|
BAP Victoria
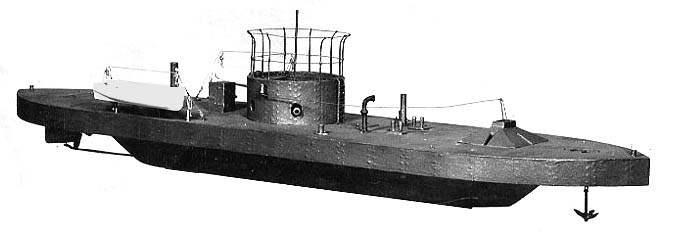
BAP Victoria was an ironclad monitor built for the Peruvian Navy in the mid-1860s. The ship participated in the Battle of Callao in 1866 during the Chincha Islands War of 1864–66 and was not damaged. Her ultimate fate is unknown. Description ''Victoria'' was long, had a beam of and a draft of . The ship displaced . She was powered by a steam engine taken from a locomotive and was thus very slow. The ship was armed with a single smoothbore 64-pounder gun. ''Victoria'' was protected by of armorGreene & Massignani, p. 265 and had a freeboard In sailing and boating, a vessel's freeboard is the distance from the waterline to the upper deck level, measured at the lowest point of sheer where water can enter the boat or ship. In commercial vessels, the latter criterion measured relativ ... of . Construction and career Designed by the brothers José Tomás and Manuel José Ramos, construction of ''Victoria'' began on 30 July 1864, when she was "commissioned" in the Peruvia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callao
Callao () is a Peruvian seaside city and Regions of Peru, region on the Pacific Ocean in the Lima metropolitan area. Callao is Peru's chief seaport and home to its main airport, Jorge Chávez International Airport. Callao municipality consists of the whole Callao Region, which is also coterminous with the Province of Callao. Founded in 1537 by the Spaniards, the city has a long naval history as one of the main ports in Latin America and the Pacific, as it was one of vital Spanish towns during the Spanish America, colonial era. Central Callao is about west of the Historic Centre of Lima. History El Callao was founded by Spanish colonists in 1537, just two years after Lima (1535). It soon became the main port for Spanish commerce in the Pacific Ocean, Pacific. The origin of its name is unknown; both Amerindian (particularly Yunga language (Peru), Yunga, or Coastal Peruvian) and Spanish sources are credited, but it is certain that it was known by that name since 1550. Other sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monitor (warship)
A monitor is a relatively small warship which is neither fast nor strongly armored but carries disproportionately large guns. They were used by some navies from the 1860s, during the First World War and with limited use in the Second World War. The original monitor was designed in 1861 by John Ericsson, who named it . They were designed for shallow waters and served as coastal ships. The term also encompassed more flexible breastwork monitors, and was sometimes used as a generic term for any turreted ship. In the early 20th century, the term was revived for shallow-draught armoured shore bombardment vessels, particularly those of the Royal Navy: the s carried guns firing heavier shells than any other warship ever has, seeing action (albeit briefly) against German targets during World War I. The ''Lord Clive'' vessels were scrapped in the 1920s. The term "monitor" also encompasses the strongest of riverine warcraft, known as river monitors. During the Vietnam War these much sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smoothbore
A smoothbore weapon is one that has a barrel without rifling. Smoothbores range from handheld firearms to powerful tank guns and large artillery mortars. History Early firearms had smoothly bored barrels that fired projectiles without significant spin. To minimize inaccuracy-inducing tumbling during flight, their projectiles required an aerodynamically uniform shape, such as a sphere. However, surface imperfections on the projectile and/or the barrel will cause even a sphere to rotate randomly during flight, and the Magnus effect will curve it off the intended trajectory when spinning on any axis not parallel to the direction of travel. Rifling the bore surface with spiral grooves or polygonal valleys imparts a stabilizing gyroscopic spin to a projectile that prevents tumbling in flight. Not only does this more than counter Magnus-induced drift, but it allows a longer, more streamlined round with greater sectional density to be fired from the same caliber barrel, improvin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ironclad
An ironclad is a steam engine, steam-propelled warship protected by Wrought iron, iron or steel iron armor, armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships to explosive or incendiary shell (projectile), shells. The first ironclad battleship, , was launched by the French Navy in November 1859 - narrowly pre-empting the British Royal Navy. They were first used in warfare in 1862 during the American Civil War, when ironclads operated against wooden ships and, in a historic confrontation, against each other at the Battle of Hampton Roads in Virginia. Their performance demonstrated that the ironclad had replaced the unarmored ship of the line as the most powerful warship afloat. City-class ironclad, Ironclad gunboats became very successful in the American Civil War. Ironclads were designed for several uses, including as high seas battleships, long-range cruisers, and Littoral (military), coast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monitor (warship)
A monitor is a relatively small warship which is neither fast nor strongly armored but carries disproportionately large guns. They were used by some navies from the 1860s, during the First World War and with limited use in the Second World War. The original monitor was designed in 1861 by John Ericsson, who named it . They were designed for shallow waters and served as coastal ships. The term also encompassed more flexible breastwork monitors, and was sometimes used as a generic term for any turreted ship. In the early 20th century, the term was revived for shallow-draught armoured shore bombardment vessels, particularly those of the Royal Navy: the s carried guns firing heavier shells than any other warship ever has, seeing action (albeit briefly) against German targets during World War I. The ''Lord Clive'' vessels were scrapped in the 1920s. The term "monitor" also encompasses the strongest of riverine warcraft, known as river monitors. During the Vietnam War these much sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peruvian Navy
The Peruvian Navy ( es, link=no, Marina de Guerra del Perú, abbreviated MGP) is the branch of the Peruvian Armed Forces tasked with surveillance, patrol and defense on lakes, rivers and the Pacific Ocean up to from the Peruvian littoral. Additional missions include assistance in safeguarding internal security, conducting disaster relief operations and participating in international peacekeeping operations. The ''Marina de Guerra del Perú'' celebrates the anniversary of its creation in 1821 on October 8 and also commemorates the decisive Battle of Angamos, the final part of the naval campaign of the War of the Pacific between Peru and Chile at the end of 1879. History 19th century The ''Marina de Guerra del Perú'' was established on 8 October 1821 by the government of general José de San Martín. Its first actions were undertaken during the War of Independence (1821–1824) using captured Spanish warships. The Peruvian Naval Infantry was also formed during the war with Spai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
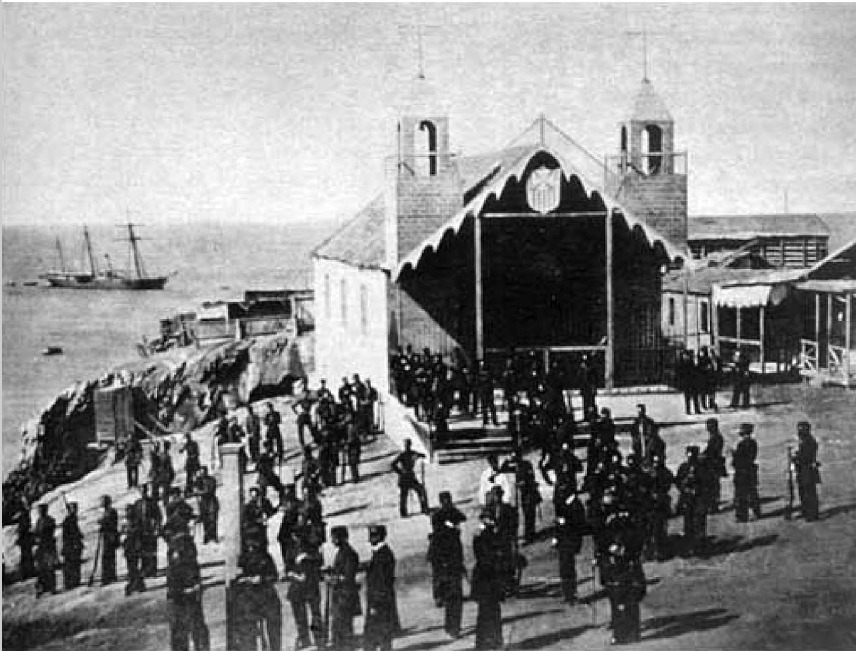
Battle Of Callao
The Battle of Callao (, as it is known in South America) occurred on May 2, 1866, between a Spanish fleet under the command of Admiral Casto Méndez Núñez and the fortified battery emplacements of the Peruvian port city of Callao during the Chincha Islands War. The Spanish fleet bombarded the port of Callao (or El Callao), and eventually withdrew without any notable damage to the city structures, according to the Peruvian and American sources; or after having silenced almost all the guns of the coastal defenses, according to the Spanish accounts and French observers. This proved to be the final battle of the war between Spanish and Peruvian forces. Background President Juan Antonio Pezet assumed the presidency of Peru in April 1863, at a time when Spain was making efforts to recover some prestige by recovering its lost colonies in America. Spain began its campaign by seizing the Chincha Islands, which were rich in guano, and demanding indemnity as recompense for the murder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chincha Islands War
The Chincha Islands War, also known as Spanish–South American War ( es, Guerra hispano-sudamericana), was a series of coastal and naval battles between Spain and its former colonies of Peru, Chile, Ecuador, and Bolivia from 1865 to 1879. The conflict began with Spain's seizure of the guano-rich Chincha Islands in one of a series of attempts by Spain, under Isabella II, to reassert its influence over its former South American colonies. The war saw the use of ironclads, including the Spanish ship '' Numancia'', the first ironclad to circumnavigate the world. Background Military expenditures were greatly increased during Isabella's reign and Spain rose to a position as the world's fourth naval power. In the 1850s and 1860s Spain engaged in colonial adventures all over the world, including Morocco, Philippines, Mexico, and the Dominican Republic, the last of which it briefly reoccupied. At the end of 1862, Spain sent a scientific expedition to South American waters with the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam (nautical)
The beam of a ship is its width at its widest point. The maximum beam (BMAX) is the distance between planes passing through the outer extremities of the ship, beam of the hull (BH) only includes permanently fixed parts of the hull, and beam at waterline (BWL) is the maximum width where the hull intersects the surface of the water. Generally speaking, the wider the beam of a ship (or boat), the more initial stability it has, at the expense of secondary stability in the event of a capsize, where more energy is required to right the vessel from its inverted position. A ship that heels on her ''beam ends'' has her deck beams nearly vertical. Typical values Typical length-to-beam ratios ( aspect ratios) for small sailboats are from 2:1 (dinghies to trailerable sailboats around ) to 5:1 (racing sailboats over ). Large ships have widely varying beam ratios, some as large as 20:1. Rowing shells designed for flatwater racing may have length to beam ratios as high as 30:1, while a cor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship's hull is the vertical distance between the waterline and the bottom of the hull (keel). The draught of the vessel is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if deployed. Draft determines the minimum depth of water a ship or boat can safely navigate. The related term air draft is the maximum height of any part of the vessel above the water. The more heavily a vessel is loaded, the deeper it sinks into the water, and the greater its draft. After construction, the shipyard creates a table showing how much water the vessel displaces based on its draft and the density of the water (salt or fresh). The draft can also be used to determine the weight of cargo on board by calculating the total displacement of water, accounting for the content of the ship's bunkers, and using Archimedes' principle. The closely related term "trim" is defined as the difference between the forward and aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacement (ship)
The displacement or displacement tonnage of a ship is its weight. As the term indicates, it is measured indirectly, using Archimedes' principle, by first calculating the volume of water displaced by the ship, then converting that value into weight. Traditionally, various measurement rules have been in use, giving various measures in long tons. Today, tonnes are more commonly used. Ship displacement varies by a vessel's degree of load, from its empty weight as designed (known as "lightweight tonnage") to its maximum load. Numerous specific terms are used to describe varying levels of load and trim, detailed below. Ship displacement should not be confused with measurements of volume or capacity typically used for commercial vessels and measured by tonnage: net tonnage and gross tonnage. Calculation The process of determining a vessel's displacement begins with measuring its draft.George, 2005. p.5. This is accomplished by means of its "draft marks" (or "load lines"). A mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine. Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term ''steam engine'' can refer to either complete steam plants (including boilers etc.), such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine. Although steam-driven devices were known as early as the aeolipile in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
