|
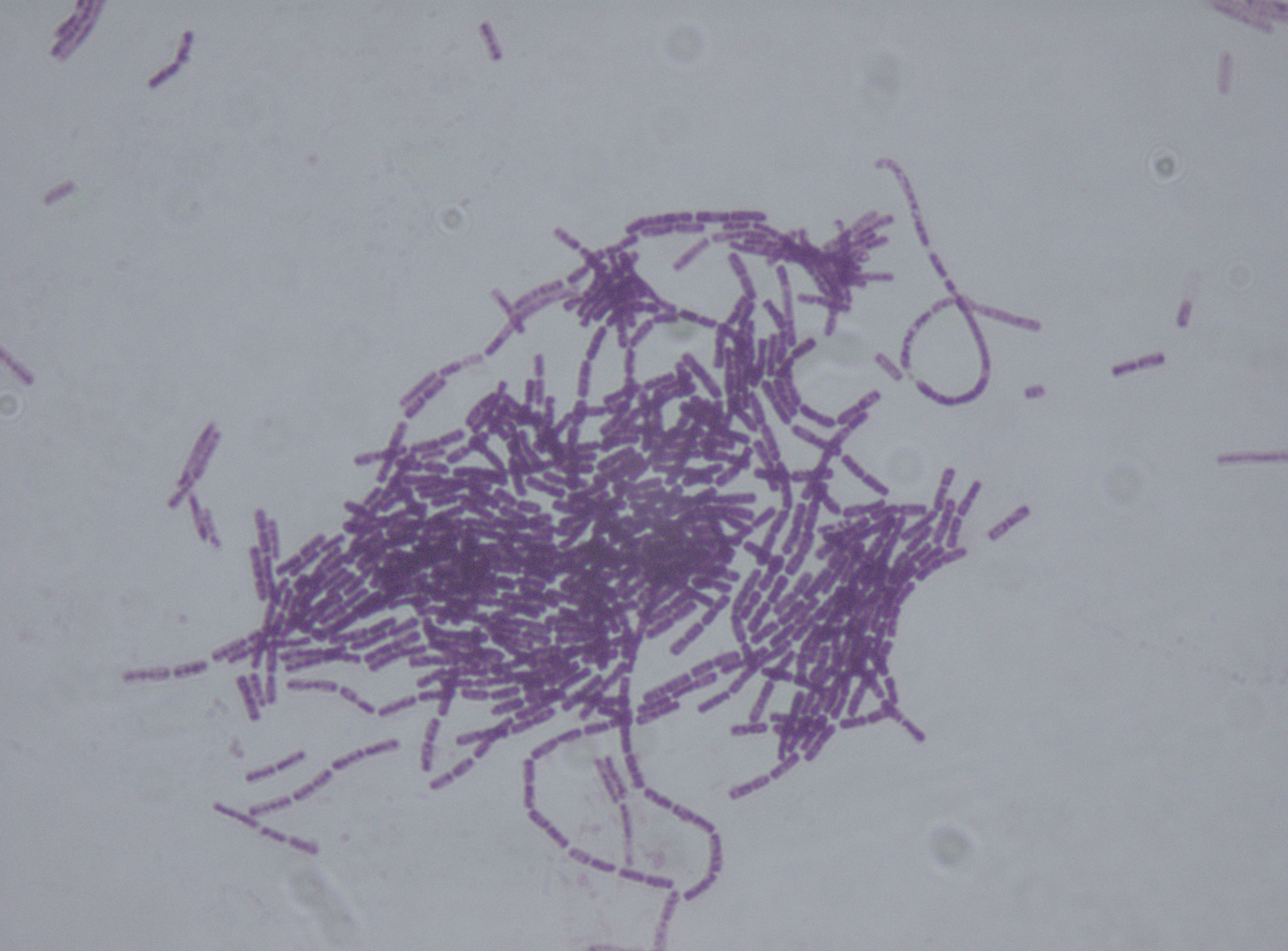
B. Thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflies, as well on leaf surfaces, aquatic environments, animal feces, insect-rich environments, and flour mills and grain-storage facilities. It has also been observed to parasitize other moths such as ''Cadra calidella''—in laboratory experiments working with ''C. calidella'', many of the moths were diseased due to this parasite. During sporulation, many Bt strains produce crystal proteins (proteinaceous inclusions), called delta endotoxins, that have insecticidal action. This has led to their use as insecticides, and more recently to genetically modified crops using Bt genes, such as Bt corn. Many crystal-producing Bt strains, though, do not have insecticidal properties. The subspecies ''israelensis'' is commonly used for control of mosqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Thuringiensis Israelensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' serotype ''israelensis'' (Bti) is a group of bacteria used as biological control agents for larvae stages of certain dipterans. Bti produces toxins which are effective in killing various species of mosquitoes, fungus gnats, and blackflies, while having almost no effect on other organisms. The major advantage of ''B. thuringiensis'' products is that they are thought to affect few non-target species. However, even though Bti may have minimal direct effects on non-target organisms, it may potentially be associated with knock-on effects on food webs and other ecosystem properties, including biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Bti strains possess the pBtoxis plasmid which encodes numerous Cry (a δ-endotoxin) and Cyt toxins, including Cry4, Cry10, Cry11, Cyt1, and Cyt2. The crystal aggregation which these toxins form contains at least four major toxic components, but the extent to which each Cry and Cyt protein is represented is not known and likel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus Gnat
Fungus gnats are small, dark, short-lived gnats, of the families Sciaridae, Diadocidiidae, Ditomyiidae, Keroplatidae, Bolitophilidae, and Mycetophilidae (order Diptera); they comprise six of the seven families placed in the superfamily Sciaroidea. Description The larvae of most species feed on fungi growing on soil, helping in the decomposition of organic matter. However some species are predatory, including those in the genus ''Arachnocampa'' of family Keroplatidae – the "glowworms" of Australia and New Zealand. The adults are long, and are occasionally pollinators of plants and carriers of mushroom spores. They also may carry diseases such as pythium (which causes "damping-off" to kill seedlings) on their feet. Most fungus gnats are weak fliers, and can often be seen walking rapidly over plants and soil, rather than flying. However when airborne, the gnats may be quite annoying to humans by flying into their faces, eyes, and noses, both indoors and outdoors. These flies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endospore
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form (''endo'' means 'within'), but it is not a true spore (i.e., not an offspring). It is a stripped-down, dormant form to which the bacterium can reduce itself. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients, and usually occurs in gram-positive bacteria. In endospore formation, the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. Endospores enable bacteria to lie dormant for extended periods, even centuries. There are many reports of spores remaining viable over 10,000 years, and revival of spores millions of years old has been claimed. There is one report of viable spores of ''Bacillus marismortui'' in salt crystals approximately 250 million years old. When the environment becomes more favorable, the endospore can reactivate itself into a vegetative state. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobe
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require molecular oxygen for growth. It may react negatively or even die if free oxygen is present. In contrast, an aerobic organism (aerobe) is an organism that requires an oxygenated environment. Anaerobes may be unicellular (e.g. protozoans, bacteria) or multicellular. Most fungi are obligate aerobes, requiring oxygen to survive. However, some species, such as the Chytridiomycota that reside in the rumen of cattle, are obligate anaerobes; for these species, anaerobic respiration is used because oxygen will disrupt their metabolism or kill them. Deep waters of the ocean are a common anoxic environment. First observation In his letter of 14 June 1680 to The Royal Society, Antonie van Leeuwenhoek described an experiment he carried out by filling two identical glass tubes about halfway with crushed pepper powder, to which some clean rain water was added. Van Leeuwenhoek sealed one of the glass tubes using a flame and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmid
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage such as antibiotic resistance. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthrax Disease
Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Bacillus anthracis''. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The skin form presents with a small blister with surrounding swelling that often turns into a painless ulcer with a black center. The inhalation form presents with fever, chest pain and shortness of breath. The intestinal form presents with diarrhea (which may contain blood), abdominal pains, nausea and vomiting. The injection form presents with fever and an abscess at the site of drug injection. According to the USA's Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the first clinical descriptions of cutaneous anthrax were given by Maret in 1752 and Fournier in 1769. Before that anthrax had been described only through historical accounts. The Prussian scientist Robert Koch (1843–1910) was the first to identify ''Bacillus anthracis'' as the bacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Anthracis
''Bacillus anthracis'' is a gram-positive and rod-shaped bacterium that causes anthrax, a deadly disease to livestock and, occasionally, to humans. It is the only permanent ( obligate) pathogen within the genus ''Bacillus''. Its infection is a type of zoonosis, as it is transmitted from animals to humans. It was discovered by a German physician Robert Koch in 1876, and became the first bacterium to be experimentally shown as a pathogen. The discovery was also the first scientific evidence for the germ theory of diseases. ''B. anthracis'' measures about 3 to 5 μm long and 1 to 1.2 μm wide. The reference genome consists of a 5,227,419 bp circular chromosome and two extrachromosomal DNA plasmids, pXO1 and pXO2, of 181,677 and 94,830 bp respectively, which are responsible for the pathogenicity. It forms a protective layer called endospore by which it can remain inactive for many years and suddenly becomes infective under suitable environmental conditions. Because of the resilie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Cereus
''Bacillus cereus'' is a Gram-positive rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in soil, food, and marine sponges. The specific name, ''cereus'', meaning "waxy" in Latin, refers to the appearance of colonies grown on blood agar. Some strains are harmful to humans and cause foodborne illness due to their spore-forming nature, while other strains can be beneficial as probiotics for animals, and even exhibit mutualism with certain plants. ''B. cereus'' bacteria may be anaerobes or facultative anaerobes, and like other members of the genus ''Bacillus'', can produce protective endospores. They have a wide range of virulence factors, including phospholipase C, cereulide, sphingomyelinase, metalloproteases, and cytotoxin K, many of which are regulated via quorum sensing. ''B. cereus'' strains exhibit flagellar motility. The ''Bacillus cereus'' group comprises seven closely related species: ''B. cereus'' ''sensu stricto'' (referred to herein as ''B. cereus''), '' B. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thuringia
Thuringia (; german: Thüringen ), officially the Free State of Thuringia ( ), is a state of central Germany, covering , the sixth smallest of the sixteen German states. It has a population of about 2.1 million. Erfurt is the capital and largest city. Other cities are Jena, Gera and Weimar. Thuringia is bordered by Bavaria, Hesse, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It has been known as "the green heart of Germany" () from the late 19th century due to its broad, dense forest. Most of Thuringia is in the Saale drainage basin, a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. Thuringia is home to the Rennsteig, Germany's best-known hiking trail. Its winter resort of Oberhof makes it a well-equipped winter sports destination – half of Germany's 136 Winter Olympic gold medals had been won by Thuringian athletes as of 2014. Thuringia was favoured by or was the birthplace of three key intellectuals and leaders in the arts: Johann Sebastian Bach, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, and Fried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephestia Kuehniella
The Mediterranean flour moth or mill moth (''Ephestia kuehniella'') is a moth of the family Pyralidae. It is a common pest of cereal grains, especially flour. This moth is found throughout the world, especially in countries with temperate climates. It prefers warm temperatures for more rapid development, but it can survive a wide range of temperatures. The Mediterranean flour moth is frequently found in warm places with stored grain products, such as flour mills and bakeries, where it can breed year round. Flour mills have a particular problem with the Mediterranean flour moth because the caterpillars spin silk that clogs machinery. The most effective pest control strategy for this moth is sanitation of facilities and sealing grain containers to prevent infestation, but some pesticides may also be used. Description Adult Mediterranean flour moths have pale gray bodies. Their forewings are gray with black zigzag markings while the hindwings are an off-white color. The wingspan is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schlaffsucht
Flacherie (literally: "flaccidness") is a disease of silkworms, caused by silkworms eating infected or contaminated mulberry leaves. Flacherie infected silkworms look weak and can die from this disease. Silkworm larvae that are about to die from Flacherie are a dark brown. There are two kinds of flacherie: essentially, infectious (viral) flacherie and noninfectious (''touffée'') flacherie. Both are technically a lethal diarrhea. Touffée flacherie is caused by heat waves. Viral flacherie is ultimately caused by infection with ''Bombyx mori'' infectious flacherie virus (BmIFV, Iflaviridae), ''Bombyx mori'' densovirus (BmDNV, Parvoviridae) or ''Bombyx mori'' cypovirus 1 (BmCPV-1, Reoviridae). This either alone or in combination with bacterial infection destroys the gut tissue. Bacterial pathogens contributing to infectious flaccherie are ''Serratia marcescens'', and species of ''Streptococcus'' and ''Staphylococcus'' in the form known as ''thatte roga''. In the nineteenth cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |