BPIFA1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
BPI fold containing family A, member 1 (BPIFA1), also known as Palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone (PLUNC), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BPIFA1'' gene. It was also formerly known as "Secretory protein in upper respiratory tracts" (SPURT). The ''BPIFA1'' gene sequence predicts 4 transcripts ( splice variants); 3 mRNA variants have been well characterized. The resulting BPIFA1 is a secreted protein, expressed at very high levels in
 Genes for the BPI/LBP/PLUNC superfamily are found in all vertebrate species, including distant homologs in non-vertebrate species such as insects, mollusks, and roundworms. Within that broad grouping is the BPIF gene family whose members encode the BPI fold
Genes for the BPI/LBP/PLUNC superfamily are found in all vertebrate species, including distant homologs in non-vertebrate species such as insects, mollusks, and roundworms. Within that broad grouping is the BPIF gene family whose members encode the BPI fold
mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is ...
of the airways (olfactory and respiratory and epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
) and salivary glands; at high levels in oropharyneal epithelium, including tongue and tonsils; and at moderate levels many other tissue types and glands including pituitary, testis, lung, bladder, blood, prostate, pancreas, levels in the digestive tract (tongue, stomach, intestinal epithelium) and pancreas. The protein can be detected on the apical side of epithelial cells and in airway surface liquid, nasal mucus, and sputum.
Superfamily
BPIFA1 is a member of a BPI foldprotein superfamily
A protein superfamily is the largest grouping (clade) of proteins for which common ancestry can be inferred (see homology (biology), homology). Usually this common ancestry is inferred from structural alignment and mechanistic similarity, even if n ...
defined by the presence of the bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein fold (BPI fold) which is formed by two similar domains in a "boomerang" shape. This superfamily is also known as the BPI/LBP/PLUNC family or the BPI/ LPB/ CETP family. The BPI fold creates apolar binding pockets that can interact with hydrophobic and amphipathic molecules, such as the acyl carbon chains of lipopolysaccharide found on Gram-negative bacteria, but members of this family may have many other functions.  Genes for the BPI/LBP/PLUNC superfamily are found in all vertebrate species, including distant homologs in non-vertebrate species such as insects, mollusks, and roundworms. Within that broad grouping is the BPIF gene family whose members encode the BPI fold
Genes for the BPI/LBP/PLUNC superfamily are found in all vertebrate species, including distant homologs in non-vertebrate species such as insects, mollusks, and roundworms. Within that broad grouping is the BPIF gene family whose members encode the BPI fold structural motif
In a polymer, chain-like biological molecule, such as a protein or nucleic acid, a structural motif is a common Biomolecular structure#Tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure that appears in a variety of different, evolutionarily unrel ...
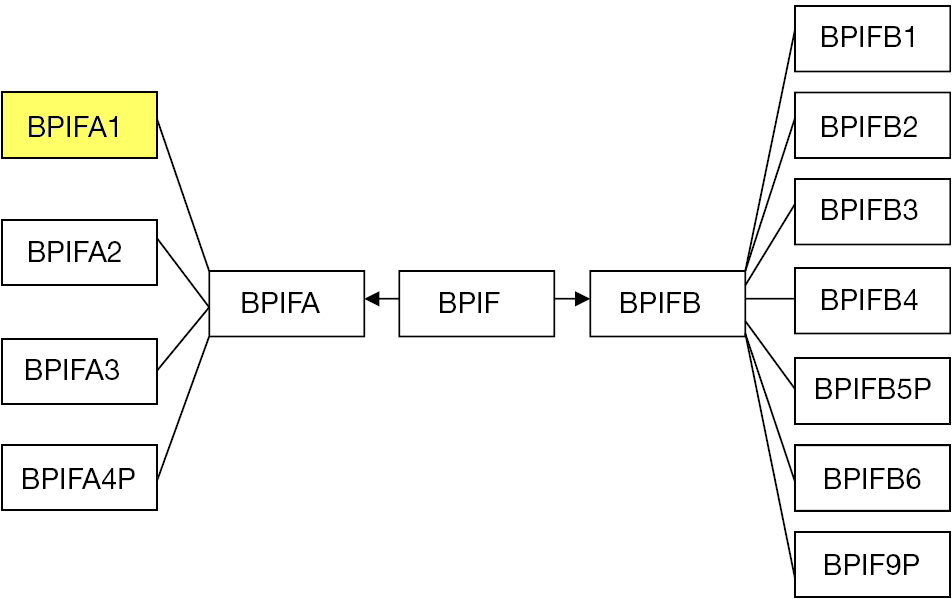
and are found clustered on a single chromosome, e.g., Chromosome 20 in humans, Chromosome 2 in mouse, Chromosome 3 in rat, Chromosome 17 in pig, Chromosome 13 in cow. The BPIF gene family is split into two groupings, BPIFA and BPIFB. In humans, BIPFA consists of 3 protein encoding genes ''BPIFA1'', '' BPIFA2'', '' BPIFA3'', and 1 pseudogene '' BPIFA4P''; while BPIFB consists of 5 protein encoding genes '' BPIFB1'', '' BPIFB2'', '' BPIFB3'', '' BPIFB4'', '' BPIFB6'' and 2 pseudogenes '' BPIFB5P'', '' BPIFB9P''. What appears as pseudogenes in humans may appear as fully functional genes in other species.
In humans, the ''BPIFA1'' gene was first identified as an ortholog of the mouse ''Plunc'' gene which had earlier been identified from a differential display Differential display (also referred to as DDRT-PCR or DD-PCR) is a laboratory technique that allows a researcher to compare and identify changes in gene expression at the mRNA level between two or more eukaryotic cell samples. It was the most commo ...
screen of the embryonic mouse palate. Subsequently, using microarray analysis techniques of human epithelial tissues, the ''SPURT'' gene and, separately, the ''SPLUNC1'' gene were identified. These were all recognized to be, in fact, the same gene within the BPI/LBP/PLUNC family.
Function
BPIFA1 has multiple functions but perhaps its most prominent ones are related to BPIFA1's localization in nasal, olfactory, oral, and respiratory epithelium and the mucous/fluids that coat them. BPIFA1/SPLUNC1 binds with high affinity and specificity to dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine, one of the major and most important surfactant phospholipids in the airway and lungs. By lowering the surface tension in mucosal fluids, BPIFA1/SPLUNC1 inhibits bacteria like '' Klebsiella'' from proliferating as a biofilm on epithelium. The protein physically interacts with pathogens, causing "bacterial cell coating" that inhibits theepithelial sodium channel
The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC), (also known as amiloride-sensitive sodium channel) is a membrane-bound ion channel that is selectively permeable to sodium ions (). It is assembled as a heterotrimer composed of three homologous subunits α ...
of bacteria, makes bacteria like '' Pseudomonas'' more permeable, and attracts macrophages and neutrophils
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in ...
for a bactericidal effect. As such, BPIFA1 plays a role in innate immune defense in the airways.
BPIFA1/PLUNC's ability to regulate ENaC is pH-sensitive and fails in acidic cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. O ...
airways. Thus, defective ''BPIFA1/PLUNC1'' gene function is thought to contribute to the development of lung pathology in cystic fibrosis patients.
It may also serve as a potential molecular marker for detection of micrometastasis in non-small-cell lung cancer.
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * {{MeshName, PLUNC+protein,+human Human proteins Genes Genes on human chromosome 20