|
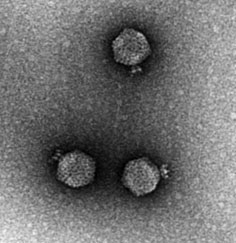
Bacteriophage T7 7-24-2021 Ps
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biomass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T4 Bacteriophage
T4 or T-4 may refer to: Airports and airlines * Heathrow Terminal 4 * Tiyas Military Airbase, also known as the T-4 Airbase Biology and medicine * T4 phage, a bacteriophage * Thyroxine (T4), a form of thyroid hormone * the T4 spinal nerve * the fourth thoracic vertebrae of the vertebral column * A non-small cell lung carcinoma staging for a type of tumour * A CD4 + T lymphocyte * T4: an EEG electrode site according to the 10-20 system Entertainment * ''T4'' (Channel 4), the former daytime teen-aimed slot on Channel 4 in the UK * ''Terminator Salvation'', sometimes referred to as ''Terminator 4'' * '' Transformers: Age of Extinction'', the fourth film in the live-action ''Transformers'' film series Computing * SPARC T4, a microprocessor introduced by Oracle Microelectronics in 2011 Software and video games * Text Template Transformation Toolkit, a technology developed by Microsoft * ''Tekken 4'', a fighting game Electricity production * Lockheed Martin's High beta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Bacteria
Marine prokaryotes are marine bacteria and marine archaea. They are defined by their habitat as prokaryotes that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. All cellular life forms can be divided into prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within membranes, whereas prokaryotes are the organisms that do not have a nucleus enclosed within a membrane. The three-domain system of classifying life adds another division: the prokaryotes are divided into two domains of life, the microscopic bacteria and the microscopic archaea, while everything else, the eukaryotes, become the third domain. Prokaryotes play important roles in ecosystems as decomposers recycling nutrients. Some prokaryotes are pathogenic, causing disease and even death in plants and animals. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encased in lipid bilayers, and they infect their target cells by causing the viral envelope and cell membrane to fuse. Although there are effective vaccines against some of these viruses, there is no preventative or curative medicine for the majority of them. In most cases, the known vaccines operate by inducing antibodies that prevent the pathogen from entering cells. This happens in the case of enveloped viruses when the antibodies bind to the viral envelope proteins. The membrane fusion event that triggers viral entrance is caused by the viral fusion protein. Many enveloped viruses only have one protein visible on the surface of the particle, which is required for both mediating adhesion to the cell surface and for the subsequent membrane fusi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ackermannviridae
''Ackermannviridae'' is a family of viruses in the order ''Caudovirales''. Gammaproteobacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota serve as natural hosts. There are 2 subfamilies, 10 genera, and 63 species in the family. Etymology The family's name, ''Ackermann'' is in honor of Hans-Wolfgang Ackermann (1936-2017), a German microbiologist, the suffix ''-viridae'' is the standard suffix for virus families.Hans-W. AckermannLife in science Bacteriophage. 2012 Oct 1; 2(4): 207. doi: 10.4161/bact.23159 . . A curriculum vitae. Taxonomy The following taxa are recognized (-''virinae'' denotes subfamily and -''virus'' denotes genus): * '' Aglimvirinae'' ** '' Agtrevirus'' ** '' Limestonevirus'' * '' Cvivirinae'' ** ''Kuttervirus'' ''incertae sedis ' () or ''problematica'' is a term used for a taxonomic group where its broader relationships are unknown or undefined. Alternatively, such groups are frequently referred to as "enigmatic taxa". In the system of open nomenclature, uncertainty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudovirales
''Caudovirales'' is an order of viruses known as the tailed bacteriophages (''cauda'' is Latin for "tail"). Under the Baltimore classification scheme, the ''Caudovirales'' are group I viruses as they have double stranded DNA (dsDNA) genomes, which can be anywhere from 18,000 base pairs to 500,000 base pairs in length. The virus particles have a distinct shape; each virion has an icosahedral head that contains the viral genome, and is attached to a flexible tail by a connector protein. The order encompasses a wide range of viruses, many containing genes of similar nucleotide sequence and function. However, some tailed bacteriophage genomes can vary quite significantly in nucleotide sequence, even among the same genus. Due to their characteristic structure and possession of potentially homologous genes, it is believed these bacteriophages possess a common origin. There are 14 families, 73 subfamilies, 927 genera, and 2,814 species in the order. This makes ''Caudovirales'' the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turriviridae
''Turriviridae'' is a family of viruses; it contains only one genus, ''Alphaturrivirus''. The archaea ''Sulfolobus solfataricus'' serve as natural hosts. There are two species in the genus ''Alphaturrivirus''. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species: * ''Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus 1 ''Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus 1'' (formerly ''Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus'') is a species of virus that infects the archaeon ''Sulfolobus solfataricus''. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belfryvirales
''Turriviridae'' is a family of viruses; it contains only one genus, ''Alphaturrivirus''. The archaea ''Sulfolobus solfataricus'' serve as natural hosts. There are two species in the genus ''Alphaturrivirus''. Taxonomy The genus contains the following species: * ''Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus 1 ''Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus 1'' (formerly ''Sulfolobus turreted icosahedral virus'') is a species of virus that infects the archaeon ''Sulfolobus solfataricus''. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterobacteria Phage T2 Transmission Electron Micrograph
Enterobacteriaceae is a large family of Gram-negative bacteria. It was first proposed by Rahn in 1936, and now includes over 30 genera and more than 100 species. Its classification above the level of family is still a subject of debate, but one classification places it in the order Enterobacterales of the class Gammaproteobacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota. In 2016, the description and members of this family were emended based on comparative genomic analyses by Adeolu et al. Enterobacteriaceae includes, along with many harmless symbionts, many of the more familiar pathogens, such as '' Salmonella'', ''Escherichia coli'', ''Klebsiella'', and ''Shigella''. Other disease-causing bacteria in this family include ''Enterobacter'' and '' Citrobacter''. Members of the Enterobacteriaceae can be trivially referred to as enterobacteria or "enteric bacteria",as several members live in the intestines of animals. In fact, the etymology of the family is enterobacterium with the suffix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteriophage P22 Casjens Lenk
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a ''phage'' (), is a duplodnaviria virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν ('), meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes (e.g. MS2) and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm. Bacteriophages are among the most common and diverse entities in the biosphere. Bacteriophages are ubiquitous viruses, found wherever bacteria exist. It is estimated there are more than 1031 bacteriophages on the planet, more than every other organism on Earth, including bacteria, combined. Viruses are the most abundant biological entity in the water column of the world's oceans, and the second largest component of biomass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (biology)
Morphology is a branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance (shape, structure, colour, pattern, size), i.e. external morphology (or eidonomy), as well as the form and structure of the internal parts like bones and organs, i.e. internal morphology (or anatomy). This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of gross structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Friedrich Burdach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Committee On Taxonomy Of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclatures for viruses. The ICTV has developed a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus that affects living organisms. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as delimiting the boundaries of species within a family, typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families. History The International Committee on Nomenclature of Viruses (ICNV) was established in 1966, at the International Congress for Microbiology in Moscow, to standardize the naming of viruses. The ICVN published its first report in 1971. For viruses infecting vertebrates, the first report included ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phage Therapy
Phage therapy, viral phage therapy, or phagotherapy is the therapeutic use of bacteriophages for the treatment of pathogenic bacterial infections. This therapeutic approach emerged at the beginning of the 20th century but was progressively replaced by the use of antibiotics in most parts of the world after the second world war. Bacteriophages, known as phages, are a form of virus that attach to bacterial cells and inject their genome into the cell. The bacteria's production of the viral genome interferes with its ability to function, halting the bacterial infection. The bacterial cell causing the infection is unable to reproduce, and instead produces additional phages. Phages are very selective in the strains of bacteria they are effective against. Advantages include reduced side-effects and reduced risk of the bacterium developing resistance since bacteriophages are much more specific than antibiotics. They are typically harmless not only to the host organism but also to ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |