of late Robert Braidwood in the 1960s. This site contains a rich archaeological sequence from Middle Paleolithic to late Epipaleolithic In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti .... References *Braidwood, R. J. (1960) Seeking the World's First Farmers in Persian Kurdistan: A Full-Scale Investigation of Prehistoric Sites Near Kermanshah. The Illustrated London News no. 237, pp. 695–97. *Dibble, H.L., & S.J. Holdaway (1993). The Middle Paleolithic Industries of Warwasi. In The Paleolithic Prehistory of the Zagros-Taurus, edited by D.I. Olszewsky and H.L. Dibble, pp. 75–99. Philadelphia: University Museum Symposium Series, Vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures In Iran
The Archaeology of Iran encompasses the following subjects: Archaeological discoveries in Iran Archaeological sites in Iran: *Rock art in Iran *Great Wall of Gorgan *Hasanlu Lovers * Islamic ceramics from the Susa site * Achaemenid inscription in the Kharg Island *Achaemenid Persian Lion Rhyton *Acropole Tomb *Apadana hoard * Bardak Siah Palace *Bushel with ibex motifs *Code of Hammurabi *Egyptian statue of Darius I *Golden bowl of Hasanlu *Luristan bronze * Musicians plate *Narundi *Nazimaruttaš kudurru stone *Parchments of Avroman *Parthian bas-relief at Mydan Mishan *Persepolis Administrative Archives *Shami statue *Statue of Hercules in Behistun *Victory Stele of Naram-Sin *Ziwiye hoard Archaeologists *Roland de Mecquenem (archaeologist) *Frank Hole *Geneviève Dollfus *Roman Ghirshman *Wolfram Kleiss *Jean Perrot *Henry T. Wright Iranian archaeologists *Kamyar Abdi (born 1969) Iranian; Iran, Neolithic to the Bronze Age *Abbas Alizadeh (born 1951) Iranian; Iran *Massoud Azarno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mousterian
The Mousterian (or Mode III) is an archaeological industry of stone tools, associated primarily with the Neanderthals in Europe, and to the earliest anatomically modern humans in North Africa and West Asia. The Mousterian largely defines the latter part of the Middle Paleolithic, the middle of the West Eurasian Old Stone Age. It lasted roughly from 160,000 to 40,000 BP. If its predecessor, known as Levallois or Levallois-Mousterian, is included, the range is extended to as early as 300,000–200,000 BP. The main following period is the Aurignacian (c. 43,000–28,000 BP) of ''Homo sapiens''. Naming The culture was named after the type site of Le Moustier, three superimposed rock shelters in the Dordogne region of France. Similar flintwork has been found all over unglaciated Europe and also the Near East and North Africa. Handaxes, racloirs, and points constitute the industry; sometimes a Levallois technique or another prepared-core technique was employed in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yafteh
Yafteh is an Upper Paleolithic cave located at the foot of Yafteh Mountain in the Zagros Mountains range, located northwest of Khoramabad in western Zagros, Lorestan Province of western Iran. Description Yafteh has yielded the largest number of C14 dates from a single Paleolithic site in Iran that are clustered around 28–35 thousand years ago. A rich collection of ornaments made of marine shells, tooth and hematite has been discovered in the early Upper Paleolithic deposits in both early and recent excavations in the Yafteh cave. This collection was analyzed and published by Sonia Shidrang in the ''Iranian Journal of Archaeology and History''. Archaeological history The site was found and later excavated by two American archaeologists, Frank Hole and Kent Flannery, in the 1960s. It contained a thick Upper Paleolithic sequence which yielded bladelets and tools. A number of C14 dates indicate that the site was occupied mainly between 30 and 35 thousand years ago. Hole and Fla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgros'' ''کویا زاگرس'') are a long mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. This mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros mountain range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of southeastern Turkey and northeastern Iraq. From this border region, the range continues to the southeast under also the waters of the Persian Gulf. It spans the southern parts of the Armenian highland, the whole length of the western and southwestern Iranian plateau, ending at the Strait of Hormuz. The highest point is Mount Dena, at . Geology The Zagros fold and thrust belt was mainly formed by the collision of two tectonic plates, the Eurasian Plate and the Arabian Plat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trialetian
Trialetian is the name for an Upper Paleolithic-Epipaleolithic stone tool industry from the South Caucasus. It is tentatively dated to the period between 16,000 / 13,000 BP and 8,000 BP. Archaeology The name of the archaeological culture derives from sites in the district of Trialeti in south Georgian Khrami river basin. These sites include Barmaksyzkaya and Edzani-Zurtaketi. In Edzani, an Upper Paleolithic site, a significant percentage of the artifacts are made of obsidian. The Caucasian-Anatolian area of Trialetian culture was adjacent to the Iraqi-Iranian Zarzian culture to the east and south as well as the Levantine Natufian to the southwest. Alan H. Simmons describes the culture as "very poorly documented". In contrast, recent excavations in the Valley of Qvirila river, to the north of the Trialetian region, display a Mesolithic culture. The subsistence of these groups were based on hunting ''Capra caucasica'', wild boar and brown bear. Trialetian sites Caucasus an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmenistan to the north, by Afghanistan and Pakistan to the east, and by the Gulf of Oman and the Persian Gulf to the south. It covers an area of , making it the 17th-largest country. Iran has a population of 86 million, making it the 17th-most populous country in the world, and the second-largest in the Middle East. Its largest cities, in descending order, are the capital Tehran, Mashhad, Isfahan, Karaj, Shiraz, and Tabriz. The country is home to one of the world's oldest civilizations, beginning with the formation of the Elamite kingdoms in the fourth millennium BC. It was first unified by the Medes, an ancient Iranian people, in the seventh century BC, and reached its territorial height in the sixth century BC, when Cyrus the Great fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burin (lithic Flake)
Burin from the Upper Paleolithic (Gravettian) (ca. 29,000–22,000 BP) In the field of lithic reduction, a burin (from the French ''burin'', meaning "cold chisel" or modern engraving burin) is a type of handheld lithic flake with a chisel-like edge which prehistoric humans used for engraving or for carving wood or bone. In archaeology, burin use is often associated with "burin spalls", which are a form of debitage created when toolmakers strike a small flake obliquely from the edge of the burin flake in order to form the graving edge. Documented use left, 180px, Carinated "burin"/microblade core with multiple facets Standardized burin usage is typical of the Middle Paleolithic and Upper Palaeolithic cultures in Europe, but archaeologists have also identified them in North American cultural assemblages, and in his book ''Early Man in China'', Jia Lanpo of Beijing University lists dihedral burins and burins for truncation among artifacts uncovered along the banks of the Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurignacian
The Aurignacian () is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic associated with European early modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the Levant, where the Emiran period and the Ahmarian period form the first periods of the Upper Paleolithic, corresponding to the first stages of the expansion of ''Homo sapiens'' out of Africa. They then migrated to Europe and created the first European culture of modern humans, the Aurignacian. An Early Aurignacian or Proto-Aurignacian stage is dated between about 43,000 and 37,000 years ago. The Aurignacian proper lasts from about 37,000 to 33,000 years ago. A Late Aurignacian phase transitional with the Gravettian dates to about 33,000 to 26,000 years ago. The type site is the Cave of Aurignac, Haute-Garonne, south-west France. The main preceding period is the Mousterian of the ''Neanderthals''. One of the oldest examples of figurative art, the Venus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradost (mountain)
Bradost or Chia-y Bradost (Nawakhin), a mountain range over 5,000 feet above sea level and about 25 miles long, stretches northwest from the Rawanduz river opposite the town of Rawanduz in Erbil Governorate, Kurdistan Region, Iraq, to Rubari kuchuk, a tributary of the Great Zab. The Shanidar Cave Shanidar Cave ( ku, Zewî Çemî Şaneder ,ئەشکەوتی شانەدەر, ) is an archaeological site located on Bradost Mountain, within the Zagros Mountains, in the Erbil Governorate of Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq. It is known for the ..., a Neanderthal archaeological site, lies about 15 km N-W from its peak. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
