|
Aprosuchus
''Aprosuchus'' is a genus of small-bodied Maastrichtian atoposaurid Eusuchian from the Hateg Basin, Romania. Discovery and naming ''Aprosuchus'' is known from an incomplete three-dimensional skull and closely associated mandibles (Holotype UBB V.562/1) as well as a cervical vertebrae found in association with the cranial remains (referred specimen UBB V.562/2). The fossils were found in Maastrichtian sediments of the Pui Gater locality in the Hateg Basin in modern day Transylvania, Romania. The name derives from the Hungarian "apró" meaning small and the Ancient Greek σοῦχος, soukhos ("crocodile"). The species name ghirai honors Ioan Ghira from the Babeș-Bolyai University, Cluj-Napoca, for his contributions to Herpetology. Description ''Aprosuchus'' was a small sized brevirostrine Eusuchian with an estimated body length of 600 mm. It differs from other crocodylomorphs through large palpebral strongly fused to the orbital margin of the prefrontals and frontals and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atoposaurid
Atoposauridae is a Family (biology), family of crocodile-line archosaurs belonging to Neosuchia. The majority of the family are known from Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous marine deposits in France, Portugal, and Bavaria in southern Germany. The discovery of the genus ''Aprosuchus'', however, extends the duration of the lineage to the end of the Cretaceous in Romania. Classification Phylogeny Cladogram modified from Buscalioni and Sanz (1988) and Buscalioni and Sanz (1990): References Late Jurassic crocodylomorphs Taxa named by Paul Gervais Prehistoric reptile families {{paleo-archosaur-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from . The Maastrichtian was preceded by the Campanian and succeeded by the Danian (part of the Paleogene and Paleocene). The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (formerly known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event) occurred at the end of this age. In this mass extinction, many commonly recognized groups such as non-avian dinosaurs, plesiosaurs and mosasaurs, as well as many other lesser-known groups, died out. The cause of the extinction is most commonly linked to an asteroid about wide colliding with Earth, ending the Cretaceous. Stratigraphic definitions Definition The Maastrichtian was introduced into scientific literature by Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1849, after studying rock strata of the Chalk Group c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tethys Ocean
The Tethys Ocean ( el, Τηθύς ''Tēthús''), also called the Tethys Sea or the Neo-Tethys, was a prehistoric ocean that covered most of the Earth during much of the Mesozoic Era and early Cenozoic Era, located between the ancient continents of Gondwana and Laurasia, before the opening of the Indian and Atlantic oceans during the Cretaceous Period. It was preceded by the Paleo-Tethys Ocean, which lasted between the Cambrian and the Early Triassic, while the Neotethys formed during the Late Triassic and lasted until the early Eocene (about 50 million years ago) when it completely closed. A portion known as the Paratethys formed during the Late Jurassic, was isolated during the Oligocene (34 million years ago) and lasted up to the Pliocene (about 5 million years ago), when it largely dried out. Many major seas and lakes of Europe and Western Asia, including the Mediterranean Sea, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, and the Aral Sea are thought to be remnants of the Paratethys. Ety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allodaposuchus
''Allodaposuchus'' is an extinct genus of crocodyliforms that lived in what is now southern Europe during the Campanian and Maastrichtian stages of the Late Cretaceous. Although generally classified as a non-crocodylian eusuchian crocodylomorph, it is sometimes placed as one of the earliest true crocodylians. ''Allodaposuchus'' is one of the most common Late Cretaceous crocodylomorphs from Europe, with fossils known from Romania, Spain, and France. Description Like many other Cretaceous crocodylomorphs, ''Allodaposuchus'' has a relatively small body size compared to living crocodylians. The largest known specimen of ''Allodaposuchus'' belongs to an individual that was probably around long. Although the shape varies between species, in general ''Allodaposuchus'' has a short, flattened, and rounded skull. ''Allodaposuchus precedens'' has a brevirostrine or "short-snouted" skull with a snout about the same length as the skull table (the region of the skull behind the eye sockets) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acynodon
''Acynodon'' is an extinct genus of eusuchian crocodylomorph from the Late Cretaceous, with fossils found throughout Southern Europe. Classification The genus ''Acynodon'' contains three species: ''A. iberoccitanus'', ''A. adriaticus'', and ''A. lopezi''. Fossils have been found in France, Spain, Italy, and Romania, dating back to the Santonian and Maastrichtian periods of the Late Cretaceous. When first described in 1997, it was placed within the family Alligatoridae. New findings a decade later led to it being reclassified as a basal globidontan. Recent studies have since resolved ''Acynodon'' as a basal eusuchian crocodylomorph, outside of the Crocodylia crown group, and a close relative to ''Hylaeochampsa''. Description The skull of ''Acynodon'' is extremely brevirostrine; it had a very short and broad snout compared to other known alligatorids. Its dentition was quite derived, with enlarged molariform teeth and a lack of maxillary and dentary In anatomy, the mandible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durophagous
Durophagy is the eating behavior of animals that consume hard-shelled or exoskeleton bearing organisms, such as corals, shelled mollusks, or crabs. It is mostly used to describe fish, but is also used when describing reptiles, including fossil turtles, placodonts and invertebrates, as well as "bone-crushing" mammalian carnivores such as hyenas. Durophagy requires special adaptions, such as blunt, strong teeth and a heavy jaw. Bite force is necessary to overcome the physical constraints of consuming more durable prey and gain a competitive advantage over other organisms by gaining access to more diverse or exclusive food resources earlier in life. Those with greater bite forces require less time to consume certain prey items as a greater bite force can increase the net rate of energy intake when foraging and enhance fitness in durophagous species. In the order Carnivora there are two dietary categories of durophagy; bonecrackers and bamboo eaters. Bonecrackers are exemplified by hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theriosuchus
''Theriosuchus'' is an extinct genus of atoposaurid neosuchian from Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of Europe (Hungary & southern England), Southeast Asia (Thailand) and western North America (Wyoming), with fragmentary records from Middle Jurassic and Early Cretaceous sites in China, Morocco, and Scotland. Taxonomy Three valid species are currently recognized: ''Theriosuchus pusillus'' from southern England, ''T. grandinaris'' from Thailand, and ''T. morrisonensis'' from the Morrison Formation of North America. ''Theriosuchus'' was previously assigned to Atoposauridae, but a 2016 cladistic analysis recovered it as a neosuchian more closely related to members of the family Paralligatoridae than to atoposaurids. Two species previously assigned to this genus, ''Theriosuchus ibericus'' and ''T. symplesiodon'', have been reassigned to the new genus ''Sabresuchus''. On the other hand, ''Theriosuchus guimarotae'' from Portugal has been reassigned to ''Knoetschkesuchus ''Knoets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alligatorium
''Alligatorium'' is an extinct genus of atoposaurid crocodylomorph from Late Jurassic marine deposits in France. Systematics The type species is ''A. meyeri'', named in 1871 from a single specimen from Cerin, eastern France. Two more nominal species, ''A. franconicum'', named in 1906, and ''A paintenense'', named in 1961, are based on now-missing specimens from Bavaria, southern Germany, and were synonymized into a single species, for which ''A. franconicum'' has priority. A 2016 review of Atoposauridae removed ''A. franconicum'' from ''Alligatorium'' and placed at Neosuchia ''incertae sedis''. ''Alligatorium depereti'', described in 1915, was reassigned to its own genus, ''Montsecosuchus ''Montsecosuchus'' is an extinct genus of atoposaurid crocodylomorphs. It is the replacement generic name for ''Alligatorium depereti'', which was described in 1915 from the Montsec Lithographic Limestone quarry of Spain. Fossils found from this ...'', in 1988. References Late Jura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
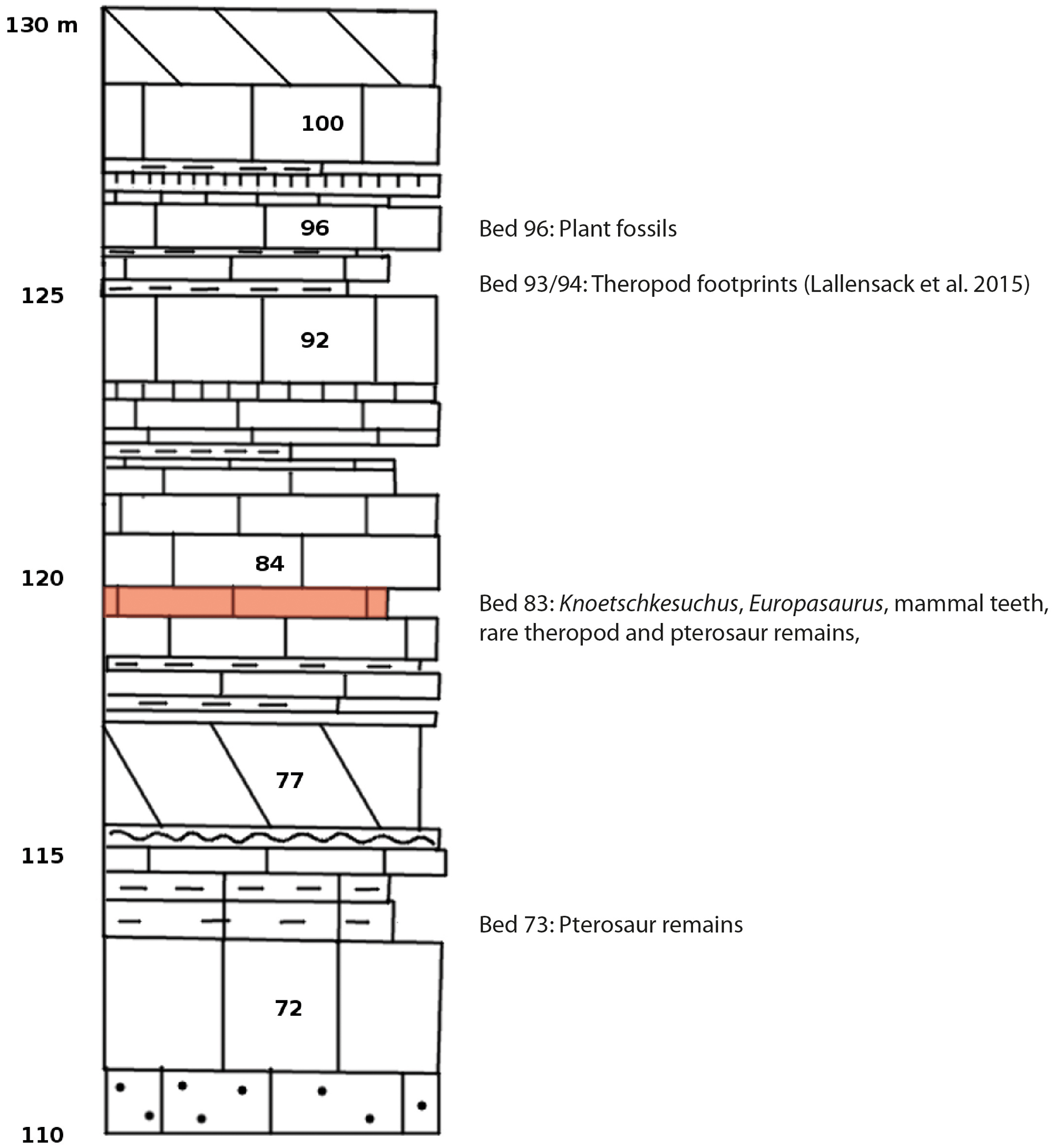
Knoetschkesuchus
''Knoetschkesuchus'' is a genus of small atoposaurid crocodylomorph from the Late Jurassic of Germany and Portugal. Two species are known: the German species ''K. langenbergensis'', described by Schwarz and colleagues in 2017 based on two partial skeletons and various isolated bones; and the Portuguese species ''K. guimarotae'', named from over 400 specimens including several partial skeletons. ''Knoetschkesuchus'' was a small and short-snouted crocodilian, measuring about in length, that primarily fed on small prey, including invertebrates, amphibians, and mammals. This specialization towards small prey ecologically separated ''Knoetschkesuchus'' from most of the other diverse crocodilians that it lived with in the island ecosystem of Jurassic Europe. Both species were formerly recognized as belonging to ''Theriosuchus''; ''K. guimarotae'' was initially named as ''T. guimarotae'', and specimens of ''K. langenbergensis'' were initially referred to ''T. pusillus'' upon their dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theriosuchus Pusillus
''Theriosuchus'' is an extinct genus of atoposaurid neosuchian from Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous of Europe (Hungary & southern England), Southeast Asia (Thailand) and western North America (Wyoming), with fragmentary records from Middle Jurassic and Early Cretaceous sites in China, Morocco, and Scotland. Taxonomy Three valid species are currently recognized: ''Theriosuchus pusillus'' from southern England, ''T. grandinaris'' from Thailand, and ''T. morrisonensis'' from the Morrison Formation of North America. ''Theriosuchus'' was previously assigned to Atoposauridae, but a 2016 cladistic analysis recovered it as a neosuchian more closely related to members of the family Paralligatoridae than to atoposaurids. Two species previously assigned to this genus, ''Theriosuchus ibericus'' and ''T. symplesiodon'', have been reassigned to the new genus ''Sabresuchus''. On the other hand, ''Theriosuchus guimarotae'' from Portugal has been reassigned to ''Knoetschkesuchus ''Knoets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wannchampsus
''Wannchampsus'' ("Wann Langston, Jr.'s crocodile") is an extinct genus of paralligatorid neosuchian, close to but not a true crocodilian. It is known from fossils discovered in Lower Cretaceous rocks in north-central Texas, United States. Description and classification ''Wannchampsus'' is based on SMU 76604, a partial skull and lower jaw. This fossil is attached by matrix to another partial skull of the same genus and species, SMU 76605. A handful of other fossils were found associated, mostly representing forelimbs and vertebrae. These fossils were found in rocks of the late Aptian-age Lower Cretaceous Twin Mountains Formation, southwest of Stephenville, in Comanche County, Texas; the site is otherwise known as the Proctor Lake dinosaur locality. ''Wannchampsus'' was described in 2014 by Thomas Adams. The type species is ''W. kirpachi'', in honor of Wesley Kirpach, "who was instrumental in the discovery and excavations of the type specimen". The skulls are descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |