|
Baopuzi
''Baopuzi'' () is a literary work written by Ge Hong (AD 283–343), (), a scholar during the turbulent Jin dynasty. ''Baopuzi'' is divided into two main sections, the esoteric ''Neipian'' () and the section intended for the public to understand: ''Waipian'' (). The Taoist Inner Chapters discuss topics such as techniques to achieve "hsien" (), Chinese alchemy, elixirs, and demonology. The Confucian Outer Chapters discuss Chinese literature, Legalism, politics, and society. Title The eponymous title ''Baopuzi'' derives from Ge Hong's ''hao'' (), the ''hao'' being a type of sobriquet or pseudonym. Baopuzi literally means "The Master Who Embraces Simplicity;" compounded from the words ''bao'' () meaning "embrace; hug; carry; hold in both arms; cherish"; '' pu'' () meaning "uncarved wood", also being a Taoist metaphor for a "person's original nature; simple; plain"; and, ''zi'' ( 子) meaning "child; offspring; master (title of respect)". ''Baopu'' (Pao-p'u; literally:"Simple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ge Hong
Ge Hong (; b. 283 – d. 343 or 364), courtesy name Zhichuan (稚川), was a Chinese linguist, philosopher, physician, politician, and writer during the Eastern Jin dynasty. He was the author of '' Essays on Chinese Characters'', the '' Baopuzi'', the ''Emergency Formulae at an Elbow's Length'', among others. He was the originator of first aid in traditional Chinese medicine and influenced later generations. He also took on the name Baopuzi (), with which translates literally as ‘embracing simplicity’—a reflection of his commitment to fundamental virtues, unadorned truth, and detachment from material temptations. Early life Ge Hong was born near Jurong county in AD 283, as the third son into a well-established family originally from Eastern Wu. His ancestor Ge Xi (葛奚) once served in the high ranking position of Dahonglu (大鸿胪) in Eastern Wu. His great-uncle was Ge Xuan (葛玄) (also known as Ge Xianweng), an alchemist during the Three Kingdoms period. He st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
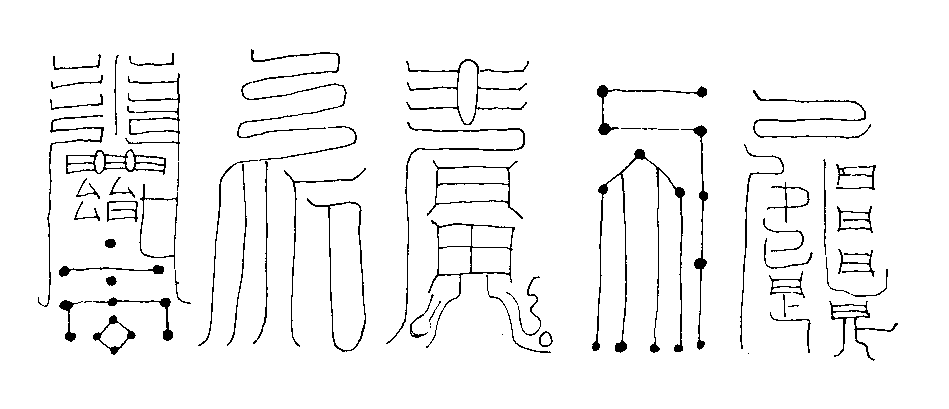
Pu (Daoism)
''Pu'' is a Chinese word meaning "unworked wood; inherent quality; simple" that was an early Daoist metaphor for the natural state of humanity, and relates with the Daoist keyword ''ziran'' (literally "self so") "natural; spontaneous". The scholar Ge Hong (283–343 CE) immortalized ''pu'' in his pen name ''Baopuzi'' "Master who Embraces Simplicity" and eponymous book ''Baopuzi''. Terminology ''Pu'' can be written with either of the variant Chinese characters or , which are linguistically complex. Characters Both and are classified as radical-phonetic characters, combining the semantically significant "tree" radical (commonly used for writing names of trees and wooden objects) with the phonetic indicators ''pu'' or ''bu'' . The Chinese character ''pu'' was first recorded on Chinese bronze inscriptions from the Spring and Autumn period (771-476 BCE), and the character ''pu'' was first recorded in Chinese classics from the Warring States period (475-221 BCE). When the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taoist
Taoism or Daoism (, ) is a diverse philosophical and religious tradition indigenous to China, emphasizing harmony with the Tao ( zh, p=dào, w=tao4). With a range of meaning in Chinese philosophy, translations of Tao include 'way', 'road', 'path', or 'technique', generally understood in the Taoist sense as an enigmatic process of transformation ultimately underlying reality. Taoist thought has informed the development of various practices within the Taoist tradition and beyond, including forms of meditation, astrology, qigong, feng shui, and internal alchemy. A common goal of Taoist practice is self-cultivation, a deeper appreciation of the Tao, and more harmonious existence. Taoist ethics vary, but generally emphasize such virtues as '' effortless action'', ''naturalness'', ''simplicity'', and the three treasures of compassion, frugality, and humility. The core of Taoist thought crystallized during the early Warring States period (), during which the epigrammatic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xian (Taoism)
A ''xian'' ( zh, s=仙, t=僊, p=xiān, w=hsien) is any manner of immortal or mythical being within the Taoist Pantheon (religion), pantheon or Chinese folklore. has often been translated into English as "immortal" or "wizard". Traditionally, ''xian'' refers to entities who have attained immortality and supernatural or Magic (supernatural), magical abilities later in life, with a connection to the heavenly realms inaccessible to mortals. This is often achieved through spiritual Self-cultivation#Taoism and the authentic self, self-cultivation, Chinese alchemy, alchemy, or worship by others. This is different from the Deity, gods (Deity, deities) in Chinese mythology and Taoism. ''Xian'' is also used as a descriptor to refer to often benevolent figures of great historical, spiritual and cultural significance. The Quanzhen School of Taoism, Daoism had a variety of definitions for during its history, including a metaphorical meaning where the term simply means a good, principl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taoism
Taoism or Daoism (, ) is a diverse philosophical and religious tradition indigenous to China, emphasizing harmony with the Tao ( zh, p=dào, w=tao4). With a range of meaning in Chinese philosophy, translations of Tao include 'way', 'road', 'path', or 'technique', generally understood in the Taoist sense as an enigmatic process of transformation Ultimate reality, ultimately underlying reality. Taoist thought has informed the development of various practices within the Taoist tradition and beyond, including forms of Taoist meditation, meditation, Chinese astrology, astrology, qigong, feng shui, and Neidan, internal alchemy. A common goal of Taoist practice is self-cultivation, a deeper appreciation of the Tao, and more harmonious existence. Taoist ethics vary, but generally emphasize such virtues as ''wu wei, effortless action'', ziran, ''naturalness'', ''pu (Taoism), simplicity'', and the Three Treasures (Taoism), three treasures of compassion, frugality, and humility. The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanzhong
Guanzhong (, formerly romanization of Chinese, romanised as Kwanchung) region, also known as the Guanzhong Basin, Wei River Basin, or uncommonly as the Shaanzhong region, is a historical region of China corresponding to the crescentic graben structural basin, basin within present-day central Shaanxi, bounded between the Qinling Mountains in the south (known as Guanzhong's "South Mountains"), and the Huanglong Mountain, Meridian Ridge and Mount Liupan, Long Mountain ranges in the north (collectively known as its "North Mountains"). The central plain, flatland area of the basin, known as the Guanzhong Plain (关中平原; pinyin: Guānzhōng Píngyuán), is made up of alluvial plains along the lower Wei River and its numerous tributaries and thus also called the Wei River Plain. The region is part of the Shanxi, Jin-Shaanxi, Shaan Basin Belt, a prominent section of the Shanxi Rift System, and is separated from its geological sibling — the Yuncheng Basin to its northeast — by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhuangzi (book)
The ''Zhuangzi'' (historically romanized ) is an ancient Chinese text that is one of the two foundational texts of Taoism, alongside the ''Tao Te Ching''. It was written during the late Warring States period (476–221 BC) and is named for its traditional author, Zhuang Zhou, who is customarily known as "Zhuangzi" ("Master Zhuang"). The ''Zhuangzi'' consists of stories and maxims that exemplify the nature of the ideal Taoist sage. It recounts many anecdotes, allegories, parables, and fables, often expressed with irreverence or humor. Recurring themes include embracing spontaneity and achieving freedom from the human world and its conventions. The text aims to illustrate the arbitrariness and false dichotomy, ultimate falsity of dichotomies normally embraced by human societies, such as those between good and bad, large and small, life and death, or human and nature. In contrast with the focus on good morals and personal duty expressed by many Chinese philosophers of the per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathan Sivin
Nathan Sivin (11 May 1931 – 24 June 2022), also known as Xiwen (), was an American sinologist, historian, essayist, educator, and writer. He taught first at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, then at the University of Pennsylvania until his retirement in 2006. The major areas of study and focus in Nathan Sivin's career and publications were history of science and technology in China, medicine in traditional China, Chinese philosophy, and Chinese religious beliefs. He was a key player in the development of their scholarly study in the West. He collaborated with prominent scholars, such as G.E.R. Lloyd, A.C. Graham and Joseph Needham, and nurtured younger ones. His wife was the artist Carole Delmore Sivin, who died in 2020. For many years they lived in Chestnut Hill, Pennsylvania. In 1977 he was elected to the American Academy of Arts & Sciences. He was president of the Philadelphia literary society, Franklin Inn Club, 1996–1998. Education and career From 1954 until 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daozang
The Daozang ( zh, c=道藏, p=Dàozàng, w=Tao Tsang) is a large canon of Taoist writings, consisting of around 1,500 texts that were seen as continuing traditions first embodied by the '' Daodejing'', '' Zhuangzi'', and '' Liezi''. The canon was assembled by monks in an attempt to bring together these disparate yet consonant teachings, and it included commentaries and expositions from various masters on material found in the aforementioned core texts of Taoism. The anthology consisted of three divisions (known as ''grottoes'') based on what were seen at that time in Southern China as Taoism's primary focuses: meditation, ritual, and exorcism. These three grottoes were ranked by skill level—with exorcism being the lowest and meditation the highest—and used for the initiation of Taoist masters. In addition to the Three Grottoes, there were the "Four Supplements" that were added to the canon . Three were primarily sourced from the older core texts, with the other taken from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of China ruled by the Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump state, rump regimes ruled by remnants of the House of Zhu, Ming imperial family, collectively called the Southern Ming, survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the naval history of China, navy's dockyards in Nanjing were the largest in the world. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |