|
BPIFB1
BPI fold containing family B, member 1 (BPIFB1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BPIFB1'' gene. BPIFB1 is a secreted protein, expressed at very high levels in mucosa of the airways (respiratory and olfactory epithelium) and salivary glands, and at moderate levels in the digestive tract (tongue, stomach, intestinal epithelium) and pancreas. Superfamily BPIFB1 is a member of a BPI fold protein superfamily defined by the presence of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein fold (BPI fold) which is formed by two similar domains in a "boomerang" shape. This superfamily is also known as the BPI/LBP/PLUNC family or the BPI/ LPB/CETP family. The BPI fold creates apolar binding pockets that can interact with hydrophobic and amphipathic molecules, such as the acyl carbon chains of lipopolysaccharide found on Gram-negative bacteria, but members of this family may have many other functions. Genes for the BPI/LBP/PLUNC superfamily are found in all vertebrate sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BPIFB5P
BPI fold containing family B, member 5 is a non-human protein encoded by the ''Bpifb5'' gene, also known as ''Lplunc5.'' The BPIFB5 protein and ''Bpifb5'' gene have been characterized in mammals such as rodents (mouse, rat) and even-toed ungulates (pig, cow) but are apparently lacking in primates and other vertebrates such as birds, reptiles, and amphibians. The protein in rodents is expressed at moderately high levels in Mucous membrane, mucosa of the airways (respiratory and olfactory epithelium) and at moderate levels in salivary glands, esophagus, and gonads (ovary, testis); in even-toed ungulates expression is high in testis, moderate in brain and striated muscle, and low in kidney. In humans no protein is expressed and it is present only as a pseudogene ''BPIFB5P''. The pseudogene was named based on its functional ortholog found in the other species. Superfamily BPIFB5 is a member of the BPI fold protein superfamily defined by the presence of the bactericidal/permeabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid-binding Serum Glycoprotein
In molecular biology, the lipid-binding serum glycoproteins family, also known as the BPI/LBP/Plunc family or LBP/BPI/CETP family represents a family which includes mammalian lipid-binding serum glycoproteins and/or proteins containing a structural motif known as the ''BPI fold''. Members of this family include: *Bactericidal permeability-increasing protein (BPI) * Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) *Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) * Phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP) * Palate, lung and nasal epithelium carcinoma-associated protein (PLUNC) Structure These proteins consist of N- and C-terminal domains, which share a similar two-layer alpha/beta structure, but show little sequence identity to each other. These domains were first described as being arranged in a "boomerang" shape that creates the BPI fold. The fold contains apolar binding pockets that can interact with hydrophobic and amphipathic molecules, such as the acyl carbon chains of lipopolysacch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
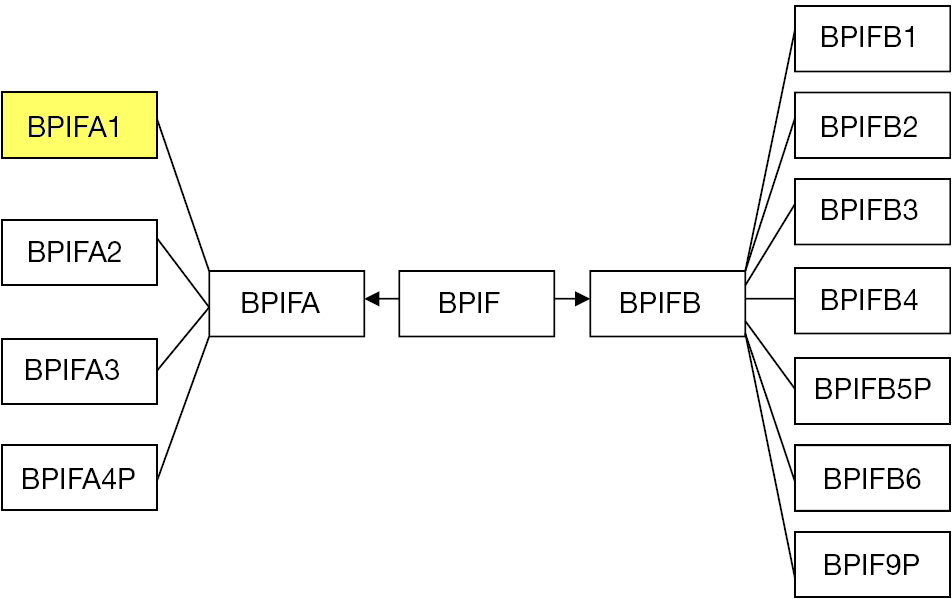
BPIFA1
BPI fold containing family A, member 1 (BPIFA1), also known as Palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone (PLUNC), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BPIFA1'' gene. It was also formerly known as "Secretory protein in upper respiratory tracts" (SPURT). The ''BPIFA1'' gene sequence predicts 4 transcripts ( splice variants); 3 mRNA variants have been well characterized. The resulting BPIFA1 is a secreted protein, expressed at very high levels in mucosa of the airways (olfactory and respiratory and epithelium) and salivary glands; at high levels in oropharyneal epithelium, including tongue and tonsils; and at moderate levels many other tissue types and glands including pituitary, testis, lung, bladder, blood, prostate, pancreas, levels in the digestive tract (tongue, stomach, intestinal epithelium) and pancreas. The protein can be detected on the apical side of epithelial cells and in airway surface liquid, nasal mucus, and sputum. Superfamily BPIFA1 is a member of a B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BPIFB9P
Vomeromodulin is a non-human protein also known as BPI fold containing family B, member 9 (BPIFB9) in the rat encoded by the ''Bpifb9/RYF3'' gene, and as BPI fold containing family B, member 9A (BPIFB9A) encoded by the ''Bpifb9a'' gene in the mouse. This protein has been characterized in mammals such as rodents, carnivores, even-toed ungulates, insectivores, bats, lagomorphs, and shrews but is apparently absent in primates and other vertebrates such as birds, reptiles, and amphibians. Its function is associated with detection of chemical odorant pheromone molecules. In humans no protein is expressed and it is present only as a pseudogene ''BPIFB9P''. The pseudogene was named based on its functional ortholog found in the other species. Superfamily Vomeromodulin/BPIFB9/BPIFB9A is a member of the BPI fold protein superfamily defined by the presence of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein fold (BPI fold) which is formed by two similar domains in a "boomerang" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 20
Chromosome 20 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Chromosome 20 spans around 66 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 2 and 2.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 20 was fully sequenced in 2001 and was reported to contain over 59 million base pairs. Since then, due to sequencing improvements and fixes, the length of chromosome 20 has been updated to just over 66 million base pairs. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 20. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BPIFB2
BPI fold-containing family B, member 2, (BPIFB2) also known as bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein-like 1, (BPI-like 1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BPIFB2'' gene. Superfamily BPIFB2 is a member of a BPI fold protein superfamily defined by the presence of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein fold (BPI fold) which is formed by two similar domains in a "boomerang" shape. This superfamily is also known as the BPI/LBP/PLUNC family or the BPI/ LPB/ CETP family. The BPI fold creates apolar binding pockets that can interact with hydrophobic and amphipathic molecules, such as the acyl carbon chains of lipopolysaccharide found on Gram-negative bacteria, but members of this family may have many other functions. Genes for the BPI/LBP/PLUNC superfamily are found in all vertebrate species, including distant homologs in non-vertebrate species such as insects, mollusks, and roundworms. Within that broad grouping is the BPIF gene family whose m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BPIFB3
BPI fold containing family B, member 3 (BPIFB3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BPIFB3'' gene. Two variants have been detected in humans. Superfamily BPIFB3 is a member of a BPI fold protein superfamily defined by the presence of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein fold (BPI fold) which is formed by two similar domains in a "boomerang" shape. This superfamily is also known as the BPI/LBP/PLUNC family or the BPI/ LPB/ CETP family. The BPI fold creates apolar binding pockets that can interact with hydrophobic and amphipathic molecules, such as the acyl carbon chains of lipopolysaccharide found on Gram-negative bacteria, but members of this family may have many other functions. Genes for the BPI/LBP/PLUNC superfamily are found in all vertebrate species, including distant homologs in non-vertebrate species such as insects, mollusks, and roundworms. Within that broad grouping is the BPIF gene family whose members encode the BPI fold structur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BPIFB6
BPI fold containing family B, member 6 (BPIFB6), also known as bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein-like 3 (BPIL3), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BPIFB6'' gene, also known as ''BPIL3'' and ''LPLUNC6''. It is expressed at high levels in hypertrophic tonsils, at relatively moderate levels in oronasal epithelium including nasal mucosa, tongue, and salivary gland, as well as esophageal mucosa at lesser levels. Orthologs are present in many vertebrate species including mammals, birds, reptiles, and amphibians. Superfamily BPIFB6 is a member of a BPI fold protein superfamily defined by the presence of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein fold (BPI fold) which is formed by two similar domains in a "boomerang" shape. This superfamily is also known as the BPI/LBP/PLUNC family or the BPI/ LPB/ CETP family. The BPI fold creates apolar binding pockets that can interact with hydrophobic and amphipathic molecules, such as the acyl carbon chains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein
Cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), also called plasma lipid transfer protein, is a plasma protein that facilitates the transport of cholesteryl esters and triglycerides between the lipoproteins. It collects triglycerides from very-low-density (VLDL) or Chylomicrons and exchanges them for cholesteryl esters from high-density lipoproteins (HDL), and vice versa. Most of the time, however, CETP does a heteroexchange, trading a triglyceride for a cholesteryl ester or a cholesteryl ester for a triglyceride. Genetics The ''CETP'' gene is located on the sixteenth chromosome (16q21). Protein Fold The crystal structure of CETP is that of dimer of two TUbular LIPid (TULIP) binding domains. Each domain consists of a core of 6 elements: 4 beta-sheets forming an extended superhelix; 2 flanking elements that tend to include some alpha helix. The sheets wrap around the helices to produce a cylinder 6 x 2.5 x 2.5 nm. CETP contains two of these domains that interact head-to-head ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
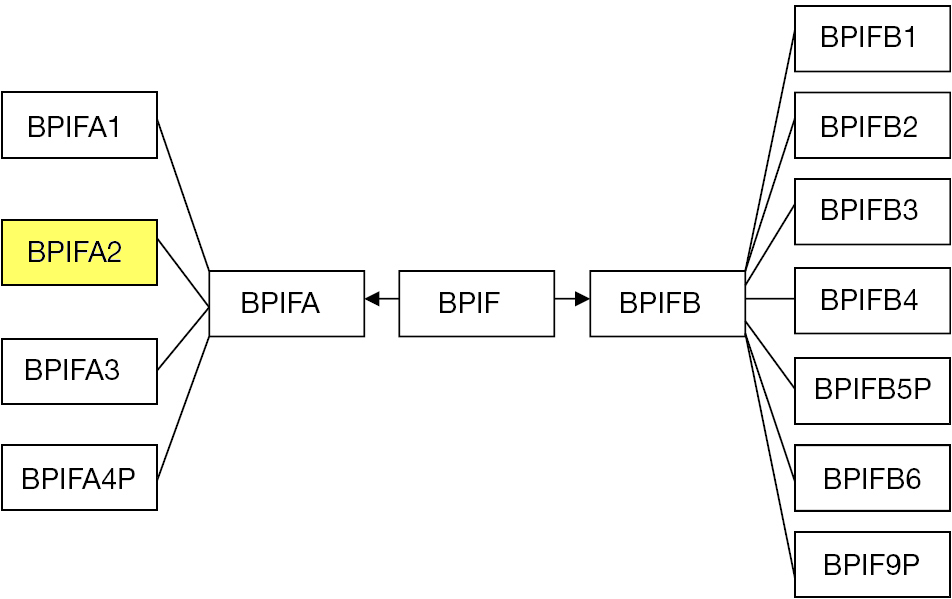
BPIFA2
BPI fold containing family A, member 2 (BPIFA2), also known as Parotid Secretory Protein (PSP), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BPIFA2'' gene. The ''BPIFA2'' gene sequence predicts multiple transcripts ( splice variants); 2 mRNA variants have been well characterized. The resulting BPIFA2 is a secreted protein, expressed at very high levels in the parotid (salivary) gland; at high levels in oropharyneal mucosa, including tongue; and at moderate levels many other tissue types and glands including mammary gland, testis, lung, bladder, blood, prostate, adrenal gland, kidney, and pancreas. Superfamily BPIFA2 is a member of a BPI fold protein superfamily defined by the presence of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein fold (BPI fold) which is formed by two similar domains in a "boomerang" shape. This superfamily is also known as the BPI/LBP/PLUNC family or the BPI/ LPB/CETP family. The BPI fold creates apolar binding pockets that can interact with hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BPIFA4P
BPI fold containing family A, member 4 (BPIFA4) is a non-human protein encoded by the ''Bpifa4'' gene in monkey and cow. It is also known as Latherin in horse, encoded by the ''Lath/Bpifa4'' gene but somewhat divergent from the other species. Latherin/BPIFA4 is a secreted protein found in saliva and sweat. In humans, no protein is normally expressed and BPIFB5P is present only as a pseudogene ''BPIFB5P''. However, it has appeared as a secreted product in breast cancer cell lines, previously named BASE (''b''reast cancer ''a''nd ''s''alivary gland ''e''xpression) protein. Superfamily BPIFA3 is a member of a BPI fold protein superfamily defined by the presence of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein fold (BPI fold) which is formed by two similar domains in a "boomerang" shape. This superfamily is also known as the BPI/LBP/PLUNC family or the BPI/ LPB/ CETP family. The BPI fold creates apolar binding pockets that can interact with hydrophobic and amphipathic mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |