|
Bab Ftouh
Bab Ftouh (also spelled Bab Fetouh) is the main southeastern gate of Fes el-Bali, the old walled city of Fes, Morocco. History The name ''Bab (al-)Ftouh'' means literally "Gate of the Opening", but historically this name (also used for Bab al-Futuh in Cairo) has been interpreted as "Gate of Conquest" or "Gate of Victory". However, the name of this gate is believed to have originated more directly with the name of a Zenata emir who was himself called al-Fetouh Ibn Dounas and who dominated the early city of ''Madinat Fas'' (now the Andalusian Quarter) from 1059 to 1061, back when Fes was still divided into two separate cities. He is said to have built the first gate in this area to go by his name. This gate replaced an earlier Idrisid gate called Bab al-Qibla (named after the fact that the gate lay in the direction of prayer, the ''qibla'', relative to the city center). Al-Fetouh was in rivalry with his brother, 'Ajissa, who controlled the other city, ''al-'Aliya'', on the oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Gate
A city gate is a gate which is, or was, set within a city wall. It is a type of fortified gateway. Uses City gates were traditionally built to provide a point of controlled access to and departure from a walled city for people, vehicles, goods and animals. Depending on their historical context they filled functions relating to defense, security, health, trade, taxation, and representation, and were correspondingly staffed by military or municipal authorities. The city gate was also commonly used to display diverse kinds of public information such as announcements, tax and toll schedules, standards of local measures, and legal texts. It could be heavily fortified, ornamented with heraldic shields, sculpture or inscriptions, or used as a location for warning or intimidation, for example by displaying the heads of beheaded criminals or public enemies. Notably in Denmark, many market towns used to have at least one city gate mostly as part of the city's fortifications, but during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bab Guissa
Bab Guissa or Bab Gisa ( or ) is the main northwestern gate of Fes el Bali, the old walled city of Fes, Morocco. History A gate by this name had existed in this part of the city walls since at least the 11th century. That gate was named after a Zenata emir, (), who dominated the early city of ''al-'Aliya'' (on the Qarawiyyin quarter of Fes), in rivalry with his brother, el-Fetouh, who dominated the city of ''Madinat Fas'' (now the Andalous quarter) on the opposite shore of the river and who probably gave his name to another gate, Bab Ftouh. The two brothers were in power between 1059 and 1061 and both were likely responsible for building these gates, meaning Bab Guissa must have been built during these years. Soon after, the two cities were definitively joined into a single city with a single set of walls by the Almoravids, who conquered the city in 1069. These walls were destroyed in 1145 by the Almohad conqueror Abd al-Mu'min and then rebuilt by one of his successors, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horseshoe Arch
