|
Babesiidae
Babesiidae is a family of protists belonging to the order Piroplasmida. Genera: * ''Babesia ''Babesia'', also called ''Nuttallia'', is an apicomplexan parasite that infects red blood cells and is transmitted by ticks. Originally discovered by the Romanian bacteriologist Victor Babeș in 1888, over 100 species of ''Babesia'' have since ...'' Starcovivi, 1893 * '' Echinozoon'' Garnham, 1951 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q18618857 Piroplasmida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piroplasmida
Piroplasmida is an order of parasites in the phylum Apicomplexa. They divide by binary fission and as sporozoan parasites they possess sexual and asexual phases (sexual reproduction occurs in the tick gut). They include the tick parasites ''Babesia'' and ''Theileria''. Description They are minute rounded or pyriform parasites found within erythrocytes, or other circulating or endothelial cells of vertebrates, where they reproduce by merogony. The trophozoite stage is separated from erythrocyte by a single membrane. This distinguishes them from other blood parasites that usually have at least two membranes. An apical complex with a polar ring and rhopteries occurs, but without a conoid and usually without associated pellicular microtubules. They lack flagella and do not form either oocysts or spores. The known vectors are ticks or leeches in which they undergo sporogony; sexual reproduction probably occurs in the vector. See also * Babesiosis Babesiosis or piroplasmos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protists
A protist () is any eukaryotic organism (that is, an organism whose cells contain a cell nucleus) that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. While it is likely that protists share a common ancestor (the last eukaryotic common ancestor), the exclusion of other eukaryotes means that protists do not form a natural group, or clade. Therefore, some protists may be more closely related to animals, plants, or fungi than they are to other protists. However, like the groups ''algae'', ''invertebrates'', and ''protozoans'', the biological category ''protist'' is used for convenience. Others classify any unicellular eukaryotic microorganism as a protist. The study of protists is termed protistology. History The classification of a third kingdom separate from animals and plants was first proposed by John Hogg in 1860 as the kingdom Protoctista; in 1866 Ernst Haeckel also proposed a third kingdom Protista as "the kingdom of primitive forms". Originally these also included prokaryotes, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
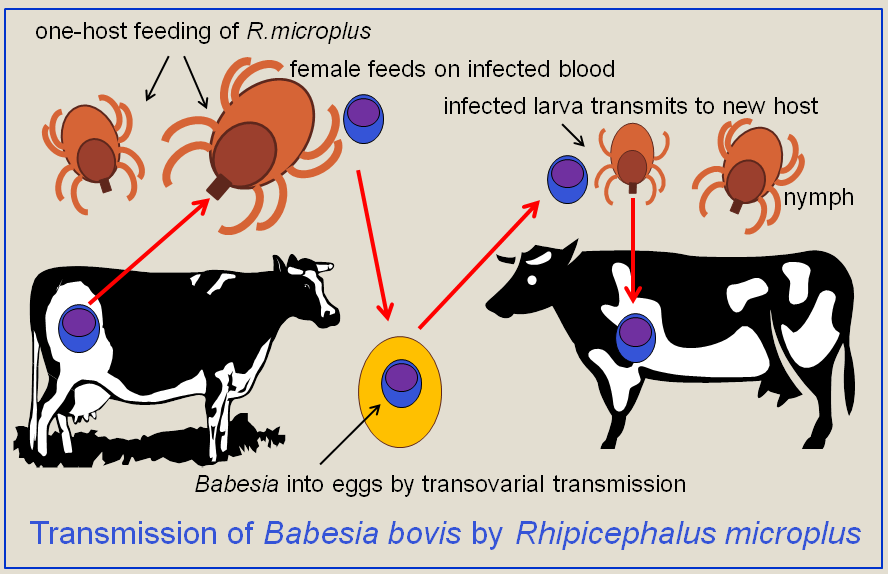
Babesia
''Babesia'', also called ''Nuttallia'', is an apicomplexan parasite that infects red blood cells and is transmitted by ticks. Originally discovered by the Romanian bacteriologist Victor Babeș in 1888, over 100 species of ''Babesia'' have since been identified. ''Babesia'' comprises more than 100 species of tick-borne parasites that infect erythrocytes (red blood cells) in many vertebrate hosts. ''Babesia'' species infect livestock worldwide, wild and domestic vertebrate animals, and occasionally humans, where they cause the disease babesiosis. In the United States, ''B. microti'' is the most common strain of the few which have been documented to cause disease in humans. Classification ''Babesia'' is a protozoan parasite found to infect vertebrate animals, mostly livestock mammals and birds, but also occasionally humans. Common names of the disease that ''Babesia microti'' causes are Texas cattle fever, redwater fever, tick fever, and Nantucket fever. The disease it caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinozoon
''Echinozoon'' is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexia. There is one species in this genus - ''Echinozoon hoogstraali''. History The species and genus was described in 1951 by Garnham. The parasite was isolated from a bush rock hyrax ('' Heterohyrax brucei hoogstraali'') in 1950 by Hoogstraal and Lawless in Torit, South Sudan. Description Filaments are present on parasitized erythrocytes making their identification easy. The earliest stages (ring forms) are less than two micrometers in size and are oval or round in shape. No filaments are evident at this stage unlike all later stages. The parasites occur singly in the erythrocytes. A vacuole is present. The nucleus is irregular. Later stages occur in two forms. The smaller of these may be up to 5 micrometers in size, circular in outline, with pale blue cytoplasm that is free of granules. The nucleus lies to the side of the vacuole. The larger form may be up to nine micrometers in size. The cytoplasm is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |