|
Bab Bachir
Bab Bachir ( ar, باب بشير) (died 1254) was a slave consort of the last Abbasid caliph, al-Musta'sim (r. 1242–1258) and mother of Abu Nasr Muhammad ibn al-Musta'sim. She was a slave bought to the Harem by the Caliph. When she gave birth to a son, prince Abu Nasr Muhammad, she became an umm walad An ''umm walad'' ( ar, أم ولد, , lit=mother of the child) was the title given to a slave-concubine in the Muslim world after she had born her master a child. She could not be sold, and became automatically free on her master's death. The off ... and was manumitted by the Caliph, who married her. After her marriage, she made herself known for her public charitable initiatives, which was a common method for the consorts of the Caliph (who could not leave the harem), to make themselves known.Ibn al-Sāʽī, Consorts of the Caliphs: Women and the Court of Baghdad, ed. by Shawkat M. Toorawa, trans. by the Editors of the Library of Arabic Literature (New York: New York Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umm Walad
An ''umm walad'' ( ar, أم ولد, , lit=mother of the child) was the title given to a slave-concubine in the Muslim world after she had born her master a child. She could not be sold, and became automatically free on her master's death. The offspring of an ''umm walad'' were free and considered legitimate children of their father, including full rights of name and inheritance. The practice was a common way for slave girls endowed with beauty and intelligence to advance in the court, especially if they gave birth to sons; under the Caliphates, quite a few of them were raised in rank to queen. Few of them had been fortunate enough to be valide sultan (mother of the king). Unacknowledged slave mother If an unmarried slave bore a child and the slave owner did not acknowledge parenthood, then the slave had to face zina charges.FREE FATHERS, SLAVE MOTHERS AND THEIR CHILDREN: A CONTRIBUTION TO THE STUDY OF FAMILY STRUCTURES IN AL-ANDALUS Cristinadela Puente; Imago TemporIs. medIum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
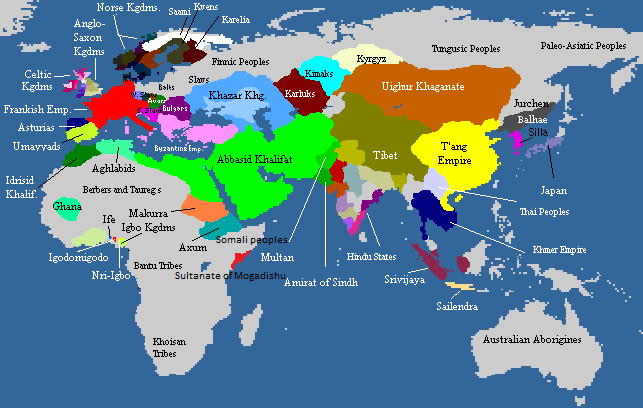
Abbasid Caliph
The Abbasid caliphs were the holders of the Islamic title of caliph who were members of the Abbasid dynasty, a branch of the Quraysh tribe descended from the uncle of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, Al-Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib. The family came to power in the Abbasid Revolution in 748–750, supplanting the Umayyad Caliphate. They were the rulers of the Abbasid Caliphate, as well as the generally recognized ecumenical heads of Islam, until the 10th century, when the Shi'a Fatimid Caliphate (established in 909) and the Caliphate of Córdoba (established in 929) challenged their primacy. The political decline of the Abbasids had begun earlier, during the Anarchy at Samarra (861–870), which accelerated the fragmentation of the Muslim world into autonomous dynasties. The caliphs lost their temporal power in 936–946, first to a series of military strongmen, and then to the Shi'a Buyid Emirs that seized control of Baghdad; the Buyids were in turn replaced by the Sunni Seljuk Turks i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. In 762 CE, Baghdad was chosen as the capital of the Abbasid Caliphate, and became its most notable major development project. Within a short time, the city evolved into a significant cultural, commercial, and intellectual center of the Muslim world. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "Center of Learning". Baghdad was the largest city in the world for much of the Abbasid era during the Islamic Golden Age, peaking at a population of more than a million. The city was largely destroyed at the hands of the Mongol Empire in 1258, resulting in a decline that would linger through many c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Musta'sim
Abu Ahmad Abdallah ibn al-Mustansir Billah (; 1213 – 20 February 1258), better known by his regnal name al-Musta'sim Billah ( ar, المستعصم بالله, al-Mustaʿṣim billāh, label=none) was the 37th and last caliph of the Abbasid dynasty, ruling from 1242 until his death in 1258. He was the last caliph to rule from Baghdad. Biography Abu Ahmad Abdallah al-Musta'sim was son of penultimate Abbasid caliph al-Mustansir, and his mother was Hajir. He was born in 1213. After the death of his father, al-Musta'sim succeeded to the throne in late 1242. He is noted for his opposition to the rise of Shajar al-Durr to the Egyptian throne during the Seventh Crusade. He sent a message from Baghdad to the Mamluks in Egypt that said: "If you do not have men there tell us so we can send you men." However, al-Musta'sim had to face the greatest menace against the Abbasid caliphate since its establishment in 750: the invasion of the Mongol forces that, under Hulagu Khan, had already wipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Death
Death is the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain an organism. For organisms with a brain, death can also be defined as the irreversible cessation of functioning of the whole brain, including brainstem, and brain death is sometimes used as a legal definition of death. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose shortly after death. Death is an inevitable process that eventually occurs in almost all organisms. Death is generally applied to whole organisms; the similar process seen in individual components of an organism, such as cells or tissues, is necrosis. Something that is not considered an organism, such as a virus, can be physically destroyed but is not said to die. As of the early 21st century, over 150,000 humans die each day, with ageing being by far the most common cause of death. Many cultures and religions have the idea of an afterlife, and also may hold the idea of judgement of good and bad deeds in one's life ( h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Dynasty
The Abbasid dynasty or Abbasids ( ar, بنو العباس, Banu al-ʿAbbās) were an Arab dynasty that ruled the Abbasid Caliphate between 750 and 1258. They were from the Qurayshi Hashimid clan of Banu Abbas, descended from Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib. The Abbasid Caliphate is divided into three main periods: Early Abbasid era (750–861), Middle Abbasid era (861–936) and Later Abbasid era (936–1258). A cadet branch of the dynasty also ruled as ceremonial rulers for the Mamluk Sultanate as Caliph (1261–1517), until their conquest by the Ottoman Empire. Ancestry The Abbasids descended from Abbas, one of Muhammad's companions (as well as his uncle) and one of the early Qur'an scholars. Therefore, their roots trace back to Hashim ibn 'Abd Manaf and also Adnan in the following line: Al-‘Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ibn Hashim ibn Abd Manaf ibn Qusai ibn Kilab ibn Murrah ibn Ka'b ibn Lu'ay ibn Ghalib ibn Fihr ibn Malik ibn An-Nadr ibn Kinanah ibn Khuzaima ibn Mudrikah ibn Ily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Musta'sim
Abu Ahmad Abdallah ibn al-Mustansir Billah (; 1213 – 20 February 1258), better known by his regnal name al-Musta'sim Billah ( ar, المستعصم بالله, al-Mustaʿṣim billāh, label=none) was the 37th and last caliph of the Abbasid dynasty, ruling from 1242 until his death in 1258. He was the last caliph to rule from Baghdad. Biography Abu Ahmad Abdallah al-Musta'sim was son of penultimate Abbasid caliph al-Mustansir, and his mother was Hajir. He was born in 1213. After the death of his father, al-Musta'sim succeeded to the throne in late 1242. He is noted for his opposition to the rise of Shajar al-Durr to the Egyptian throne during the Seventh Crusade. He sent a message from Baghdad to the Mamluks in Egypt that said: "If you do not have men there tell us so we can send you men." However, al-Musta'sim had to face the greatest menace against the Abbasid caliphate since its establishment in 750: the invasion of the Mongol forces that, under Hulagu Khan, had already wipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Harem
The harem of the caliphs of the Abbasid Caliphate (750–1258) in Baghdad was composed of his mother, wives, slave concubines, female relatives and slave servants (women and eunuchs), occupying a secluded portion of the Abbasid household. This institution played an important social function within the Abbasid court and was that part were the women were confined and secluded. The senior woman in rank in the harem was the mother of the Caliph. The Abbasid harem acted as a role model for the harems of other Islamic dynasties, as it was during the Abbasid Caliphate that the harem system was fully enforced in the Muslim world. Background and origin The harem system first became fully institutionalized in the Islamic world under the Abbasid caliphate. Although the term ''harem'' does not denote women's quarters in the Quran, a number of Quranic verses discussing modesty and seclusion were held up by Quranic commentators as religious rationale for the separation of women f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umm Walad
An ''umm walad'' ( ar, أم ولد, , lit=mother of the child) was the title given to a slave-concubine in the Muslim world after she had born her master a child. She could not be sold, and became automatically free on her master's death. The offspring of an ''umm walad'' were free and considered legitimate children of their father, including full rights of name and inheritance. The practice was a common way for slave girls endowed with beauty and intelligence to advance in the court, especially if they gave birth to sons; under the Caliphates, quite a few of them were raised in rank to queen. Few of them had been fortunate enough to be valide sultan (mother of the king). Unacknowledged slave mother If an unmarried slave bore a child and the slave owner did not acknowledge parenthood, then the slave had to face zina charges.FREE FATHERS, SLAVE MOTHERS AND THEIR CHILDREN: A CONTRIBUTION TO THE STUDY OF FAMILY STRUCTURES IN AL-ANDALUS Cristinadela Puente; Imago TemporIs. medIum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1254 Deaths
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wives Of Abbasid Caliphs
A wife ( : wives) is a female in a marital relationship. A woman who has separated from her partner continues to be a wife until the marriage is legally dissolved with a divorce judgement. On the death of her partner, a wife is referred to as a widow. The rights and obligations of a wife in relation to her partner and her status in the community and in law vary between cultures and have varied over time. Etymology The word is of Germanic origin, from Proto-Germanic *''wībam'', "woman". In Middle English it had the form ''wif'', and in Old English ''wīf'', "woman or wife". It is related to Modern German ''Weib'' (woman, female), and Danish ''viv'' (wife, usually poetic); The original meaning of the phrase "wife" as simply "woman", unconnected with marriage or a husband/wife, is preserved in words such as "midwife", "goodwife", "fishwife" and " spaewife". Summary In many cultures, marriage is generally expected that a woman will take her husband's surname, though that is not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slaves From The Abbasid Caliphate
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perform some form of work while also having their location or residence dictated by the enslaver. Many historical cases of enslavement occurred as a result of breaking the law, becoming indebted, or suffering a military defeat; other forms of slavery were instituted along demographic lines such as Racism, race. Slaves may be kept in bondage for life or for a fixed period of time, after which they would be Manumission, granted freedom. Although slavery is usually involuntary and involves coercion, there are also cases where people voluntary slavery, voluntarily enter into slavery to pay a debt or earn money due to poverty. In the course of human history, slavery was a typical feature of civilization, and was legal in most societies, but it is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


%2C_Iran%2C_Herat%2C_early_15th_century.jpg)