|
Bacterial Phylodynamics
Bacterial phylodynamics is the study of immunology, epidemiology, and phylogenetics of bacterial pathogens to better understand the evolutionary role of these pathogens. Phylodynamic analysis includes analyzing genetic diversity, natural selection, and population dynamics of infectious disease pathogen phylogenies during pandemics and studying intra-host evolution of viruses. Phylodynamics combines the study of phylogenetic analysis, ecological, and evolutionary processes to better understand of the mechanisms that drive spatiotemporal incidence and phylogenetic patterns of bacterial pathogens. Bacterial phylodynamics uses genome-wide single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) in order to better understand the evolutionary mechanism of bacterial pathogens. Many phylodynamic studies have been performed on viruses, specifically RNA viruses (see Viral phylodynamics) which have high mutation rates. The field of bacterial phylodynamics has increased substantially due to the advancement of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunology
Immunology is a branch of medicineImmunology for Medical Students, Roderick Nairn, Matthew Helbert, Mosby, 2007 and biology that covers the medical study of immune systems in humans, animals, plants and sapient species. In such we can see there is a difference of human immunology and comparative immunology in veterinary medicine and animal biosciences. Immunology measures, uses charts and differentiate in context in medicine the studies of immunity on cell and molecular level, and the immune system as part of the physiological level as its functioning is of major importance. In the different states of both health, occurring symptoms and diseases; the functioning of the immune system and immunological responses such as autoimmune diseases, allergic hypersensitivities, or in some cases malfunctioning of immune system as for example in immunological disorders or in immune deficiency, and the specific transplant rejection) Immunology has applications in numerous disciplines of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
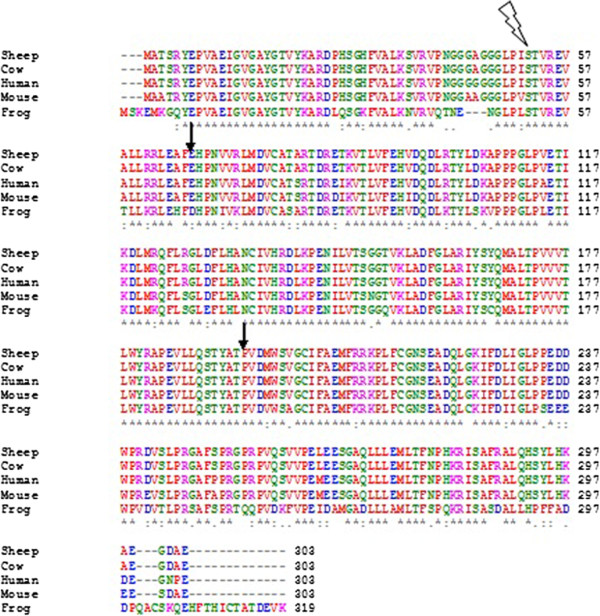
Clustal
Clustal is a series of widely used computer programs used in bioinformatics for multiple sequence alignment. There have been many versions of Clustal over the development of the algorithm that are listed below. The analysis of each tool and its algorithm are also detailed in their respective categories. Available operating systems listed in the sidebar are a combination of the software availability and may not be supported for every current version of the Clustal tools. Clustal Omega has the widest variety of operating systems out of all the Clustal tools. History There have been many variations of the Clustal software, all of which are listed below: * Clustal: The original software for multiple sequence alignments, created by Des Higgins in 1988, was based on deriving phylogenetic trees from pairwise sequences of amino acids or nucleotides. * ClustalV: The second generation of the Clustal software was released in 1992 and was a rewrite of the original Clustal package. It intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Clock
The molecular clock is a figurative term for a technique that uses the mutation rate of biomolecules to deduce the time in prehistory when two or more life forms diverged. The biomolecular data used for such calculations are usually nucleotide sequences for DNA, RNA, or amino acid sequences for proteins. The benchmarks for determining the mutation rate are often fossil or archaeological dates. The molecular clock was first tested in 1962 on the hemoglobin protein variants of various animals, and is commonly used in molecular evolution to estimate times of speciation or radiation. It is sometimes called a gene clock or an evolutionary clock. Early discovery and genetic equidistance The notion of the existence of a so-called "molecular clock" was first attributed to Émile Zuckerkandl and Linus Pauling who, in 1962, noticed that the number of amino acid differences in hemoglobin between different lineages changes roughly linearly with time, as estimated from fossil evidence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Inference
Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference in which Bayes' theorem is used to update the probability for a hypothesis as more evidence or information becomes available. Bayesian inference is an important technique in statistics, and especially in mathematical statistics. Bayesian updating is particularly important in the dynamic analysis of a sequence of data. Bayesian inference has found application in a wide range of activities, including science, engineering, philosophy, medicine, sport, and law. In the philosophy of decision theory, Bayesian inference is closely related to subjective probability, often called "Bayesian probability". Introduction to Bayes' rule Formal explanation Bayesian inference derives the posterior probability as a consequence of two antecedents: a prior probability and a "likelihood function" derived from a statistical model for the observed data. Bayesian inference computes the posterior probability according to Bayes' theorem: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Probability
The posterior probability is a type of conditional probability that results from updating the prior probability with information summarized by the likelihood via an application of Bayes' rule. From an epistemological perspective, the posterior probability contains everything there is to know about an uncertain proposition (such as a scientific hypothesis, or parameter values), given prior knowledge and a mathematical model describing the observations available at a particular time. After the arrival of new information, the current posterior probability may serve as the prior in another round of Bayesian updating. In the context of Bayesian statistics, the posterior probability distribution usually describes the epistemic uncertainty about statistical parameters conditional on a collection of observed data. From a given posterior distribution, various point and interval estimates can be derived, such as the maximum a posteriori (MAP) or the highest posterior density interval (HPD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Likelihood Estimation
In statistics, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a method of estimating the parameters of an assumed probability distribution, given some observed data. This is achieved by maximizing a likelihood function so that, under the assumed statistical model, the observed data is most probable. The point in the parameter space that maximizes the likelihood function is called the maximum likelihood estimate. The logic of maximum likelihood is both intuitive and flexible, and as such the method has become a dominant means of statistical inference. If the likelihood function is differentiable, the derivative test for finding maxima can be applied. In some cases, the first-order conditions of the likelihood function can be solved analytically; for instance, the ordinary least squares estimator for a linear regression model maximizes the likelihood when all observed outcomes are assumed to have Normal distributions with the same variance. From the perspective of Bayesian inference, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bootstrapping (statistics)
Bootstrapping is any test or metric that uses random sampling with replacement (e.g. mimicking the sampling process), and falls under the broader class of resampling methods. Bootstrapping assigns measures of accuracy (bias, variance, confidence intervals, prediction error, etc.) to sample estimates.software This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods. Bootstrapping estimates the properties of an (such as its ) by measuring those properties when sampling from an approximating distribution. One standard choice for an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Analysis
Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference in which Bayes' theorem is used to update the probability for a hypothesis as more evidence or information becomes available. Bayesian inference is an important technique in statistics, and especially in mathematical statistics. Bayesian updating is particularly important in the dynamic analysis of a sequence of data. Bayesian inference has found application in a wide range of activities, including science, engineering, philosophy, medicine, sport, and law. In the philosophy of decision theory, Bayesian inference is closely related to subjective probability, often called "Bayesian probability". Introduction to Bayes' rule Formal explanation Bayesian inference derives the posterior probability as a consequence of two antecedents: a prior probability and a "likelihood function" derived from a statistical model for the observed data. Bayesian inference computes the posterior probability according to Bayes' theorem: P(H\ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Likelihood
In statistics, maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a method of estimation theory, estimating the Statistical parameter, parameters of an assumed probability distribution, given some observed data. This is achieved by Mathematical optimization, maximizing a likelihood function so that, under the assumed statistical model, the Realization (probability), observed data is most probable. The point estimate, point in the parameter space that maximizes the likelihood function is called the maximum likelihood estimate. The logic of maximum likelihood is both intuitive and flexible, and as such the method has become a dominant means of statistical inference. If the likelihood function is Differentiable function, differentiable, the derivative test for finding maxima can be applied. In some cases, the first-order conditions of the likelihood function can be solved analytically; for instance, the ordinary least squares estimator for a linear regression model maximizes the likelihood when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Parsimony
In phylogenetics, maximum parsimony is an optimality criterion under which the phylogenetic tree that minimizes the total number of character-state changes (or miminizes the cost of differentially weighted character-state changes) is preferred. Under the maximum-parsimony criterion, the optimal tree will minimize the amount of homoplasy (i.e., convergent evolution, parallel evolution, and evolutionary reversals). In other words, under this criterion, the shortest possible tree that explains the data is considered best. Some of the basic ideas behind maximum parsimony were presented by James S. Farris in 1970 and Walter M. Fitch in 1971. Maximum parsimony is an intuitive and simple criterion, and it is popular for this reason. However, although it is easy to ''score'' a phylogenetic tree (by counting the number of character-state changes), there is no algorithm to quickly ''generate'' the most-parsimonious tree. Instead, the most-parsimonious tree must be sought in "tree space" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neighbor Joining
In bioinformatics, neighbor joining is a bottom-up (agglomerative) clustering method for the creation of phylogenetic trees, created by Naruya Saitou and Masatoshi Nei in 1987. Usually based on DNA or protein sequence data, the algorithm requires knowledge of the distance between each pair of taxa (e.g., species or sequences) to create the phylogenetic tree. The algorithm Neighbor joining takes a distance matrix, which specifies the distance between each pair of taxa, as input. The algorithm starts with a completely unresolved tree, whose topology corresponds to that of a star network, and iterates over the following steps, until the tree is completely resolved, and all branch lengths are known: # Based on the current distance matrix, calculate a matrix Q (defined below). # Find the pair of distinct taxa i and j (i.e. with i \neq j) for which Q(i,j) is smallest. Make a new node that joins the taxa i and j, and connect the new node to the central node. For example, in part (B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UPGMA
UPGMA (unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean) is a simple agglomerative (bottom-up) hierarchical clustering method. The method is generally attributed to Sokal and Michener. The UPGMA method is similar to its ''weighted'' variant, the WPGMA method. Note that the unweighted term indicates that all distances contribute equally to each average that is computed and does not refer to the math by which it is achieved. Thus the simple averaging in WPGMA produces a weighted result and the proportional averaging in UPGMA produces an unweighted result ('' see the working example''). Algorithm The UPGMA algorithm constructs a rooted tree (dendrogram) that reflects the structure present in a pairwise similarity matrix (or a dissimilarity matrix). At each step, the nearest two clusters are combined into a higher-level cluster. The distance between any two clusters \mathcal and \mathcal, each of size (''i.e.'', cardinality) and , is taken to be the average of all distances d(x,y) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |