|
Antonov A-40
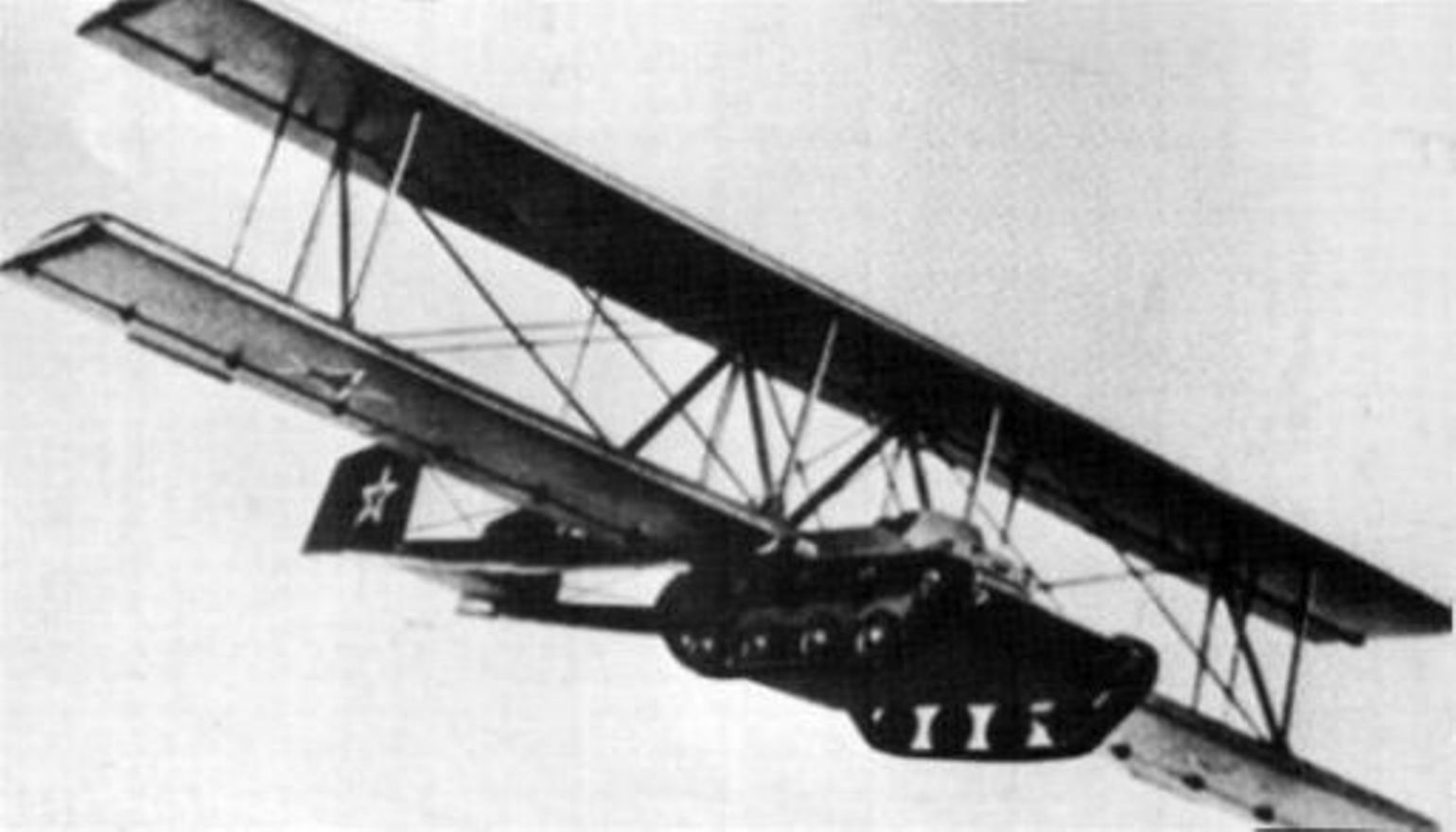
The Antonov A-40 ''Krylya Tanka'' (russian: крылья танка, meaning "tank wings") was a Soviet attempt to allow a tank to glide onto a battlefield after being towed aloft by an airplane, to support airborne forces or partisans.Winchester 2005, p. 62 A prototype was built and tested in 1942, but was found to be unworkable. This vehicle is sometimes called the ''A-40T'' or ''KT''. Design and development Instead of loading light tanks onto gliders, as other nations had done, Soviet airborne forces had strapped T-27 tankettes underneath heavy bombers and landed them on airfields. In the 1930s, there were experimental efforts to parachute tanks or simply drop them into water. During the 1940 occupation of Bessarabia, light tanks may have been dropped from a few meters up by TB-3 bombers, which, as long as the gearbox was in neutral, would allow them to roll to a stop. The biggest problem with air-dropping vehicles is if their crews are dropped separately, they may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonov
Antonov State Enterprise ( uk, Державне підприємство «Антонов»), formerly the Aeronautical Scientific-Technical Complex named after Antonov (Antonov ASTC) ( uk, Авіаційний науково-технічний комплекс імені Антонова, �НТК ім. Антонова}), and earlier the Antonov Design Bureau, for its chief designer, Oleg Antonov, is a Ukrainian aircraft manufacturing and services company. Antonov's particular expertise is in the fields of very large aeroplanes and aeroplanes using unprepared runways. Antonov (model prefix "An-") has built a total of approximately 22,000 aircraft, and thousands of its planes are operating in the former Soviet Union and in developing countries. Antonov StC is a state-owned commercial company. Its headquarters and main industrial grounds were originally located in Novosibirsk, and in 1952 were transferred to Kyiv. On 12 May 2015 it was transferred from the Ministry of Economi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biplane
A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two main wings stacked one above the other. The first powered, controlled aeroplane to fly, the Wright Flyer, used a biplane wing arrangement, as did many aircraft in the early years of aviation. While a biplane wing structure has a structural advantage over a monoplane, it produces more drag than a monoplane wing. Improved structural techniques, better materials and higher speeds made the biplane configuration obsolete for most purposes by the late 1930s. Biplanes offer several advantages over conventional cantilever monoplane designs: they permit lighter wing structures, low wing loading and smaller span for a given wing area. However, interference between the airflow over each wing increases drag substantially, and biplanes generally need extensive bracing, which causes additional drag. Biplanes are distinguished from tandem wing arrangements, where the wings are placed forward and aft, instead of above and below. The term is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
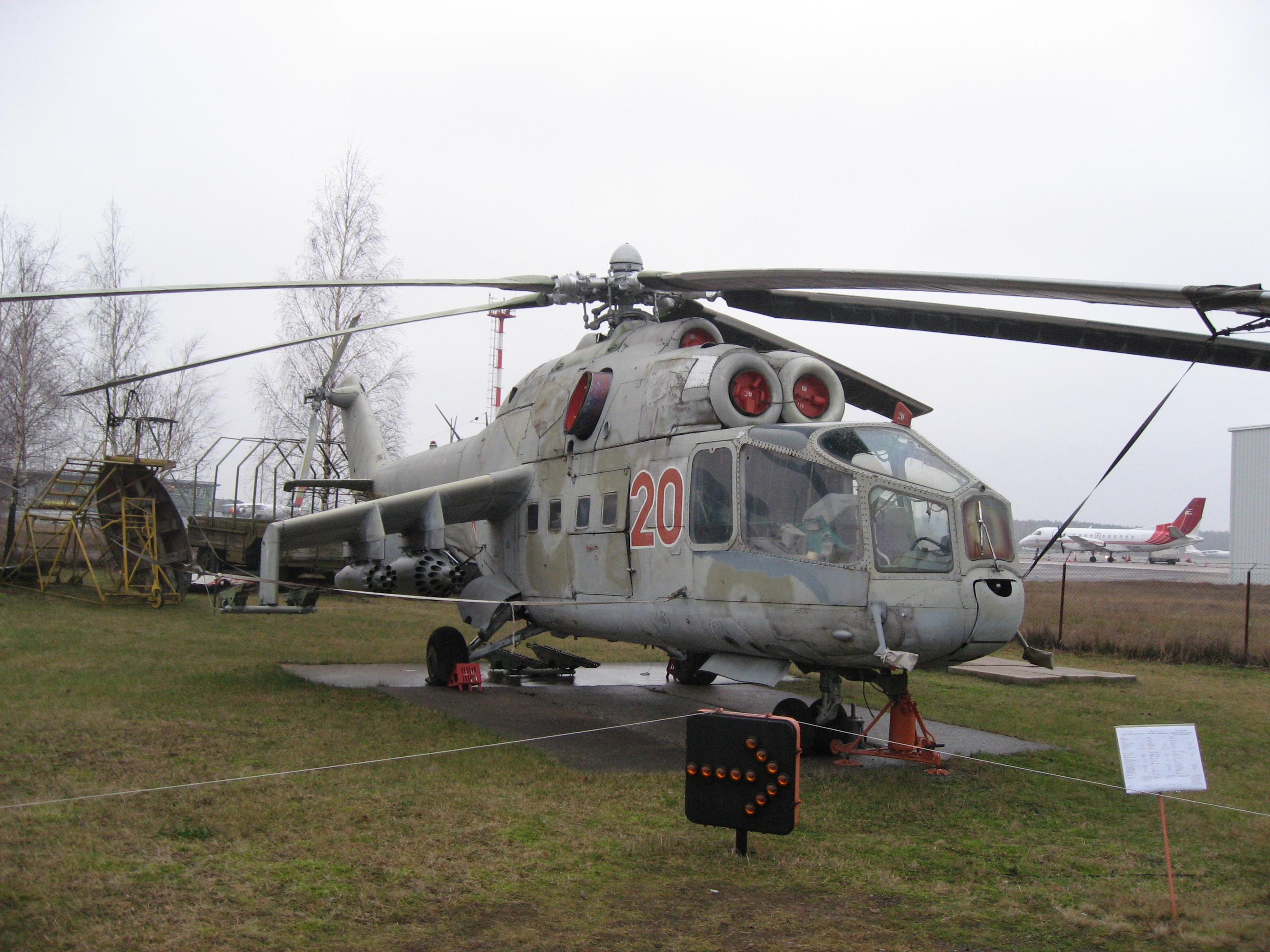
Mil Mi-24
The Mil Mi-24 (russian: Миль Ми-24; NATO reporting name: Hind) is a large helicopter gunship, attack helicopter and low-capacity troop transport with room for eight passengers. It is produced by Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant and has been operated since 1972 by the Soviet Air Force and its successors, along with 48 other nations. In NATO circles, the export versions, Mi-25 and Mi-35, are denoted with a letter suffix as "Hind D" and "Hind E". Soviet pilots called the Mi-24 the "flying tank" (russian: летающий танк, letayushchiy tank, links=no), a term used historically with the famous World War II Soviet Il-2 ''Shturmovik'' armored ground attack aircraft. More common unofficial nicknames were "Galina" (or "Galya"), "Crocodile" (russian: Крокодил, Krokodil, links=no), due to the helicopter's camouflage scheme, and "Drinking Glass" (russian: Стакан, Stakan, links=no), because of the flat glass plates that surround earlier Mi-24 variants' cockpits. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-84
The T-84 is a Ukrainian main battle tank (MBT), based on the Soviet T-80 MBT introduced in 1976, specifically the diesel engine version: T-80UD. The T-84 was first built in 1994 and entered service in the Ukrainian Armed Forces in 1999. Its high-performance opposed-piston engine makes it a fast tank, comparable to other modern MBTs with a power-to-weight ratio of about 26 horsepower per tonne (19 kW/t). The T-84 Oplot is an advanced version incorporating an armoured ammunition compartment in a new turret bustle. Ten of these entered Ukrainian service in 2001. The T-84-120 Yatagan is a prototype model intended for export, mounting a 120 mm gun able to fire standard NATO ammunition and guided missiles. Development history After the adoption of the T-80 tank, the Soviets began improving its design. The disadvantages of the gas-turbine engine were readily apparent, and so several design projects were initiated to adopt a diesel alternative. Development of the T-80UD L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-80
The T-80 is a main battle tank (MBT) that was designed and manufactured in the former Soviet Union and manufactured in Russia. The T-80 is based on the T-64, while incorporating features from the later T-72. The chief designer of the T-80 was Soviet engineer Nikolay Popov. When it entered service in 1976, it was the second MBT in the world to be equipped with a gas turbine engine, after the Swedish Stridsvagn 103, and the first to use it as a main propulsion engine. The T-80U was last produced in 2001 in a factory in Omsk, Russia. The Ukrainian T-80UD diesel engine variant continued to be produced in Ukraine. The T-80 and its variants are in service in Belarus, Cyprus, Egypt, Kazakhstan, Pakistan, Russia, South Korea, Ukraine and Uzbekistan. Ukraine further developed the T-80UD as the T-84. History Development The project to build the first Soviet turbine powered tank began in 1949. Its designer was A. Ch. Starostienko, who worked at the Leningrad Kirov Plant (LKZ). The ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junkers Ju 322
The Junkers Ju 322 ''Mammut'' (German for mammoth) was a heavy transport military glider, resembling a giant flying wing, proposed for use by the ''Luftwaffe'' in World War II; only two prototypes were completed, a further 98 were scrapped before completion. Development Designed in late 1940 by Junkers as the Junkers EF 094, the Ju 322 was to fulfill the same role as the Me 321 ''Gigant'' heavy transport glider. Fulfilling a requirement to be built out of non-strategic materials, using all-wooden construction, the Ju322 was to be able to carry of cargo, equivalent to either a Panzer IV tank, a 88mm anti-aircraft gun, a half-track or a self propelled gun, including attendant personnel, ammunition and fuel. The cargo door was located in the centre section of the leading edge of the wing, with the cockpit offset to the port side above the cargo bay. The glider's tailplane extended from the centre section, and had a typical arrangement of stabilizing fins and vertical rudder. Armame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messerschmitt Me 321
The Messerschmitt Me 321 ''Gigant'' was a large German cargo glider developed and used during World War II. Intended to support large scale invasions, the Me 321 saw very limited use due to the low availability of suitable tug aircraft, high vulnerability whilst in flight and the difficult ground handling, both at base and at destination landing sites. The Me 321 was developed, in stages, into the six-engined Messerschmitt Me 323 ''Gigant'', which removed some of the problems with ground handling, but vulnerability to ground fire and aerial attack remained a constant problem during operations of all variants. Development During the preparations for a possible invasion of Britain during World War II (Operation Sea Lion) it became obvious to the ''Luftwaffe''s Transport Command that there was a need for a larger capacity cargo- and troop-carrying aircraft than its mainstay, the Junkers Ju 52. When the plans for Operation Sea Lion were shelved in December 1940, and planning began f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Aircraft Hamilcar
The General Aircraft Limited GAL. 49 Hamilcar or Hamilcar Mark I was a large British military glider produced during the Second World War, which was designed to carry heavy cargo, such as the Tetrarch or M22 Locust light tank. When the British airborne establishment was formed in 1940 by the order of Prime Minister Winston Churchill it was decided to develop a large glider which would be able to transport heavy equipment in support of airborne troops. General Aircraft Limited were chosen in January 1941 to develop this glider, which they designated the GAL. 49 'Hamilcar'. It was designed to transport a light tank or two Universal Carriers. A number of problems, which included vacillation by the War Office on the number of gliders it wanted and poor management by GAL, led to delays in the production of the Hamilcar and it was not until mid-1943 that the first production glider was assembled. These problems were only partially solved and production of the glider continued to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baynes Bat
The Baynes Bat (or sometimes Slingsby-Baynes Bat) was an experimental glider of the Second World War, designed by L. E. Baynes. It was used to test the tailless design that he had suggested as a means to convert tanks into temporary gliders so they could be flown into battle. Design and development In the late 1930s, armies were looking for a way to airlift heavy military units. There were then no cargo aircraft big enough to lift a tank, and even if such a large aircraft had been created it would have needed many special facilities. A solution which was explored during the Second World War was to tow tanks as gliders, and for this wings had to be added. Most designs were based on straight wings with extended empennage and stabilizers. The design of L.E. Baynes AFRAeS in 1941 was for a 100 ft wingspan "Carrier Wing Glider" consisting chiefly of a swept wing with vertical stabilizers on the wingtips. A 1/3 scale prototype was built entirely of wood in 1943 by Slingsby S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winged Tank
Tanks with glider wings were the subject of several unsuccessful experiments in the 20th century. It was intended that these could be towed behind, or carried under, an airplane, to glide into a battlefield, in support of infantry forces. In war, airborne forces use parachutes to drop soldiers behind enemy lines to capture and hold important objectives until more heavily equipped friendly troops can arrive. Military planners have always sought ways to provide airborne troops with combat support equipment in the form of light armored vehicles or artillery which can be dropped by parachute or military glider. The biggest problem with air-dropping vehicles is that their crews drop separately, and may be delayed or prevented from bringing them into action. Military gliders allow crews to arrive at the drop zone along with their vehicles. They also minimize exposure of the valuable towing aircraft, which need not appear over the battlefield. An improvement would be a tank which coul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonov A-40
The Antonov A-40 ''Krylya Tanka'' (russian: крылья танка, meaning "tank wings") was a Soviet attempt to allow a tank to glide onto a battlefield after being towed aloft by an airplane, to support airborne forces or partisans.Winchester 2005, p. 62 A prototype was built and tested in 1942, but was found to be unworkable. This vehicle is sometimes called the ''A-40T'' or ''KT''. Design and development Instead of loading light tanks onto gliders, as other nations had done, Soviet airborne forces had strapped T-27 tankettes underneath heavy bombers and landed them on airfields. In the 1930s, there were experimental efforts to parachute tanks or simply drop them into water. During the 1940 occupation of Bessarabia, light tanks may have been dropped from a few meters up by TB-3 bombers, which, as long as the gearbox was in neutral, would allow them to roll to a stop. The biggest problem with air-dropping vehicles is if their crews are dropped separately, they may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Anokhin (test Pilot)
Sergey Nikolaevich Anokhin (Russian: Серге́й Никола́евич Ано́хин; – 15 April 1986) was a Soviet test pilot. Early life and education Sergei Anokhin was born in Moscow on 19 March 1910. He worked on the railroads until the 1930s when he enrolled at a Higher Air Force School. From there, he became a glider pilot, instructor and established numerous world records for gliding flights. During its one and only flight on 2 September 1942, Anokhin piloted the Antonov A-40, an experimental Soviet glider T-60 tank. After being released by the tow aircraft, he landed the tank glider to a field near the airport, and after dropping the glider wings and tail, the T-60 was driven back to its base. However, due to the lack of a sufficiently-powerful aircraft to tow the tank at the required speed of , the project was abandoned. In World War II, Anokhin assumed command of an Air Force regiment in Belarus. Test pilot and space program In 1943, Anokhin joined the Fli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




