|
Axiochus (Alcmaeonid)
Axiochus of Scambonidae, son of Alcibiades (II) (Greek: ß╝ê╬¥╬»╬┐¤ç╬┐¤é ß╝ê╬╗╬║╬╣╬▓╬╣╬¼╬┤╬┐¤à ╬ú╬║╬▒╬╝╬▓¤ë╬¢╬»╬┤╬À¤é, ''Ax├¡ochos Alkibi├ídou Skamb┼ìn├¡d─ôs''; mid-5th century ÔÇô late 5th century BCE) was an ancient Athenian political figure and aristocrat of the Alcmaeonidae family. He was the uncle and cohort of the famous general and statesman Alcibiades (III), whom he accompanied in domestic and foreign affairs.Debra Nails, ''The People of Plato'', Indianapolis: Hackett Publishing, 2002; pp. 63ÔÇô64 This association led to his recurrence within ancient literature, including works attributed to Plato and Lysias. Life The son of the famous Alcibiades' grandfather, brother of Cleinias and perhaps the nephew of Aspasia, Axiochus' lineage placed him within the elite and controversial Athenian family known as the Alcmaeonidae. Both the historical record and Lysias' apocryphal "Funeral Oration" speech imply Axiochus' close association with Alcibiades. Axiochus had a son, Cleinias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scambonidae
Scambonidae or Skambonidai ( grc, ╬ú╬║╬▒╬╝╬▓¤ë╬¢╬»╬┤╬▒╬╣) was a deme of ancient Attica, located in the city of Athens. It was located within the Themistoclean Wall, north of the Acropolis. Etymology In the past it was believed that this deme was closely related to that of Melite because of its name: according to tradition, in fact, Myrmex or Dius, the father of Melite who would give the name to the other deme, built a street called Scambonidae. Today, however, it is believed that the name of the deme derives from its streets that, due to the hilly nature of the place, were full of curves ( grc, ¤â╬║╬▒╬╝╬▓¤î¤é, skamb├│s, "crooked"). Description The sacred calendar of Scambonidae, dating back to 460 BCE, is the oldest of its kind and also represents the first decree of a deme found to date. It regulates some religious issues, including the distribution of sacrificial meats and the participation of the deme in some festivals in the city. It also orders the distribution of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Arginusae
The naval Battle of Arginusae took place in 406 BC during the Peloponnesian War near the city of Canae in the Arginusae islands, east of the island of Lesbos. In the battle, an Athenian fleet commanded by eight strategoi defeated a Spartan fleet under Callicratidas. The battle was precipitated by a Spartan victory which led to the Athenian fleet under Conon being blockaded at Mytilene; to relieve Conon, the Athenians assembled a scratch force composed largely of newly constructed ships manned by inexperienced crews. This inexperienced fleet was thus tactically inferior to the Spartans, but its commanders were able to circumvent this problem by employing new and unorthodox tactics, which allowed the Athenians to secure a dramatic and unexpected victory. Slaves and metics who participated in the battle may have been granted Athenian citizenship. The news of the victory itself was met with jubilation at Athens. Their joy was tempered, however, by the aftermath of the battle, in whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Athenian Generals
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5th-century BC Athenians
The 5th century is the time period from 401 ( CDI) through 500 ( D) ''Anno Domini'' (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia. It saw the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, which came to an end in 476 AD. This empire had been ruled by a succession of weak emperors, with the real political might being increasingly concentrated among military leaders. Internal instability allowed a Visigoth army to reach and ransack Rome in 410. Some recovery took place during the following decades, but the Western Empire received another serious blow when a second foreign group, the Vandals, occupied Carthage, capital of an extremely important province in Africa. Attempts to retake the province were interrupted by the invasion of the Huns under Attila. After Attila's defeat, both Eastern and Western empires joined forces for a final assault on Vandal North Africa, but this campaign was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Speakers In Plato's Dialogues
following is a list of the speakers found in the dialogues traditionally ascribed to Plato, including extensively quoted, indirect and conjured speakers. Dialogues, as well as Platonic '' Epistles'' and ''Epigrams'', in which these individuals appear dramatically but do not speak are listed separately. ;Unnamed speakers Notes Bibliography * Debra Nails. ''The People of Plato: A Prosopography of Plato and Other Socratics''. Hackett Publishing, 2002. . * Plato Plato ( ; grc-gre, ╬á╬╗╬¼¤ä¤ë╬¢ ; 428/427 or 424/423 ÔÇô 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution .... ''Complete Works''. Ed: John M. Cooper. Hackett Publishing, 1997. {{Socrates navbox * * Platos Dialogues Speakers in Plato's dialogues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionysodorus (sophist)
Dionysodorus (Greek: ╬ö╬╣╬┐╬¢¤à¤â¤î╬┤¤ë¤ü╬┐¤é, ''Dionys├│d┼ìros'', c. 430 ÔÇô late 5th century or early 4th century BC) was an ancient Greek sophistic philosopher and teacher of martial arts, generalship, and oration. Closely associated with his brother and fellow sophist Euthydemus, he is depicted in the writing of Plato and Xenophon. Life Plato's '' Euthydemus'' features Dionysodorus and Euthydemus as prominent interlocutors. According to the dialogue, the brothers were born on the Aegean island of Chios before relocating as colonists to Thurii in Magna Graecia of modern-day Italy. After being exiled from Thurii, perhaps in 413, Debra Nails, ''The People of Plato'', Indianapolis: Hackett Publishing, 2002; pp. 136ÔÇô137 they came to Athens. According to Socrates in the ''Euthydemus'', the two taught fighting in armor and legal oration before developing an interest in sophism. Xenophon in the ''Memorabilia'' further attributes the teaching of generalship to Dionysodorus specif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euthydemus (Socratic Literature)
Euthydemus (Greek: ╬òߢÉ╬©¤ì╬┤╬À╬╝╬┐¤é) is the name of three characters in Socratic literature. In Book I of the ''Memorabilia'', Xenophon relates Critias' passion for the young Euthydemus and how Socrates mocked him for it: Socrates had observed that Critias loved Euthydemus. Therefore Socrates tried to argue him out of it, saying that it was degrading for a free man and ill became someone "beautiful in body and mind" to importune, moreover for nothing good, his beloved to whom he should be a shining example. Critias, an Athenian sophist and politician, was the leader of the Thirty Tyrants who after the Peloponnesian War ruled for a short while over Athens circa 404 BCE. Another Euthydemus is the eponymous character in one of Plato's dialogues, '' Euthydemus'', written on logic and logical fallacies, or sophisms. The characters Euthydemus and his brother Dionysodorus are sophists questioned by SocratesPlato, ''Euthydemus'', 273aÔÇô304c in a confrontation of the Euthydemian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophists
A sophist ( el, ¤â╬┐¤å╬╣¤â¤ä╬«¤é, sophistes) was a teacher in ancient Greece in the fifth and fourth centuries BC. Sophists specialized in one or more subject areas, such as philosophy, rhetoric, music, athletics, and mathematics. They taught ''arete'' ÔÇô "virtue" or "excellence" ÔÇô predominantly to young statesmen and nobility. In the present day, however, a sophist refers to someone who deliberately argues using fallacious arguments or reasoning, in order to mislead; see the section below. Etymology The Greek word el, ¤â╬┐¤å¤î¤é, sophos, a wise man, label=none is related to the noun el, ¤â╬┐¤å╬»╬▒, sophia, wisdom, label=none. Since the times of Homer it commonly referred to an expert in his profession or craft. Charioteers, sculptors, or military experts could be referred to as in their occupations. The word has gradually come to connote general wisdom and especially wisdom in human affairs such as politics, ethics, and household management. This was the meaning ascr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socrates
Socrates (; ; ÔÇô399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no texts and is known mainly through the posthumous accounts of classical writers, particularly his students Plato and Xenophon. These accounts are written as dialogues, in which Socrates and his interlocutors examine a subject in the style of question and answer; they gave rise to the Socratic dialogue literary genre. Contradictory accounts of Socrates make a reconstruction of his philosophy nearly impossible, a situation known as the Socratic problem. Socrates was a polarizing figure in Athenian society. In 399 BC, he was accused of impiety and corrupting the youth. After a trial that lasted a day, he was sentenced to death. He spent his last day in prison, refusing offers to help him escape. Plato's dialogues are among the most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euthydemus (dialogue)
''Euthydemus'' ( el, ╬òߢÉ╬©¤ì╬┤╬À╬╝╬┐¤é, ''Euthydemes''), written c. 384 BC, is a dialogue by Plato which satirizes what Plato presents as the logical fallacies of the Sophists. In it, Socrates describes to his friend Crito a visit he and various youths paid to two brothers, Euthydemus and Dionysodorus, both of whom were prominent Sophists and pankrationists from Chios and Thurii. The ''Euthydemus'' contrasts Socratic argumentation and education with the methods of Sophism, to the detriment of the latter. Throughout the dialogue, Euthydemus and Dionysodorus continually attempt to ensnare Socrates with what are presented as deceptive and meaningless arguments, primarily to demonstrate their professed philosophical superiority. As in many of the Socratic dialogues, the two Sophists against whom Socrates argues were indeed real people. Euthydemus was somewhat famous at the time the dialogue was written, and is mentioned several times by both Plato and Aristotle. Likewise, Dionyso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axiochus (dialogue)
''Axiochus'' ( el, ß╝ê╬¥╬»╬┐¤ç╬┐¤é) is a Socratic dialogue attributed to Plato, but which has been considered spurious for over 400 years. The work dates from the Hellenistic era, c. 1st century BC. The author was probably a Platonist,John Madison Cooper, D. S. Hutchinson, (1997), ''Plato, Complete works'', page 1734. Hackett Publishing. or perhaps a Neopythagorean.William Keith Chambers Guthrie (1986), A history of Greek philosophy, page 395. Cambridge University Press It forms part of the consolation literature which was popular in Hellenistic and Roman era, although it is unusual in being addressed to someone who is close to death, rather than someone who has lost a loved-one. In the dialogue, Axiochus has come close to death, and is scared by the experience, despite his familiarity with the arguments which were supposed to make him scorn the fear of death. Socrates is summoned to his bedside, and consoles him with a wide variety of teachings to help Axiochus welcome death as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
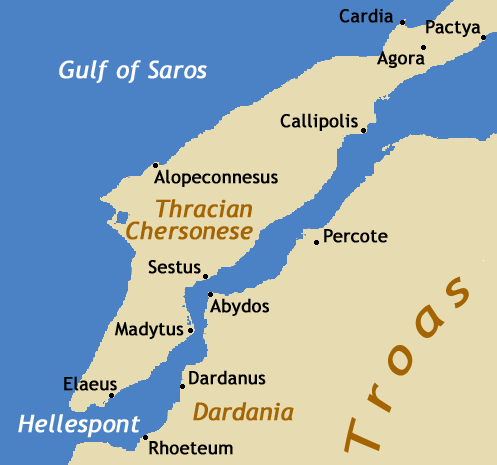
Abydos (Hellespont)
Abydos ( grc, ß╝î╬▓¤à╬┤╬┐¤é, la, Abydus) was an ancient city and bishopric in Mysia. It was located at the Nara Burnu promontory on the Asian coast of the Hellespont (the straits of Dardanelles), opposite the ancient city of Sestos, and near the city of ├çanakkale in Turkey. Abydos was founded in c. 670 BC at the most narrow point in the straits, and thus was one of the main crossing points between Europe and Asia, until its replacement by the crossing between Lampsacus and Kallipolis in the 13th century, and the abandonment of Abydos in the early 14th century. In Greek mythology, Abydos is presented in the myth of Hero and Leander as the home of Leander. The city is also mentioned in ''Rodanthe and Dosikles'', a novel written by Theodore Prodromos, a 12th-century writer, in which Dosikles kidnaps Rodanthe at Abydos. Archaeology In 1675, the site of Abydos was first identified, and was subsequently visited by numerous classicists and travellers, such as Robert Wood, Richard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)