|
BRM Argos
The BRM Argos is a Portuguese ultralight aircraft, designed and produced by BRM Costruções Aeronáuticas. The aircraft is supplied as a kit for amateur construction.Bayerl, Robby; Martin Berkemeier; et al: ''World Directory of Leisure Aviation 2011-12'', page 33. WDLA UK, Lancaster UK, 2011. ISSN 1368-485XTacke, Willi; Marino Boric; et al: ''World Directory of Light Aviation 2015-16'', page 36. Flying Pages Europe SARL, 2015. Design and development The Argos was designed to comply with the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale microlight rules. It features a cantilever low-wing, a two-seats-in-side-by-side configuration enclosed cockpit, fixed tricycle landing gear and a single engine in tractor configuration. The aircraft is made from 6061-T6 aluminum sheet, with its cockpit strengthened with steel roll-over protection. Its span wing has an area of and electrically actuated flaps. Standard engines available are the Rotax 912ULS, Jabiru 2200 and the Jabiru 3300 f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6061-T6 Aluminum
6061 ( Unified Numbering System (UNS) designation A96061) is a precipitation-hardened aluminium alloy, containing magnesium and silicon as its major alloying elements. Originally called "Alloy 61S", it was developed in 1935. It has good mechanical properties, exhibits good weldability, and is very commonly extruded (second in popularity only to 6063). It is one of the most common alloys of aluminium for general-purpose use. It is commonly available in pre-tempered grades such as 6061-O (annealed), tempered grades such as 6061-T6 (solutionized and artificially aged) and 6061-T651 (solutionized, stress-relieved stretched and artificially aged). Chemical composition 6061 Aluminium alloy composition by mass: Properties The mechanical properties of 6061 depend greatly on the temper, or heat treatment, of the material. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-sport Aircraft
A light-sport aircraft (LSA), or light sport aircraft, is a fairly new category of small, lightweight aircraft that are simple to fly. LSAs tend to be heavier and more sophisticated than ultralight (aka "microlight") aircraft, but LSA restrictions on weight and performance separates the category from established GA aircraft. There is no standard worldwide description of an LSA . LSAs in different countries The civil aviation authorities in different countries have their own particular specifications and regulations which define the LSA category. For example, in Australia the Civil Aviation Safety Authority defines a light-sport aircraft as a heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft, other than a helicopter, with a maximum gross takeoff weight of not more than for lighter-than-air craft; for heavier-than-air craft not intended for operation on water; or for aircraft intended for operation on water. It must have a maximum stall speed of in landing configuration; a maximum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010s Portuguese Ultralight Aircraft
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft Engine
An aircraft engine, often referred to as an aero engine, is the power component of an aircraft propulsion system. Most aircraft engines are either piston engines or gas turbines, although a few have been rocket powered and in recent years many small UAVs have used electric motors. Manufacturing industry In commercial aviation the major Western manufacturers of turbofan engines are Pratt & Whitney (a subsidiary of Raytheon Technologies), General Electric, Rolls-Royce, and CFM International (a joint venture of Safran Aircraft Engines and General Electric). Russian manufacturers include the United Engine Corporation, Aviadvigatel and Klimov. Aeroengine Corporation of China was formed in 2016 with the merger of several smaller companies. The largest manufacturer of turboprop engines for general aviation is Pratt & Whitney. General Electric announced in 2015 entrance into the market. Development history * 1848: John Stringfellow made a steam engine for a 10-foot wingspan mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Stroke
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed: #Intake: Also known as induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins at top dead center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom dead center (B.D.C.). In this stroke the intake valve must be in the open position while the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing vacuum pressure into the cylinder through its downward motion. The piston is moving down as air is being sucked in by the downward motion against the piston. #Compression: This stroke begins at B.D.C, or just at the end of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. In this stroke the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke (below). Both the intake and exhaust valves are clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four-stroke
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either direction. The four separate strokes are termed: #Intake: Also known as induction or suction. This stroke of the piston begins at top dead center (T.D.C.) and ends at bottom dead center (B.D.C.). In this stroke the intake valve must be in the open position while the piston pulls an air-fuel mixture into the cylinder by producing vacuum pressure into the cylinder through its downward motion. The piston is moving down as air is being sucked in by the downward motion against the piston. #Compression: This stroke begins at B.D.C, or just at the end of the suction stroke, and ends at T.D.C. In this stroke the piston compresses the air-fuel mixture in preparation for ignition during the power stroke (below). Both the intake and exhaust valves are close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
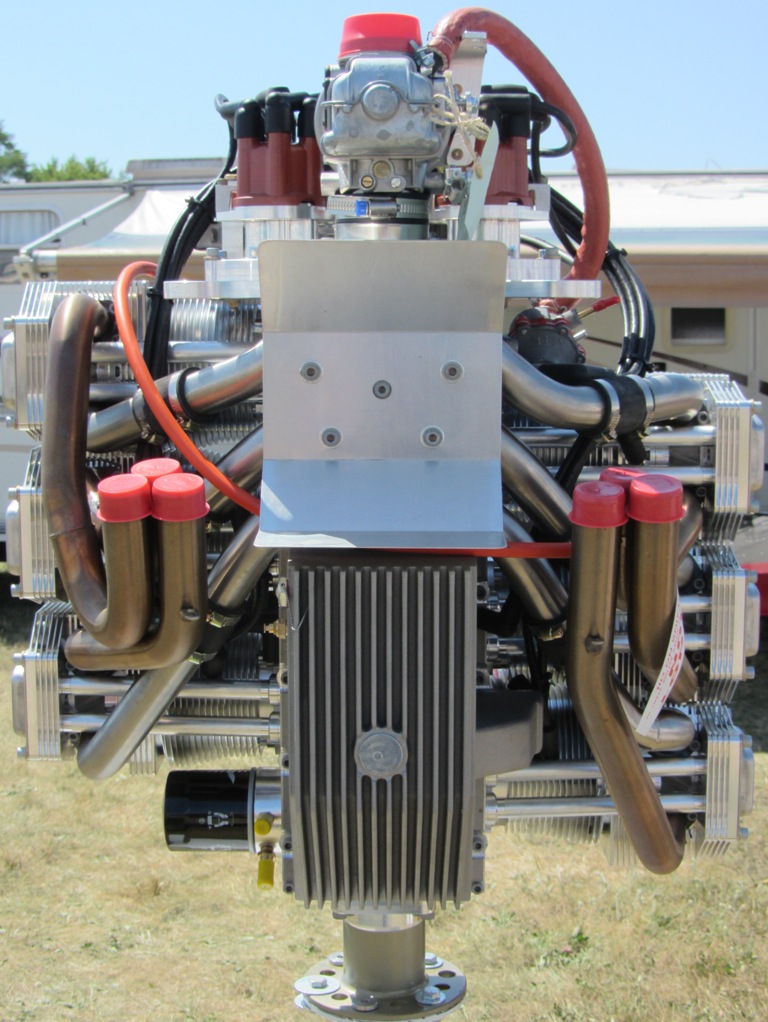
Jabiru 3300
The Jabiru 3300 is a lightweight four-stroke, horizontally opposed "flat-six" air-cooled aircraft engine produced by Jabiru Aircraft. The engines are direct drive and fitted with alternators, silencers, vacuum pump drives and dual ignition systems as standard. The engine is used to power homebuilt and ultralight aircraft. History Jabiru Aircraft began as a builder of small two-seater aircraft in Bundaberg, Australia. It turned to producing its own engines when supplies of the Italian-sourced engines previously used dried up. Jabiru engines are designed to be manufactured in small batch quantities, so the firm uses CNC machines to mill major engine parts such as cylinder blocks and heads, rather than using cast items. The 3300 is a modular development of Jabiru's flat-four 2200 engine. In November 2014, the Australian Civil Aviation Safety Authority proposed restricting all Jabiru-powered aircraft to day-visual flight rules only, without passengers or solo students and within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jabiru 2200
The Jabiru 2200 is a lightweight naturally aspirated, pushrod four-stroke, flat four, air-cooled aircraft engine produced by Jabiru Aircraft. Design and development The conventional direct-drive engine is fitted with an alternator, silencers, vacuum pump drives and dual ignition systems as standard. The engine generates up to 80 bhp at 3,300 rpm. In Europe the engine competes with the Rotax 912, another flat four four-stroke engine, but one that has water-cooled cylinder heads and a geared reduction drive to the propeller. Jabiru Aircraft began as a builder of small two-seater aircraft in Bundaberg, Australia. It turned to producing its own engines when supplies of the Italian-sourced engines previously used dried up. Jabiru engines are designed to be manufactured in small batch quantities, so the firm uses CNC machines to mill major engine parts such as cylinder blocks and heads, rather than using cast items. A larger variant of this engine is the flat-six Jabiru 3300 w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotax 912ULS
The Rotax 912 is a horizontally-opposed four-cylinder, naturally aspirated, four-stroke aircraft engine with a reduction gearbox. It features liquid-cooled cylinder heads and air-cooled cylinders. Originally equipped with carburetors, later versions are fuel injected. Dominating the market for small aircraft and kitplanes, Rotax produced its 50,000th 912-series engine in 2014. Originally available only for light sport aircraft, ultralight aircraft, autogyros and drones, the 912-series engine was approved for certified aircraft in 1995. Design and development The Rotax 912 was first sold in 1989 in non- certificated form for use in ultralights and motorgliders. The original 912 UL engine has a capacity of and a compression ratio of 9.1:1. The engine differs from previous generation aircraft engines (such as the Lycoming O-235) in that it has air-cooled cylinders with liquid-cooled heads and uses a 2.43:1 PSRU reduction gearbox to reduce the engine's relatively high 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flap (aircraft)
A flap is a high-lift device used to reduce the stalling speed of an aircraft wing at a given weight. Flaps are usually mounted on the wing trailing edges of a fixed-wing aircraft. Flaps are used to reduce the take-off distance and the landing distance. Flaps also cause an increase in drag so they are retracted when not needed. The flaps installed on most aircraft are partial-span flaps; spanwise from near the wing root to the inboard end of the ailerons. When partial-span flaps are extended they alter the spanwise lift distribution on the wing by causing the inboard half of the wing to supply an increased proportion of the lift, and the outboard half to supply a reduced proportion of the lift. Reducing the proportion of the lift supplied by the outboard half of the wing is accompanied by a reduction in the angle of attack on the outboard half. This is beneficial because it increases the margin above the stall of the outboard half, maintaining aileron effectiveness and reduci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tractor Configuration
In aviation, the term tractor configuration refers to an aircraft constructed in the standard configuration with its engine mounted with the propeller in front of it so that the aircraft is "pulled" through the air. Oppositely, the pusher configuration places the airscrew behind and propels the aircraft forward. Through common usage, the word "propeller" has come to mean any airscrew, whether it actually propels or pulls the plane. In the early years of powered aviation both tractor and pusher designs were common. However, by the midpoint of the First World War, interest in pushers declined and the tractor configuration dominated. Today, propeller-driven aircraft are assumed to be tractors unless it is stated otherwise. Origins The first airplane to have a "tractor" configuration was the Goupy No.2 (first flight on 11 March 1909) designed by Mario Calderara and financed by Ambroise Goupy at the French firm Blériot Aéronautique. When it was constructed, it was the fast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |