|
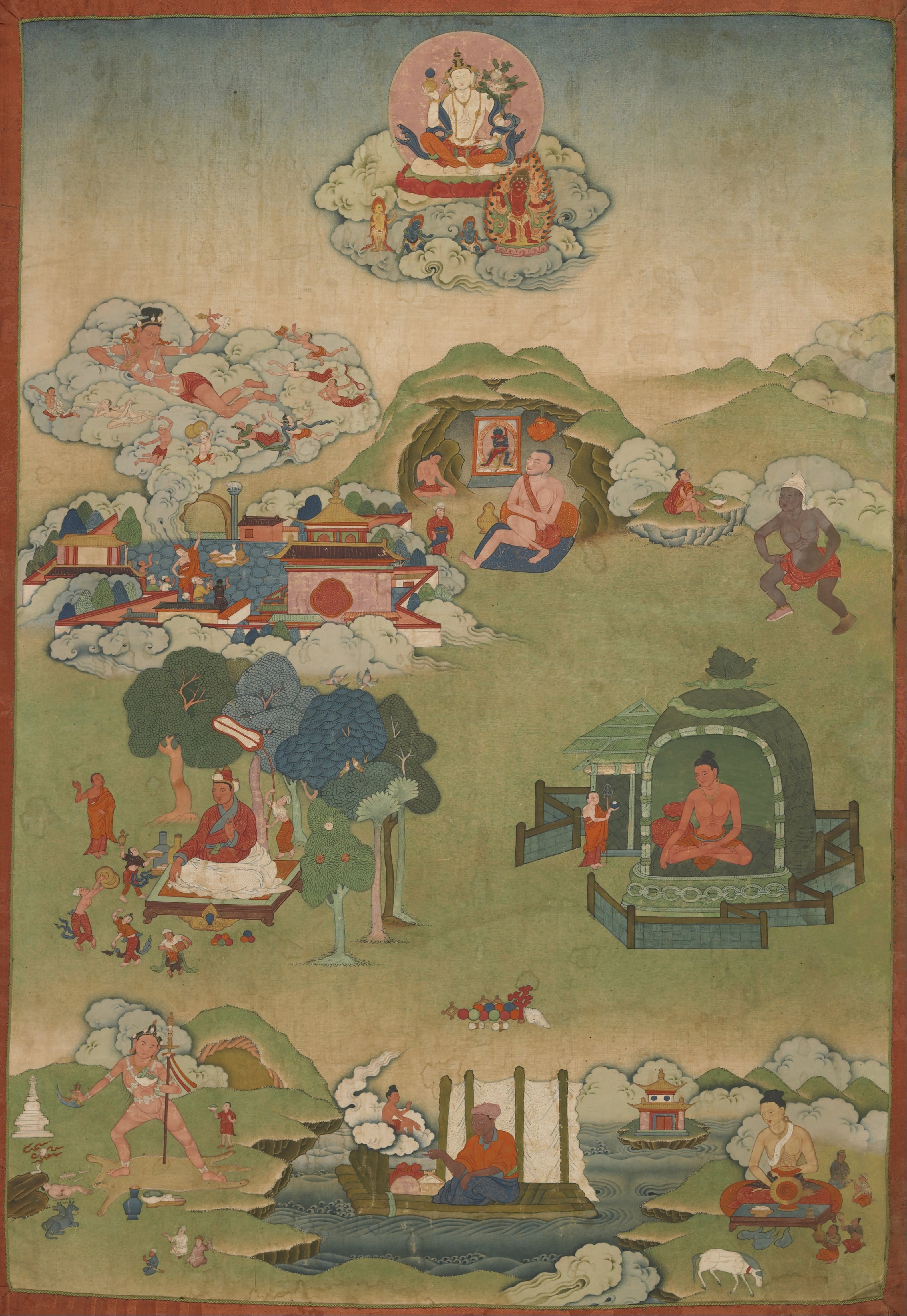
Bajracharya
A vajrācārya (vajra + acharya, Tib. རྡོ་རྗེ་སློབ་དཔོན་, ''dorje lopön'', Wyl. ''rdo rje slob dpon,'' Jp. “kongō ajari” 金剛阿闍梨) is a Vajrayana Buddhist master, guru or priest. It is a general term for a tantric master in Vajrayana Buddhist traditions, including Tibetan Buddhism, Shingon, Bhutanese Buddhism, Newar Buddhism. Tibetan Buddhism In Tibetan Buddhism, Dorje Lopön is a title given to high-level religious leaders who preside over tantric rituals and initiations. Dorje is the Tibetan equivalent of the Sanskrit vajra and therefore the term appears frequently in Tibetan Buddhist terminology relating to Vajrayana. A Dorje Lopön is usually well educated and trained in tantric practice, and is therefore a well respected figure. They might be the heads of monasteries or spiritual communities. Newar Buddhism Bajracharyas are a married priestly class among the Newar communities of Nepal. They are knowledgeable in Newa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar People
Newar (; new, नेवार, endonym: Newa; new, नेवा, Pracalit script:) or Nepami, are the historical inhabitants of the Kathmandu Valley and its surrounding areas in Nepal and the creators of its historic heritage and civilisation. Page 15. Newars form a linguistic and cultural community of primarily Indo-Aryan and Tibeto-Burman ethnicities following Hinduism and Buddhism with Nepal Bhasa as their common language. Newars have developed a division of labour and a sophisticated urban civilisation not seen elsewhere in the Himalayan foothills. Newars have continued their age-old traditions and practices and pride themselves as the true custodians of the religion, culture and civilisation of Nepal. Newars are known for their contributions to culture, art and literature, trade, agriculture and cuisine. Today, they consistently rank as the most economically and socially advanced community of Nepal, according to the annual Human Development Index published by UNDP. Nepal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar
Newar (; new, नेवार, endonym: Newa; new, नेवा, Pracalit script:) or Nepami, are the historical inhabitants of the Kathmandu Valley and its surrounding areas in Nepal and the creators of its historic heritage and civilisation. Page 15. Newars form a linguistic and cultural community of primarily Indo-Aryan and Tibeto-Burman ethnicities following Hinduism and Buddhism with Nepal Bhasa as their common language. Newars have developed a division of labour and a sophisticated urban civilisation not seen elsewhere in the Himalayan foothills. Newars have continued their age-old traditions and practices and pride themselves as the true custodians of the religion, culture and civilisation of Nepal. Newars are known for their contributions to culture, art and literature, trade, agriculture and cuisine. Today, they consistently rank as the most economically and socially advanced community of Nepal, according to the annual Human Development Index published by UNDP. Nep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
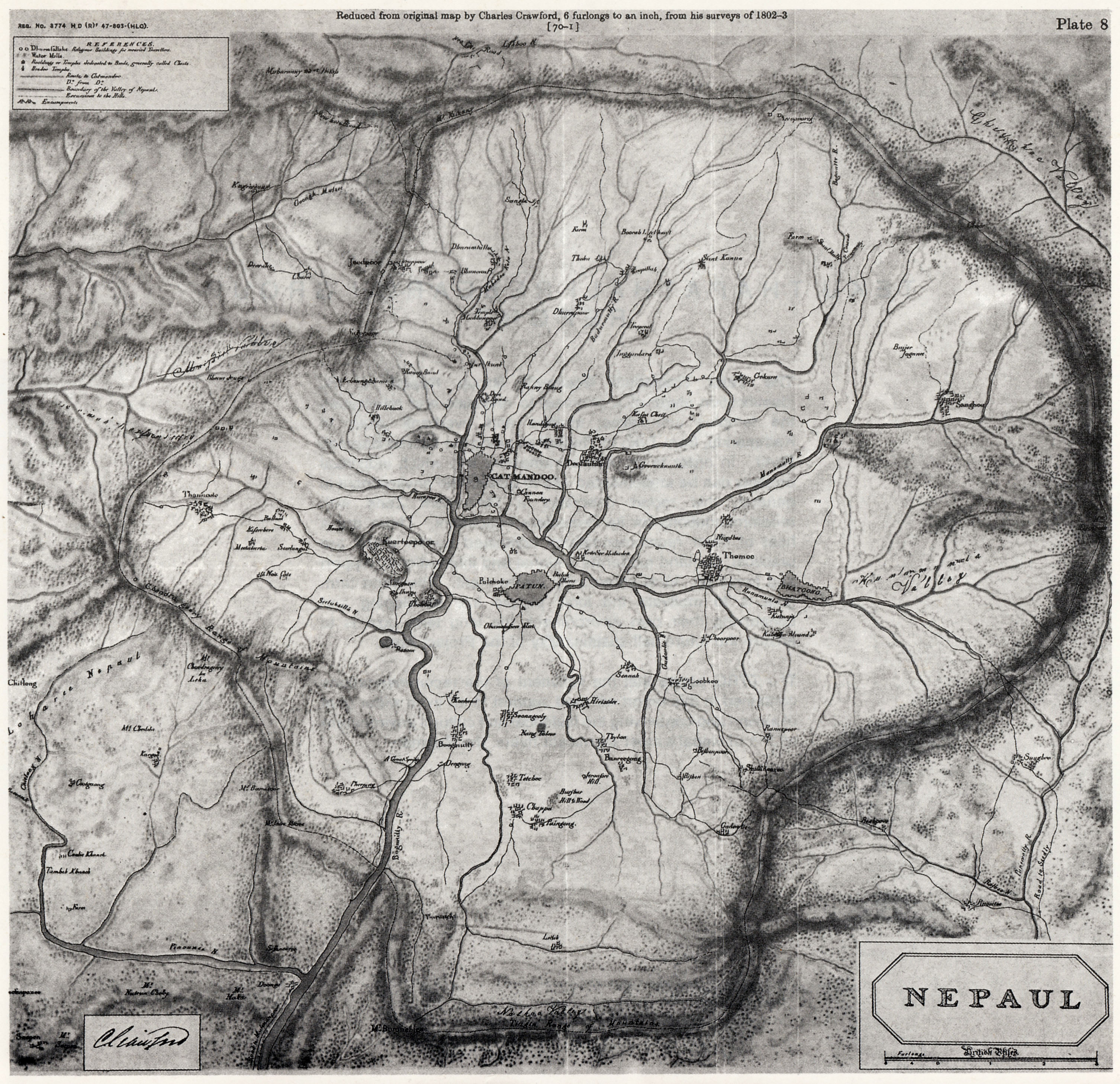
Nepal
Nepal (; ne, नेपाल ), formerly the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal ( ne, सङ्घीय लोकतान्त्रिक गणतन्त्र नेपाल ), is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, bordering the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north, and India in the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a diverse geography, including fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious and multi-cultural state, with Nepali as the official language. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and the largest city. The name "Nepal" is first recorded in texts from the Vedic period of the India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar Buddhism
Newar Buddhism is the form of Vajrayana Buddhism practiced by the Newar people of the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. It has developed unique socio-religious elements, which include a non-monastic Buddhist society based on the Newar caste system and patrilineality. The ritual priestly (''guruju'') caste, vajracharya (who perform rituals for others) and ''shakya'' (who perform rituals mostly within their own families) form the non-celibate religious clergy caste while other Buddhist Newar castes like the Urāy act as patrons. Uray also patronise Tibetan Vajrayana, Theravadin, and even Japanese clerics. It is the oldest known sect of the Vajrayana tradition outdating the Tibetan school of Vajrayana by more than 600 years. Although there was a vibrant regional tradition of Buddhism in the Kathmandu Valley during the first millennium, the transformation into a distinctive cultural and linguistic form of Buddhism appears to have taken place in the fifteenth century, at about the same tim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newar Caste System
Newar caste system is the system by which Newārs, the historical inhabitants of Kathmandu Valley, are divided into groups on the basis of Vedic varna model and divided according to their hereditary occupations. First introduced at the time of the Licchavis (A.D. 300 – c. 879), the Newar caste system assumed its present shape during the medieval Malla period (A.D. 1201–1769). The Newar caste structure resembles more closely to North India and Madheshis than that of the Khas 'Parbatiyas' in that all four Varna ( Brahmin, Kshatriya, Vaishya and Shudra) and untouchables are represented. The social structure of Newars is unique as it is the last remaining example of a pre-Islamic North Indic civilisation in which Buddhist elements enjoy equal status with the Brahmanic elements. History of Assimilation According to various historical sources, even though the presence of ''varna'' and caste had been a known element in the social structure of the Kathmandu Valley since t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahātmā
Mahatma (English pronunciation: , sa, महात्मा, translit=mahātmā) is an honorific used in India. The term is commonly used for Mahatma Gandhi, Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, who is often referred to simply as "Mahatma Gandhi". Albeit less frequently, this epithet has also been used with regard to such people as Basava (1131–1167), Swami Shraddhanand (1856–1926), Lalon, Lalon Shah (1772–1890), Ayyankali (1863–1941), and Jyotirao Phule (1827–1890). The term ''mahātmā'' has also been historically used for a class of religious scholars in Jainism; for the selected religious leaders in Theosophy; and for local religious teachers in the Divine Light Mission church. Etymology The term ''Mahatma'' derives from the Sanskrit terms महा (mahā), meaning "great" and आत्मा (ātmā), meaning "soul". In Theosophy The word, used in a technical sense, was popularized in Theosophy (Blavatskian), theosophical literature in the late 19th century, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesian Esoteric Buddhism
Indonesian Esoteric Buddhism or Esoteric Buddhism in Maritime Southeast Asia refers to the traditions of Esoteric Buddhism found in Maritime Southeast Asia which emerged in the 7th century along the maritime trade routes and port cities of the Indonesian islands of Java and Sumatra as well as in Malaysia. These esoteric forms were spread by pilgrims and Tantric masters who received royal patronage from royal dynasties like the Sailendras and the Srivijaya.Acri, Andrea. Esoteric Buddhism in Mediaeval Maritime Asia: Networks of Masters, Texts, Icons, page 7. This tradition was also linked by the maritime trade routes with Indian Vajrayana, Tantric Buddhism in Sinhala, Cham and Khmer lands and in China and Japan, to the extent that it is hard to separate them completely and it is better to speak of a complex of "Esoteric Buddhism of Mediaeval Maritime Asia." Many key Indian port cities saw the growth of Esoteric Buddhism, a tradition which coexisted alongside Shaivism. Java under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahasiddhas
Mahasiddha (Sanskrit: ''mahāsiddha'' "great adept; ) is a term for someone who embodies and cultivates the "siddhi of perfection". A siddha is an individual who, through the practice of sādhanā, attains the realization of siddhis, psychic and spiritual abilities and powers. Mahasiddhas were practitioners of yoga and tantra, or ''tantrika''s. Their historical influence throughout the Indian subcontinent and the Himalayas was vast and they reached mythic proportions as codified in their songs of realization and hagiographies, or namtars, many of which have been preserved in the Tibetan Buddhist canon. The Mahasiddhas are the founders of Vajrayana traditions and lineages such as Dzogchen and Mahamudra. Robert Thurman explains the symbiotic relationship between Tantric Buddhist communities and the Buddhist universities such as Nalanda which flourished at the same time. Genealogy and historical dates The exact genealogy and historical dates of the Mahasiddhas are contentious. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist Monasticism
Buddhist monasticism is one of the earliest surviving forms of organized monasticism and one of the fundamental institutions of Buddhism. Monks and nuns, called bhikkhu (Pali, Skt. bhikshu) and bhikkhuni (Skt. bhikshuni), are responsible for the preservation and dissemination of the Buddha's teaching and the guidance of Buddhist lay people. Three surviving traditions of monastic discipline ( Vinaya), govern modern monastic life in different regional traditions: Theravada (Sri Lanka and Southeast Asia), Dharmaguptaka (East Asia), and Mulasarvastivada (Tibet and the Himalayan region). History and development Buddhism originated as a renunciant tradition, practiced by ascetics who had departed from lay life. According to Buddhist tradition, the order of monks and nuns was founded by Gautama Buddha during his lifetime between the fifth and fourth centuries BCE when he accepted a group of fellow renunciants as his followers. The Buddhist monastic lifestyle grew out of the lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantras
Tantras ("''doctrine''" or "''framework''" or "''system''" ) refers to numerous and varied scriptures pertaining to any of several esoteric traditions rooted in Hindu and Buddhist philosophy. The religious culture of the Tantras is essentially Hindu, and Buddhist Tantric material can be shown to have been derived from Hindu sources. And although Hindu and Buddhist Tantra have many similarities from the outside, they do have some clear distinctions. The rest of this article deals with Hindu Tantra. Buddhist Tantras are described in the article on Buddhist Tantras. Classes of Hindu Tantra The word ''tantra'' is made up by the joining (''sandhi'' in Sanskrit) of two Sanskrit words: ''tanoti'' (expansion) and ''rayati'' (liberation). Tantra means liberation of energy and expansion of consciousness from its gross form. It is a method to expand the mind and liberate the dormant potential energy, and its principles form the basis of all yogic practices. Hence, the Hindu Tantra scriptur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alms
Alms (, ) are money, food, or other material goods donated to people living in poverty. Providing alms is often considered an act of virtue or Charity (practice), charity. The act of providing alms is called almsgiving, and it is a widespread practice in a number of different religions and cultures. Etymology The word ''alms'' comes from the Old English ', ', which comes from Late Latin ', from Greek language, Greek ' ("pity, alms"), from , ' ("merciful"), from , ', meaning "pity or mercy". Buddhism ''Dāna'' in Buddhism In Buddhism, both "almsgiving" and "giving" are called "Dana (Buddhism), dāna" (Pāli). Such giving is one of the three elements of the path of practice as formulated by the Gautama Buddha, Buddha for Householder (Buddhism), laypeople. This path of practice for laypeople is Dana (Buddhism), dāna, Śīla, sīla, and Bhavana, bhāvanā. Generosity towards other sentient beings is also emphasized in Mahayana as one of the perfections (paramita). As sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)