The horseshoe arch (; Spanish: "arco de herradura"), also called the Moorish arch and the keyhole arch, is an emblematic arch of Islamic architecture, especially Moorish architecture. Horseshoe arches can take rounded, pointed or lobed form. History Origins and early uses The origins of the horseshoe arch are controversial. It appeared in pre-Islamic Sasanian architecture such as the Taq-i Kasra in present-day Iraq and the Palace of Ardashir in southwestern Iran (3rd century CE). It also appeared in Late Roman or Byzantine architecture in pre-Islamic Syria, where the form was used in the Baptistery of Saint Jacob at Nusaybin (4th century CE) and in Qasr Ibn Wardan (564 CE). However, the horseshoe arch allowed more height than the classical (semi-circular) arch as well as better aesthetic and decorative use. Muslims used this arch to develop their famous ultra-semicircular arch, around which the whole of Islamic architecture evolved, thus more likely suggesting that the hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bent Entrance
A bent or indirect entrance is a defensive feature in medieval fortification.Adrian Boas, On a Necessary Vulnerability, https://www.adrianjboas.com/post/on-a-necessary-vulnerability In a castle with a bent entrance, the gate passage is narrow and turns sharply. Its purpose is to slow down attackers attempting to rush the gate and impede the use of battering rams against doors. It is often combined with means for an active defence, such as machicolations, in effect confining intruders to a narrow killing zone. Its defensive function is related to that of a barbican in front of the gate. Indirect entrances are typical of Arab and Armenian fortifications, as well as crusader castles. The Citadel of Aleppo is a good example of the former, with a massive gate tower enclosing a complicated passage. The most elaborate bent entrance among crusader castles is the turning entrance ramp at Crac des Chevaliers, which is defensible from several towers and via machicolations, but the indirect en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taza
Taza ( ber, ⵜⴰⵣⴰ, ar, تازة) is a city in northern Morocco occupying the corridor between the Rif mountains and Middle Atlas mountains, about 120 km east of Fez and 150 km west of Al hoceima. It recorded a population of 148,406 in the 2019 Moroccan census and is the capital of Taza Province. History Historically Taza was known first as ''Ribāt Taza'' (), a military camp belonging to the Fatimid state, founded by the local governor ''Mussa ibn abi al-'Afiya ''() who was also the leader of the Miknasa. Up to at least the early 20th century, Taza was a considerable trading centre on the route between Fez and the Algerian frontier. Taza as a toponym could be derivative from Tizi (Tamazight for a hill that lies between mountains) which is where it stands up. Taza was first settled by Miknasa tribesmen, who gave it its name: ''Miknasa Taza'', similar to ''Miknasa al-Zeitoun'' (present-day Meknes, another Miknasa settlement). The Almoravid empire took over Taza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
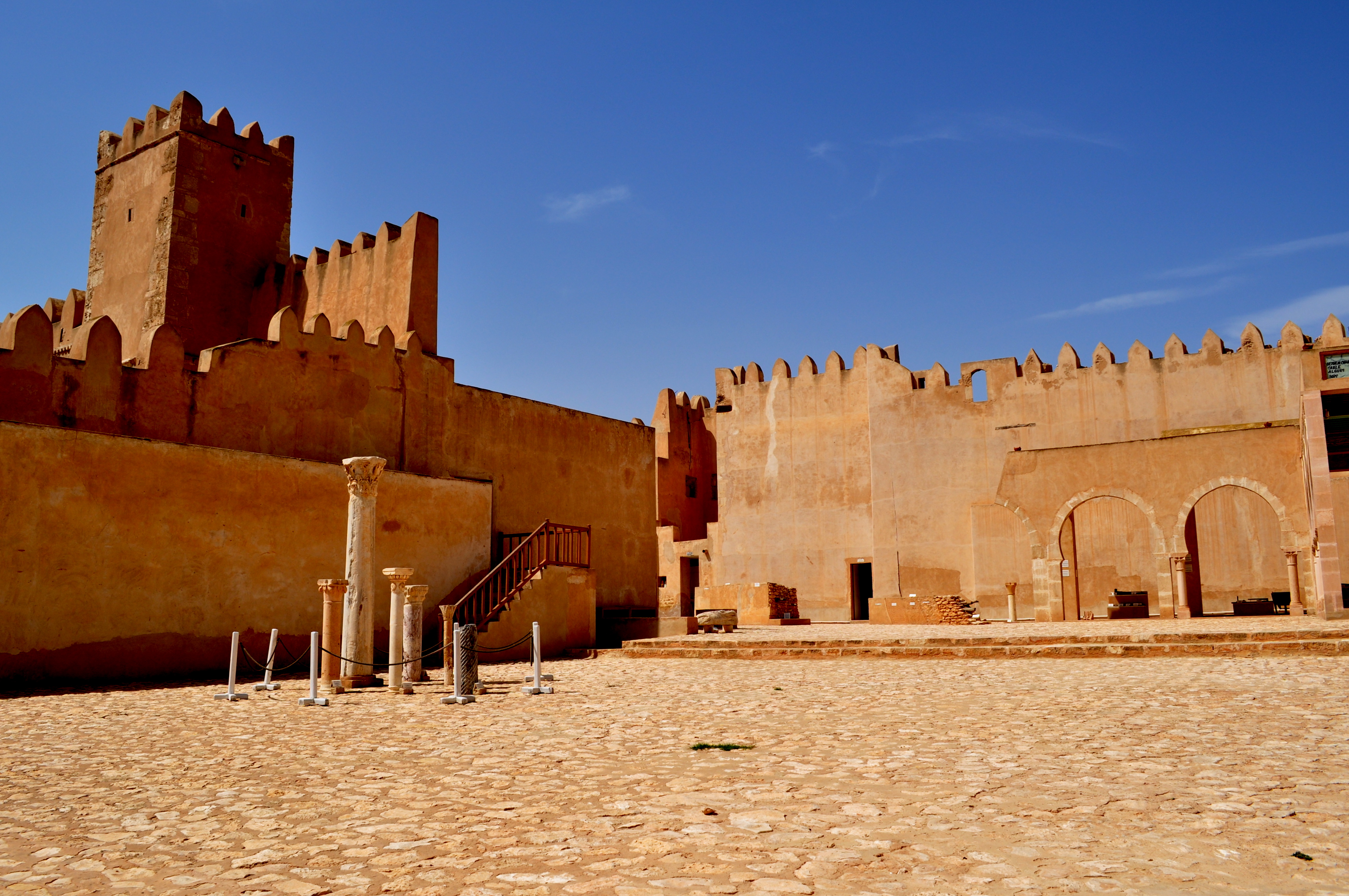
Kasbah Tamdert
Kasbah Tamdert is a fortress and kasbah in Fes, Morocco. It is located near Bab Ftouh in southern Fes el-Bali. History The kasbah was built in the 16th century on the orders of the Saadian sultan Muhammad al-Shaykh in 1549. The Saadians, who had their capital at Marrakech, built forts around Fes to keep its population under control as much as for defending it from outside enemies. Kasbah Tamdert was the first of the Saadian fortifications built in the city, consisting of a simple walled enclosure (a kasbah), while years later the Saadians built the heavier fortresses of Borj Nord Borj Nord or Burj al-Shamal (), Al-Burj ash-Shamali () is a fort in the city of Fez, Morocco. It was first established in 1582 by the Saadi dynasty, modeled after the Portuguese forts in the 16th century. It is among the largest defense structur ..., Borj Sud, and the bastions on the eastern side of Fes Jdid, Fes el-Jdid. The name ''Tamdert'' was a local Berbers, Amazigh (Berber) name. The kasbah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kasbah
A kasbah (, also ; ar, قَـصَـبَـة, qaṣaba, lit=fortress, , Maghrebi Arabic: ), also spelled qasba, qasaba, or casbah, is a fortress, most commonly the citadel or fortified quarter of a city. It is also equivalent to the term ''alcazaba'' in Spanish (), which derives from the same Arabic word. By extension, the term can also refer to a medina quarter, particularly in Algeria. In various languages, the Arabic word, or local words borrowed from the Arabic word, can also refer to a settlement, a fort, a watchtower, or a blockhouse. Citadel or fortress The term ''qasaba'' was historically flexible but it essentially denotes a fortress, commonly a citadel that protects a city or settlement area, or that serves as the administrative center. A kasbah citadel typically housed the military garrison and other privileged buildings such as a palace, along with other amenities such as a mosque and a hammam (bathhouse). Some kasbahs are built in a strategic elevated position o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saadi Dynasty
The Saadi Sultanate (also rendered in English as Sa'di, Sa'did, Sa'dian, or Saadian; ar, السعديون, translit=as-saʿdiyyūn) was a state which ruled present-day Morocco and parts of West Africa in the 16th and 17th centuries. It was led by the Saadi dynasty, an Arabs, Arab Moroccan Sharifism, Sharifian dynasty. The dynasty's rise to power started in 1510 when Abu Abdallah al-Qaim, Muhammad al-Qa'im was declared leader of the tribes of the Sous valley in their resistance against the Portugal, Portuguese who occupied Agadir and other coastal cities. Al-Qai'm's son, Ahmad al-Araj, secured control of Marrakesh by 1525 and, after a period of rivalry, his brother Mohammed ash-Sheikh, Muhammad al-Shaykh captured Agadir from the Portuguese and eventually captured Fez, Morocco, Fez from the Wattasid dynasty, Wattasids, securing control over nearly all of Morocco. After Muhammad al-Shaykh's assassination by the Ottoman Empire, Ottomans in 1557 his son Abdallah al-Ghalib enjoyed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohammed Ben Abdallah
''Sidi'' Mohammed ben Abdallah ''al-Khatib'' ( ar, سيدي محمد بن عبد الله الخطيب), known as Mohammed III ( ar, محمد الثالث), born in 1710 in Fes and died on 9 April 1790 in Meknes, was the Sultan of Morocco from 1757 to 1790 as a member of the 'Alawi dynasty. He was the governor of Marrakesh around 1750. He was also briefly sultan in 1748. He rebuilt many cities after the earthquake of 1755, including Mogador, Casablanca, and Rabat, and Abdallah Laroui described him as "the architect of modern Morocco." He also defeated the French in the Larache expedition in 1765 and expelled the Portuguese from Mazagan ( ''al-Jadīda'') in 1769. He is notable for having been the leader of one of the first nations to recognize American independence in his alliance with Luis de Unzaga 'le Conciliateur' through correspondence and Unzaga's secret intelligence service and led by his brothers-in-law Antonio and Matías de Gálvez from the Canary Islands. He was the son o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who claimed almost full sovereignty (i.e., not having dependence on any higher ruler) without claiming the overall caliphate, or to refer to a powerful governor of a province within the caliphate. The adjectival form of the word is "sultanic", and the state and territories ruled by a sultan, as well as his office, are referred to as a sultanate ( '. The term is distinct from king ( '), despite both referring to a sovereign ruler. The use of "sultan" is restricted to Muslim countries, where the title carries religious significance, contrasting the more secular ''king'', which is used in both Muslim and non-Muslim countries. Brunei and Oman are the only independent countries which retain the ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaouite Dynasty
The Alawi dynasty ( ar, سلالة العلويين الفيلاليين, translit=sulālat al-ʿalawiyyīn al-fīlāliyyīn) – also rendered in English as Alaouite, Alawid, or Alawite – is the current Morocco, Moroccan royal family and reigning dynasty. They are an Arab Sharifism, sharifian dynasty and claim descent from the Islamic prophet Muhammad through his grandson, Hasan ibn Ali. Their ancestors originally migrated to the Tafilalt region, in present-day Morocco, from Yanbu on the coast of the Hejaz in the 12th or 13th century. The dynasty rose to power in the 17th century, beginning with Sharif ibn Ali, Mawlay al-Sharif who was declared sultan of the Tafilalt in 1631. His son Al-Rashid of Morocco, Al-Rashid, ruling from 1664 to 1672, was able to unite and pacify the country after a long period of regional divisions caused by the weakening of the Saadi Dynasty. His brother Ismail Ibn Sharif, Isma'il presided over a period of strong central rule between 1672 and 1727, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Al-Nasir
Muhammad al-Nasir (,'' al-Nāṣir li-dīn Allāh Muḥammad ibn al-Manṣūr'', – 1213) was the fourth Almohad Caliph from 1199 until his death.Évariste Lévi-Provençalal-Nāṣir Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition. Brill Online, 2013. Reference. 9 January 2013. Contemporary Christians referred to him as Miramamolin. On 25 January 1199, al-Nasir's father Abu Yusuf Yaqub al-Mansur died; al-Nasir was proclaimed the new caliph that very day. Al-Nasir inherited from his father an empire that was showing signs of instability. Because of his father's victories against the Christians in the Iberian Peninsula (Al-Andalus), he was temporarily relieved from serious threats on that front and able to concentrate on combating and defeating Banu Ghaniya attempts to seize Ifriqiya (Tunisia). Needing, after this, to deal with problems elsewhere in the empire, he appointed Abu Mohammed ibn Abi Hafs as governor of Ifriqiya, so unwittingly inaugurating the rule of the Hafsid d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |