|
Asagel
Esegels (aka ''Izgil'' ( otk, 𐰔𐰏𐰠), ''Äsägel'', ''Askel'', ''Askil'', ''Ishkil'', ''Izgil'') were a dynastic tribe, of Turkic linguistic affiliation, in the Middle Ages who joined and would be assimilated into the Volga Bulgars. Numerous records about Esegels in sources and works of many languages across the span of the Eurasia left numerous variations of their name. M. Räsänen suggested Uralo-Altai etymology of this word: ''Es-kil'', ''Es-gil'' "Old city", Gumilyov initially linked the Izgils to the ''Sijie'' (思结) of the Toquz Oghuz; only to later re-identify Izgils with ''Xijie'' (奚結), another Tiele tribe. However, Zuev (2002) distinguished Izgil (> Ch. *''a-siək-kiet'' 阿悉結 > ''Axijie'', a Western Tujue tribe according to Chinese sources) from Igil (> Ch. *''ɣiei-kiet'' 奚結 > ''Xijie'', a Tiele tribe) though Zuev controversially links the Igils 奚結 to the Bulgarian clan Uokil and the Indo-European-speaking ''Augaloi'' in Transoxania. Róna-Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria, was a historic Bulgar state that existed between the 7th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now European Russia. Volga Bulgaria was a multi-ethnic state with large numbers of Turkic Bulgars, a variety of Finnic and Ugric peoples, and many East Slavs. Its strategic position of allowed it to create a monopoly between the trade of Arabs, Norse and Avars. History Origin and creation of the state The Bulgars were Turkic tribes of Oghuric origin, who settled north of the Black Sea. During their westward migration across the Eurasian steppe, they came under the overlordship of the Khazars, leading other ethnic groups, including Finnic and Iranic peoples. In about 630 they founded Old Great Bulgaria, which was destroyed by the Khazars in 668. Kubrat's son and appointed heir, Batbayan Bezmer, moved from the Azov region in about AD 665, commanded by the Kazarig Khagan Kotrag, to whom he had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia (Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turkic languages originated in a region of East Asia spanning from Mongolia to Northwest China, where Proto-Turkic is thought to have been spoken, from where they expanded to Central Asia and farther west during the first millennium. They are characterized as a dialect continuum. Turkic languages are spoken by some 200 million people. The Turkic language with the greatest number of speakers is Turkish language, Turkish, spoken mainly in Anatolia and the Balkans; its native speakers account for about 38% of all Turkic speakers. Characteristic features such as vowel harmony, agglutination, subject-object-verb order, and lack of grammatical gender, are almost universal within the Turkic family. There is a high degree of mutual intelligibility, upon mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiele People
The Tiele (, Mongolian ''*Tegreg'' " eople of theCarts"), also transliterated as Dili (), Chile (), Zhile (), Tele (), also named Gaoche or Gaoju (, "High Carts"), were a tribal confederation of Turkic ethnic origins living to the north of China proper and in Central Asia, emerging after the disintegration of the confederacy of the Xiongnu. Chinese sources associate them with the earlier Dingling (). Chile and Gaoche The name "Chile" and "Gaoche" first appear in Chinese records during the campaigns of Former Yan and Dai in 357 and 363 respectively. However, the protagonists were also addressed as "Dingling" in the records of the Southern Dynasties. The name ''Gaoche'' ("high cart") was a nickname given by the Chinese.Pulleyblank, "Central Asia and Non-Chinese Peoples of Ancient China", p. VII 21–26. Book of Jin, compiled by Fang Xuanling et al., listed Chile as the fifth of 19 Southern Xiongnu tribes (種). By the time of the Rouran domination, the Gaoche comprised six tribe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theophanes The Confessor
Theophanes the Confessor ( el, Θεοφάνης Ὁμολογητής; c. 758/760 – 12 March 817/818) was a member of the Byzantine aristocracy who became a monk and chronicler. He served in the court of Emperor Leo IV the Khazar before taking up the religious life. Theophanes attended the Second Council of Nicaea in 787 and resisted the iconoclasm of Leo V the Armenian, for which he was imprisoned. He died shortly after his release. Theophanes the Confessor, venerated on 12 March in both the Eastern Orthodox and the Roman Catholic churches, should not be confused with Theophanes of Nicaea, whose feast is commemorated on 11 October. Biography Theophanes was born in Constantinople of wealthy and noble iconodule parents: Isaac, governor of the islands of the Aegean Sea, and Theodora, of whose family nothing is known. His father died when Theophanes was three years old, and the Byzantine Emperor Constantine V (740–775) subsequently saw to the boy's education and upbringing at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xionite
Xionites, Chionites, or Chionitae (Middle Persian: ''Xiyōn'' or ''Hiyōn''; Avestan: ''Xiiaona''; Sogdian ''xwn''; Pahlavi ''Xyon'') were a nomadic people in the Central Asian regions of Transoxiana and Bactria. The Xionites appear to be synonymous with the Huna peoples of the South Asian regions of classical/medieval India, and possibly also the Huns of European late antiquity, who were in turn connected onomastically to the Xiongnu in Chinese history. They were first described by the Roman historian, Ammianus Marcellinus, who was in Bactria during 356–357 CE; he described the ''Chionitæ'' as living with the Kushans. Ammianus indicates that the Xionites had previously lived in Transoxiana and, after entering Bactria, became vassals of the Kushans, were influenced culturally by them and had adopted the Bactrian language. They had attacked the Sassanid Empire, but later (led by a chief named Grumbates), served as mercenaries in the Persian Sassanian army. Within the Xio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nushibi
Nushibi (Nu-shibi, ; Middle Chinese: *''nuoXɕiɪt̚piɪt̚'') was a Chinese collective name for five tribes of the right (western) wingYu. Zuev, ''"The Strongest tribe - Izgil"''//Historical And Cultural Relations Between Iran And Dasht-i Kipchak in the 13th through 18th Centuries, Materials of International Round Table, Almaty, 2004, p. 53, in the Western Turkic Khaganate, and members of "ten arrows" confederation found in the Chinese literature (十箭 ''shíjiàn''; otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸, On Oq). The references to Nushibi appeared in Chinese sources in 651 and disappeared after 766. The Nushibi tribes occupied the lands of the Western Turkic Kaganate west of the Ili River of contemporary Kazakhstan. Name's Etymology Yury Zuev reconstructs ''Nushibis Middle Chinese pronunciation as ''nou siet-piet'',Yu. Zuev, ''"The Strongest tribe - Esgil", p. 53, which, he asserts, transcribes Turkic ''oŋ šadapït'' "right wing". ''Šadapït'' either means "entourage of the Shad" ( Clauso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yury Zuev
Yuri Alexeyevich Zuev or Zuyev (russian: Юрий Алексеевич Зуев; 8 December 1932 – 5 December 2006) was a Russian-born Kazakh sinologist and turkologist. Biography Zuev was born in the Siberian city of Tümen in a white-collar family. Zuev studied at the Leningrad State University and majored in the historical studies of the Eastern Asian countries, successfully learning Classical Chinese, Middle Chinese, and modern Chinese. In 1955, Zuev received a B.A. diploma and was sent to work in the Institute of History, Archeology and Ethnography of the Kazakh SSR Academy of Sciences. He received his Ph.D. in 1967. His PhD thesis "Ancient Turkic genealogical legends as a source on early history of Turkic people" included a number of new discoveries about the socio-political history of the Turks, suggested the etymology of the name of the Ashina tribe, traced the historical past of the Turkic tribes in the Chinese genealogical legends, and suggested a hypothesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Turkic Khaganate
The Second Turkic Khaganate ( otk, 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰:𐰃𐰠, Türük el, State of the Turks, , known as ''Turk Bilge Qaghan country'' ( otk, 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰝:𐰋𐰃𐰠𐰏𐰀:𐰴𐰍𐰣:𐰃𐰠𐰭𐰀, Türük Bilgä Qaγan eli) in Bain Tsokto inscriptions. 682–744), was a khaganate in Central and Eastern Asia founded by Ashina clan of the Göktürks. It was preceded by the Eastern Turkic Khaganate (552-630) and then a period of Tang dynasty rule (630-682). The Second Khaganate was centered on Ötüken in the upper reaches of the Orkhon River. It was succeeded by its subject Toquz Oghuz confederation, which became the Uyghur Khaganate. Outline After the fall of Eastern Turkic Khaganate in 679, Ashina Nishufu was declared qaghan and revolted against the Tang dynasty.Sima Guang, ''Zizhi Tongjian'', Vol. 202 In 680, he was defeated by Pei Xingjian. Shortly afterwards, Nishufu was killed by his men. Following Nishufu's death, Ashina Funian, another scion of the roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Göktürks
The Göktürks, Celestial Turks or Blue Turks ( otk, 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, Türük Bodun; ; ) were a nomadic confederation of Turkic peoples in medieval Inner Asia. The Göktürks, under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan (d. 552) and his sons, succeeded the Rouran Khaganate as the main power in the region and established the First Turkic Khaganate, one of several nomadic dynasties that would shape the future geolocation, culture, and dominant beliefs of Turkic peoples. Etymology Origin Strictly speaking, the common name "Göktürk" emerged from the misreading of the word "Kök" meaning Ashina, ruling clan of the historical ethnic group's endonym: which was attested as otk, 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰, Türük, labels=no ''trwkc'', ''trukč''; Khotanese Saka ''Ttūrka''/''Ttrūka'', Ruanruan ''to̤ro̤x''/''türǖg'' and Old Tibetan ''Drugu''. Definition According to Chinese sources, Tūjué meant " combat helmet" (), reportedly because the shape of the Altai Mountains, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
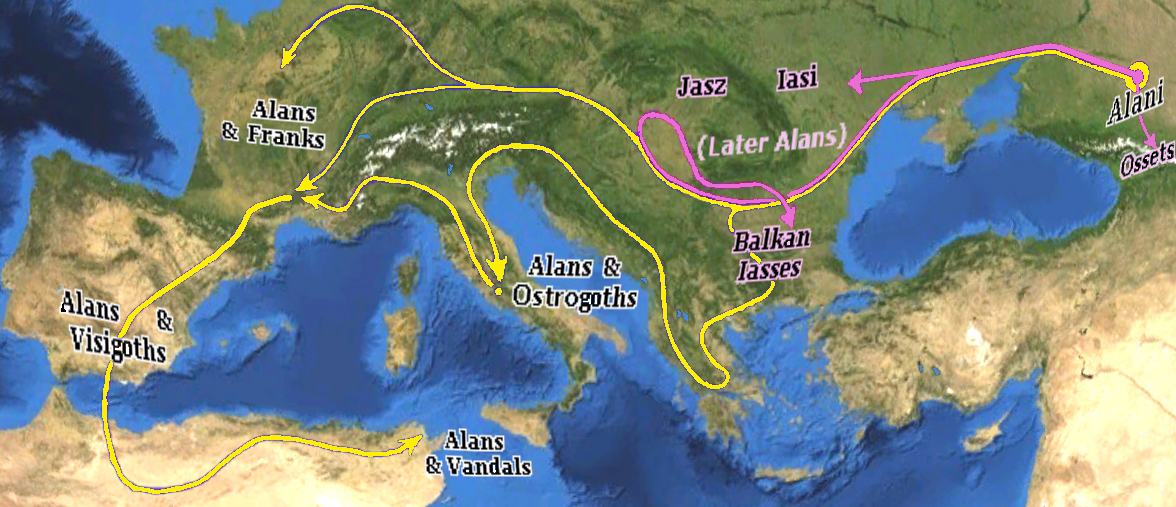
Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the Alans with the Central Asian Yancai of Chinese sources and with the Aorsi of Roman sources. Having migrated westwards and becoming dominant among the Sarmatians on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, the Alans are mentioned by Roman sources in the . At that time they had settled the region north of the Black Sea and frequently raided the Parthian Empire and the Caucasian provinces of the Roman Empire. From the Goths broke their power on the Pontic Steppe. Upon the Hunnic defeat of the Goths on the Pontic Steppe around , many of the Alans migrated westwards along with various Germanic tribes. They crossed the Rhine in 406CE along with the Vandals and Suebi, settling in Orléans and Valence. Around 409 CE they joined the Vandals and Suebi in cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massagetae
The Massagetae or Massageteans (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Sakā tigraxaudā (Old Persian: , "wearer of pointed caps") or Orthocorybantians (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ),: As for the term “Orthocorybantii”, this is a translation of Iranian “wearers of pointed caps”: "The (who wear pointed caps) were known to Greek authors as the , a direct translation of the Old Persian name" were an ancient Eastern Iranian Saka people who inhabited the steppes of Central Asia and were part of the wider Scythian cultures. The Massagetae rose to power in the 8th to 7th centuries BCE, when they kickstarted a series of events with wide-reaching consequences by expelling the Scythians out of Central Asia and into the Caucasian and Pontic Steppes. The Massagetae are most famous for their queen Tomyris's defeating and killing of Cyrus, the founder of the Persian Achaemenid Empire. The Massagetae declined after the 3rd century BCE, after which they merged with some other trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asii
The Asii, Osii, Ossii, Asoi, Asioi, Asini or Aseni were an ancient Indo-European people of Central Asia, during the 2nd and 1st centuries BCE. Known only from Classical Greek and Roman sources, they were one of the peoples held to be responsible for the downfall of the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom. In Greek Mythology they were the children of Iapetus and Asia. Modern scholars have attempted to identify the Asii with other peoples known from European and Chinese sources including the: Yuezhi, Tocharians, Issedones/Wusun and/or Alans. Historical sources The classical European sources relating to the Asii are brief. They sometimes survive only as quotations in other ancient sources, with textual variations that have led to widely varying translations and interpretations. During the 4th and 3rd Centuries BCE, Megasthenes, who lived in Arachosia and was an ambassador to the Mauryan court in Pataliputra, refers in his work ''Indika'' to three tribes with similar and possibly related names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)