|
Ban Chiang Archaeological Site
Ban Chiang ( th, บ้านเชียง, ) is an archaeological site in Nong Han district, Udon Thani province, Thailand. It has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1992. Discovered in 1966, the site first attracted interest due to its ancient red-painted pottery. More recently, it gained international attention in 2008 when the United States Department of Justice, following an undercover investigation begun in 2003, raided several museums for their role in trafficking in Ban Chiang antiquities. Discovery Villagers had uncovered some of the pottery in prior years without insight into their age or historical importance. In August 1966, Steve Young, a political science student at Harvard College, was living in the village conducting interviews for his senior honors thesis. Young, a speaker of Thai, was familiar with the work of Wilhelm Solheim and his theory of the possible ancient origins of civilization in Southeast Asia. One day while walking down a path in Ban Chian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nong Han District
Nong Han (, ) is a district (''amphoe'') of Udon Thani province, northeastern Thailand. Geography Neighboring districts are (from the south clockwise) Chai Wan, Ku Kaeo, Prachaksinlapakhom, Mueang Udon Thani, Phibun Rak and Thung Fon of Udon Thani province, and Sawang Daen Din of Sakon Nakhon province. History The Ban Chiang ( th, มู่ที่ 13 ตำบล บ้านเชียง, translit=Hamlet 13 Tambon Ban Chiang) archaeological site has been a world heritage site since 1992. It was settled from the Neolithic to the Iron Age, and then abandoned from about 300 CE until the early-19th century. It is best known for its red painted pottery. ''Mueang'' Nong Han was one of the four original subdivisions of Udon Thani, which were converted into ''amphoe'' during the ''monthon'' ''Thesaphiban'' administrative reforms in 1908. Economy Tambon Phak Top is to be the site of Thailand's largest biomass-fired power plant if plans by its owner, the Thai Appliance Industr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (also known as Penn or UPenn) is a private research university in Philadelphia. It is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and is ranked among the highest-regarded universities by numerous organizations and scholars. While the university dates its founding to 1740, it was created by Benjamin Franklin and other Philadelphia citizens in 1749. It is a member of the Ivy League. The university has four undergraduate schools as well as twelve graduate and professional schools. Schools enrolling undergraduates include the College of Arts and Sciences, the School of Engineering and Applied Science, the Wharton School, and the School of Nursing. Among its highly ranked graduate schools are its law school, whose first professor wrote the first draft of the United States Constitution, its medical school, the first in North America, and Wharton, the first collegiate business school. Penn's endowment is US$20.7 billio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
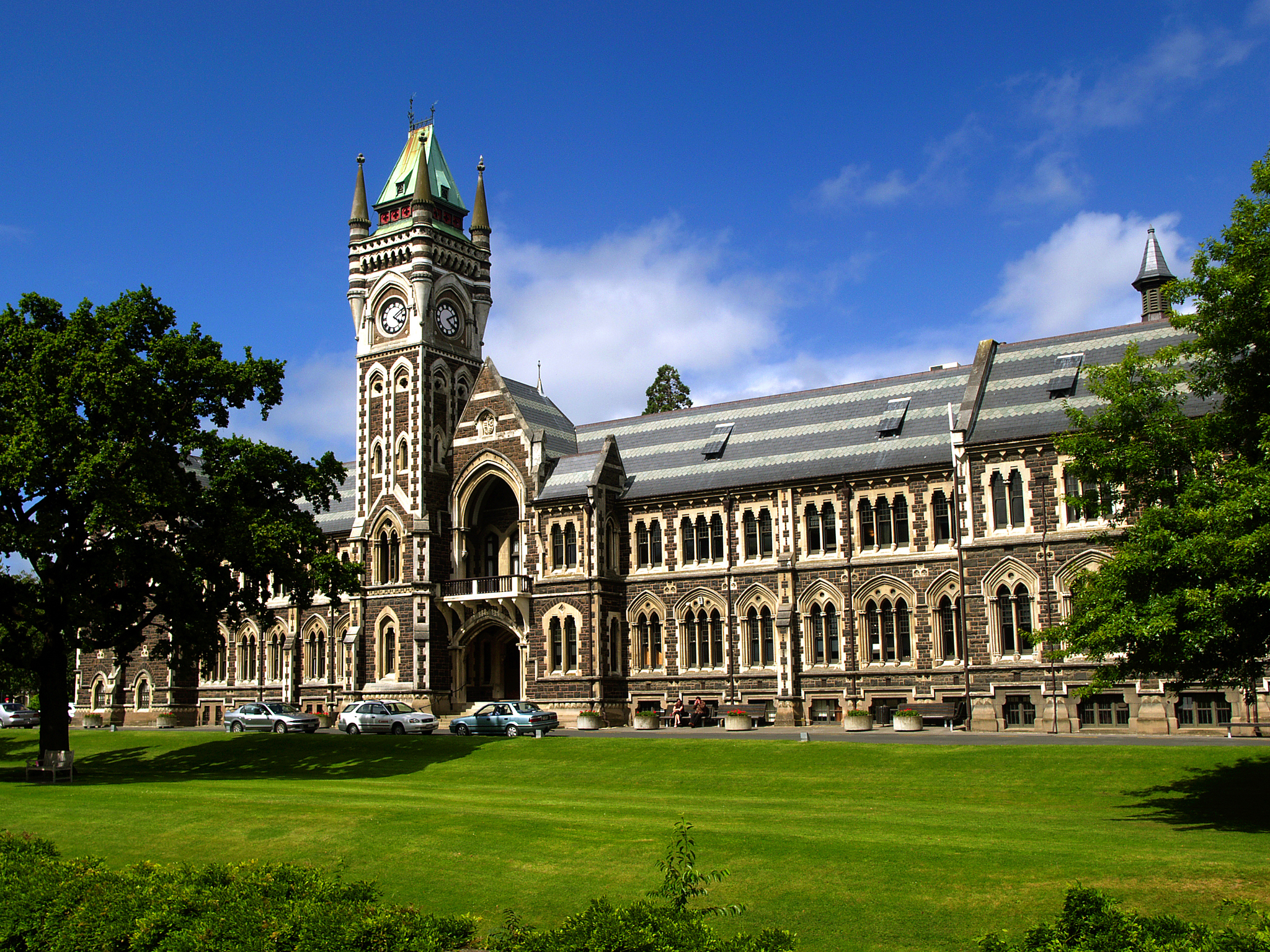
University Of Otago
, image_name = University of Otago Registry Building2.jpg , image_size = , caption = University clock tower , motto = la, Sapere aude , mottoeng = Dare to be wise , established = 1869; 152 years ago , type = Public research collegiate university , endowment = NZD $279.9 million (31 December 2021) , budget = NZD $756.8 million (31 December 2020) , chancellor = Stephen Higgs , vice_chancellor = David Murdoch , administrative_staff = 2,246 (2019) , academic_staff = 1,744 (2019) , students = 21,240 (2019) , undergrad = 15,635 (2014) , postgrad = 4,378 (2014) , doctoral = 1,579 (2019) , other = , city = Dunedin , province = Otago , country = New Zealand (Māori: ''Ōtepoti, Ōtākou, Aotearoa'') , coor = , campus = Urban/University town 45 ha (111 acres) , colours = Dunedin Blue and Gold , free_label = Student Magazine , free = ''Critic'' , affiliations = MNU , website https://www.otago.ac.nz, logo = Logo of the University of Otago.svg The Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
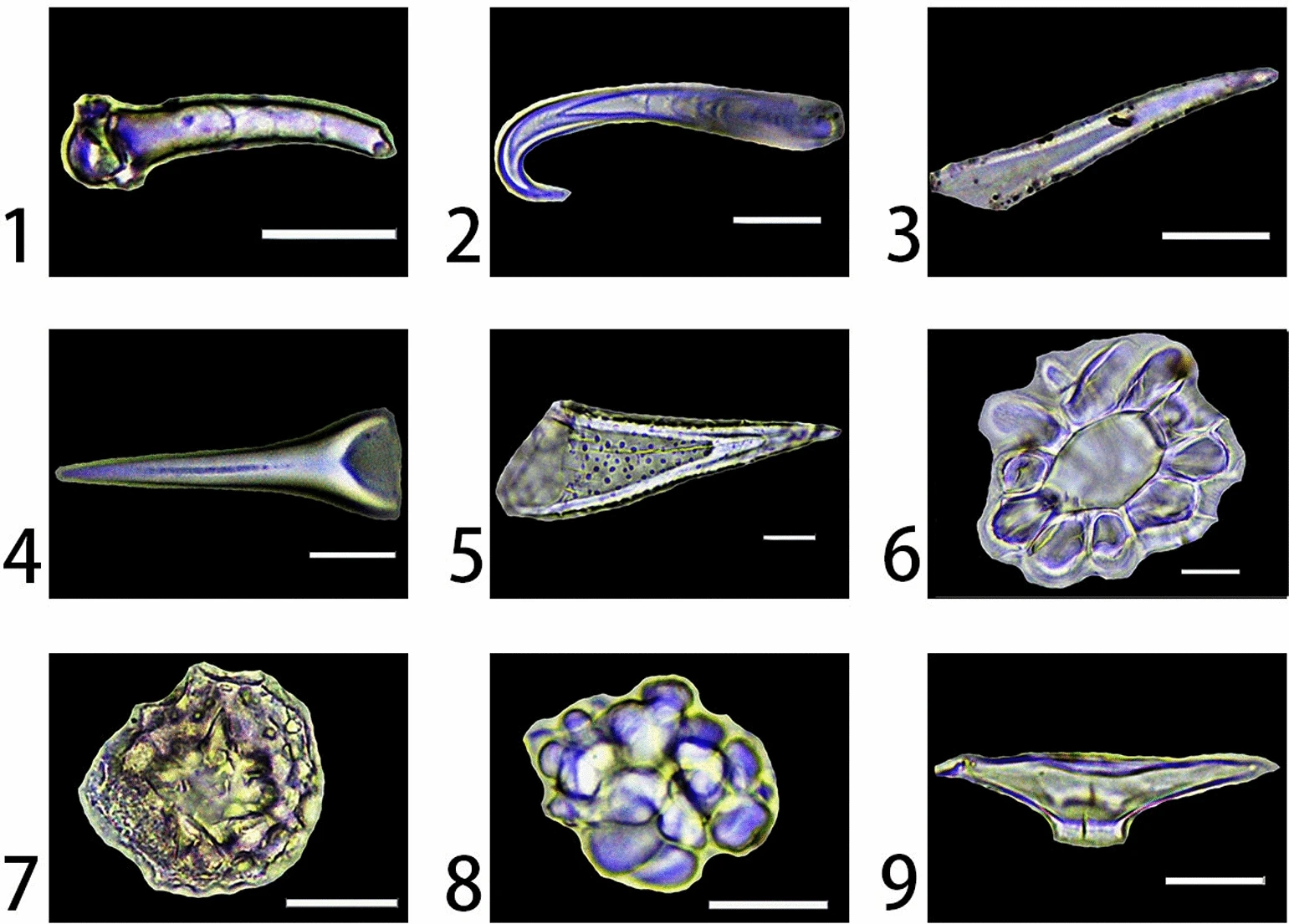
Phytolith
Phytoliths (from Greek, "plant stone") are rigid, microscopic structures made of silica, found in some plant tissues and persisting after the decay of the plant. These plants take up silica from the soil, whereupon it is deposited within different intracellular and extracellular structures of the plant. Phytoliths come in varying shapes and sizes. Although some use "phytolith" to refer to all mineral secretions by plants, it more commonly refers to siliceous plant remains. In contrast, mineralized calcium secretions in cacti are composed of calcium oxalates.Piperno, Dolores R. (2006). Phytoliths: A Comprehensive Guide for Archaeologists and Paleoecologists. AltaMira Press . The silica is absorbed in the form of monosilicic acid (Si(OH)4), and is carried by the plant's vascular system to the cell walls, cell lumen, and intercellular spaces. Depending on the plant taxa and soil condition, absorbed silica can range from 0.1% to 10% of the plant's total dry weight. When deposited, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiocarbon Dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon. The method was developed in the late 1940s at the University of Chicago by Willard Libby. It is based on the fact that radiocarbon () is constantly being created in the Earth's atmosphere by the interaction of cosmic rays with atmospheric nitrogen. The resulting combines with atmospheric oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide, which is incorporated into plants by photosynthesis; animals then acquire by eating the plants. When the animal or plant dies, it stops exchanging carbon with its environment, and thereafter the amount of it contains begins to decrease as the undergoes radioactive decay. Measuring the amount of in a sample from a dead plant or animal, such as a piece of wood or a fragment of bone, provides information that can be used to calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoluminescence Dating
Thermoluminescence dating (TL) is the determination, by means of measuring the accumulated radiation dose, of the time elapsed since material containing crystalline minerals was either heated (lava, ceramics) or exposed to sunlight (sediments). As a crystalline material is heated during measurements, the process of thermoluminescence starts. Thermoluminescence emits a weak light signal that is proportional to the radiation dose absorbed by the material. It is a type of luminescence dating. The technique has wide application, and is relatively cheap at some US$300–700 per object; ideally a number of samples are tested. Sediments are more expensive to date. , University of Wollongong, Australia [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ban Non Wat
Ban Non Wat is a village in Thailand, in the Non Sung district, Nakhon Ratchasima Province, located near the small city of Phimai. It has been the subject of excavation since 2002. The cultural sequence encompasses 11 prehistoric phases, which include 640 burials.Higham, C. F. W. (2011). The Bronze Age of Southeast Asia: New insight on social change from Ban Non Wat. Cambridge Archaeological Journal, 21(3), 365-389. The site is associated with consistent occupation, and in modern-day Ban Non Wat the occupied village is located closer to the Mun River. Excavations show that people were occupying the region during the Neolithic, Bronze, and Iron Ages. This unique sequence has been proven by 76 radiocarbon determinations treated with Bayesian analyses. Bayesian analysis is the use of Bayesian statistics to calibrate radiocarbon dates to receive a more accurate date. Soil in the Ban Non Wat area may displace the Bayesian analysis. These reveal that the initial Neolithic settlement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crucible
A crucible is a ceramic or metal container in which metals or other substances may be melted or subjected to very high temperatures. While crucibles were historically usually made from clay, they can be made from any material that withstands temperatures high enough to melt or otherwise alter its contents. History Typology and chronology The form of the crucible has varied through time, with designs reflecting the process for which they are used, as well as regional variation. The earliest crucible forms derive from the sixth/fifth millennium B.C. in Eastern Europe and Iran. Chalcolithic Crucibles used for copper smelting were generally wide shallow vessels made from clay that lacks refractory properties which is similar to the types of clay used in other ceramics of the time. During the Chalcolithic period, crucibles were heated from the top by using blowpipes.Hauptmann A., 2003, ''Developments in copper Metallurgy During the Fourth and Third Millennia B.C. at Feinan'', Jorda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chester Gorman
Chester F. Gorman (March 11, 1938 – June 7, 1981) was an American anthropologist and archaeologist. Born in Oakland, California, he grew up on his parents' dairy farm in Elk Grove, California, Elk Grove. He studied at the Sacramento State University and the University of Hawaii, where he also got his MA and his PhD. Chester Gorman worked mostly in Southeast Asia. Among the most significant sites he worked are Ban Chiang in northeast Thailand and Spirit Cave, Thailand, Spirit Cave in northwest Thailand, one of the major Hoabinhian sites. While surveying for sites in northeast Thailand with Wilhelm Solheim between 1963-1964, Gorman also discovered the site of Non Nok Tha. Gorman excavated Spirit Cave, Thailand, Spirit Cave (Tham Phii Man) once in 1966 for his dissertation research, and again in 1971. He also excavated Banyan Valley Cave (Tham Sai) in 1972 and Steep Cliff Cave (Tham Phaa Can) in 1973. He died of cancer at age 43 in Sacramento, California, Sacramento. Publication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Pennsylvania Museum
The University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology—commonly known as the Penn Museum—is an archaeology and anthropology museum at the University of Pennsylvania. It is located on Penn's campus in the University City neighborhood of Philadelphia, at the intersection of 33rd and South Streets. Housing over 1.3 million artifacts, the museum features one of the most comprehensive collections of middle and near-eastern art in the world. History The University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology—which has conducted more than 300 archaeological and anthropological expeditions around the world—was founded during the administration of Provost William Pepper. In 1887, Provost Pepper persuaded the trustees of the University of Pennsylvania to erect a fireproof building to house artifacts from an upcoming expedition to the ancient site of Nippur in modern-day Iraq (then part of the Ottoman Empire). During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly applied to Iron Age Europe and the Ancient Near East, but also, by analogy, to other parts of the Old World. The duration of the Iron Age varies depending on the region under consideration. It is defined by archaeological convention. The "Iron Age" begins locally when the production of iron or steel has advanced to the point where iron tools and weapons replace their bronze equivalents in common use. In the Ancient Near East, this transition took place in the wake of the Bronze Age collapse, in the 12th century BC. The technology soon spread throughout the Mediterranean Basin region and to South Asia (Iron Age in India) between the 12th and 11th century BC. Its further spread to Central Asia, Eastern Europe, and Central Europe is somewhat dela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |