|
Baldwin II, Margrave Of Flanders
Baldwin II ( 865 – 10 September 918) was the second margrave (or count) of Flanders, ruling from 879 to 918. He was nicknamed the Bald (''Calvus'') after his maternal grandfather, Emperor Charles the Bald. Rule Baldwin II was born around 865 to Margrave Baldwin I of Flanders and Judith, daughter of Emperor Charles the Bald.Detlev Schwennicke, '' Europäische Stammtafeln: Stammtafeln zur Geschichte der Europäischen Staaten'', Neue Folge, Band II (Verlag von J. A. Stargardt, Marburg, Germany, 1984), Tafel 5 The early years of Baldwin II's rule were marked by a series of devastating Viking raids into Flanders.David Nicholas, Medieval Flanders (Longman Group UK, Ltd., 1992)pp. 17–18 By 883, he was forced to move north to Pagus Flandransis, which became the territory most closely associated with the Counts of Flanders. Baldwin constructed a series of wooden fortifications at Saint-Omer, Bruges, Ghent, and Kortrijk. He then seized lands that were abandoned by royal and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margrave Of Flanders
The count of Flanders was the ruler or sub-ruler of the county of Flanders, beginning in the 9th century. Later, the title would be held for a time, by the rulers of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain. During the French Revolution, in 1790, the county of Flanders was annexed to France and ceased to exist. In the 19th century, the title was appropriated by Belgium and granted twice to younger sons of Belgian kings. The most recent holder died in 1983. In 862 Baldwin I was appointed as the first Margrave of Flanders by King Charles II. It was a military appointment, responsible for repelling the Viking raids from the coast of Francia. The title of margrave (or marquis) evolved into that of count. Arnulf I was the first to name himself as count, by the Grace of God. The title of margrave largely fell out of use by the 12th century. Since then, the rulers of Flanders have only been referred to as counts. The counts of Flanders enlarged their estate through a series of diplomatic mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castellany
A castellan is the title used in Medieval Europe for an appointed official, a governor of a castle and its surrounding territory referred to as the castellany. The title of ''governor'' is retained in the English prison system, as a remnant of the medieval idea of the castellan as head of the local prison. The word stems from the Latin ''Castellanus'', derived from ''castellum'' "castle". Sometimes also known as a ''constable'' of the castle district, the Constable of the Tower of London is, in fact, a form of castellan, with representative powers in the local or national assembly. A castellan was almost always male, but could occasionally be female, as when, in 1194, Beatrice of Bourbourg inherited her father's castellany of Bourbourg upon the death of her brother, Roger. Similarly, Agnes became the castellan of Harlech Castle upon the death of her husband John de Bonvillars in 1287. Initial functions After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, foreign tribes migrated into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnulf I Of Flanders
Arnulf I (c. 893/899 – 27 March 965), called "the Great", was the first Count of Flanders. Life Arnulf was the son of margrave Baldwin II of Flanders and Ælfthryth of Wessex, daughter of Alfred the Great.Detlev Schwennicke, '' Europäische Stammtafeln: Stammtafeln zur Geschichte der Europäischen Staaten'', Neue Folge, Band II (Verlag von J. A. Stargardt, Marburg, Germany, 1984), Tafel 5 Through his mother he was a descendant of the Anglo-Saxon kings of England, and through his father, a descendant of Charlemagne.''The Annals of Flodoard of Reims, 919–966'', ed. Steven Fanning & Bernard S. Bachrach (University of Toronto Press, CA, 2011), p. xx Presumably Arnulf was named either after Saint Arnulf of Metz, a progenitor of the Carolingian dynasty, or King Arnulf of Carinthia, whom his father supported. At the death of their father in 918, Arnulf became Count of Flanders while his brother Adeloft or Adelolf succeeded to the County of Boulogne. However, in 933 Adeloft die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canche
The river Canche (; nl, Kwinte) is one of the rivers that flow from the plateau of southern Boulonnais and Picardy, into the English Channel, of which the Somme is the largest example. It is long. The basin of the Canche extends to and lies in the south of the département of Pas-de-Calais. Forming an alluvial valley from wide, the Canche valley also contains marshes, meadows and small woods. The gentle gradient, averaging 1.5 percent, gives the river a meandering course. The river rises at Gouy-en-Ternois and passes Frévent, Hesdin, and Montreuil-sur-Mer before leaving the chalk to flow to the coast between Étaples and Le Touquet-Paris-Plage. Its principal tributaries are the Ternoise, the Planquette, the Créquoise, the Bras de Bronne, the Course, the Dordogne (not to be confused with the Dordogne) and the Huitrepin which all join on its right bank, i.e. to the north of the Canche. The lie of the land means there is no notable tributary from the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred The Great
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who both died when Alfred was young. Three of Alfred's brothers, Æthelbald, Æthelberht and Æthelred, reigned in turn before him. Under Alfred's rule, considerable administrative and military reforms were introduced, prompting lasting change in England. After ascending the throne, Alfred spent several years fighting Viking invasions. He won a decisive victory in the Battle of Edington in 878 and made an agreement with the Vikings, dividing England between Anglo-Saxon territory and the Viking-ruled Danelaw, composed of northern England, the north-east Midlands and East Anglia. Alfred also oversaw the conversion of Viking leader Guthrum to Christianity. He defended his kingdom against the Viking attempt at conquest, becoming the dominan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbey Of St
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christian monks and nuns. The concept of the abbey has developed over many centuries from the early monastic ways of religious men and women where they would live isolated from the lay community about them. Religious life in an abbey may be monastic. An abbey may be the home of an enclosed religious order or may be open to visitors. The layout of the church and associated buildings of an abbey often follows a set plan determined by the founding religious order. Abbeys are often self-sufficient while using any abundance of produce or skill to provide care to the poor and needy, refuge to the persecuted, or education to the young. Some abbeys offer accommodation to people who are seeking spiritual retreat. There are many famous abbeys across the Mediterranean Basin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
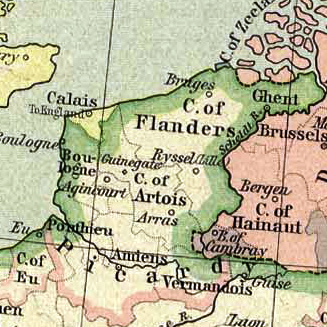
Artois
Artois ( ; ; nl, Artesië; English adjective: ''Artesian'') is a region of northern France. Its territory covers an area of about 4,000 km2 and it has a population of about one million. Its principal cities are Arras (Dutch: ''Atrecht''), Saint-Omer, Lens, and Béthune. It is the eponym for the term '' artesian''. Location Artois occupies the interior of the Pas-de-Calais ''département'',"Artois" in '' The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th ed., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 607. the western part of which constitutes the former Boulonnais. Artois roughly corresponds to the arrondissements of Arras, Béthune, Saint Omer, and Lens, and the eastern part of the arrondissement of Montreuil. It occupies the western end of the coalfield which stretches eastward through the neighbouring Nord ''département'' and across central Belgium. History Originally a feudal county itself, Artois was annexed by the county of Flanders. It came to France in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbey Of Saint Bertin
The Abbey of St. Bertin was a Benedictine monastic abbey in Saint-Omer, France. The buildings are now in ruins, which are open to the public. It was initially dedicated to but was rededicated to its second abbot, . The abbey is known for its Latin cartulary (') whose first part is attributed to . The abbey was founded on the banks of the Aa in the 7th century by Bishop Audomar of Thérouanne, who is now better known as . He sent the monks Bertin, Momelin, and Ebertram from Sithiu (now St-Omer) to proselytize among the pagans in the region. The abbey soon became one of the most influential monasteries in northern Europe and ranked in importance with Elnon (now St-Amand Abbey) and . Its library included the codex of the Leiden Aratea, from which two copies were made. The Annals of St Bertin are an important source of the history of 9th-century France. Already in the 9th century, the abbey had a priory in Poperinge. A Romanesque church was constructed in the mid-11th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odo, Count Of Paris
Odo (french: Eudes; c. 857 – 1 January 898) was the elected King of West Francia from 888 to 898. He was the first king from the Robertian dynasty. Before assuming the kingship, Odo was the count of Paris. His reign marked the definitive separation of West Francia from the Carolingian Empire, which would never reunite. Family and inheritance Odo was the eldest son of Robert the Strong, who was Duke of the Franks, Margrave of Neustria, and Count of Anjou. After his father's death at the Battle of Brissarthe in 866, Odo inherited the Margraviate of Neustria. Odo lost this title in 868 when King Charles the Bald appointed Hugh the Abbot to the title. Odo regained it following the death of Hugh in 886. After 882 he was the count of Paris. Odo was also the lay abbot of St. Martin of Tours. In 882 or 883 Odo married Théodrate of Troyes. The eleventh-century chronicler Adémar de Chabannes wrote that they had a son, Arnoul (c.882–898), who died shortly after his fathe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robertians
The Robertians (sometimes called the Robertines in modern scholarship) are the proposed Frankish family which was ancestral to the Capetian dynasty, and thus to the royal families of France and of many other countries. The Capetians appear first in the records as powerful nobles serving under the Carolingian dynasty of Charlemagne in West Francia, which later became France. As their power increased, they came into conflict with the older royal family and attained the crown several times before the eventual start of the continuous rule of the descendants of Hugh Capet (ruled 987–996). Hugh's paternal ancestral family, the Robertians, appear in documents that can trace them back to his great-grandfather Robert the Strong (d. 866). His origins remain unclear, but medieval records hint at an origin in East Francia, in present-day Germany, an area then still also ruled by the Carolingians. In particular, Regino of Prüm (died 915 CE) states that Robert the Strong's son Odo was said ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnulf Of Carinthia
Arnulf of Carinthia ( 850 – 8 December 899) was the duke of Carinthia who overthrew his uncle Emperor Charles the Fat to become the Carolingian king of East Francia from 887, the disputed king of Italy from 894 and the disputed emperor from February 22, 896, until his death at Regensburg, Bavaria. Early life Illegitimacy and early life Arnulf was the illegitimate son of Carloman of Bavaria, and Liutswind, who may have been the sister of Ernst, Count of the Bavarian Nordgau Margraviate, in the area of the Upper Palatinate, or perhaps the burgrave of Passau, according to other sources. After Arnulf's birth, Carloman married, before 861, a daughter of that same Count Ernst, who died after 8 August 879. As it is mainly West-Franconian historiography that speaks of Arnulf's illegitimacy, it is quite possible that the two females are actually the same person and that Carloman married Arnulf's mother, thus legitimizing his son. Arnulf was granted the rule over the Duchy of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the former empire into three kingdoms. The east–west division, enforced by the Germanic-Latin language split, "gradually hardened into the establishment of separate kingdoms", with East Francia becoming the Kingdom of Germany and West Francia becoming the Kingdom of France. Terminology The term ''orientalis Francia'' originally referred to Franconia and ''orientales Franci'' to its inhabitants, the ethnic Franks living east of the Rhine. The use of the term in a broader sense, to refer to the eastern kingdom, was an innovation of Louis the German's court. Since eastern Francia could be identified with old Austrasia, the Frankish heartland, Louis's choice of terminology hints at his ambitions. Under his grandson, Arnulf of Carinthia, the terminology was l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |