|
Anini
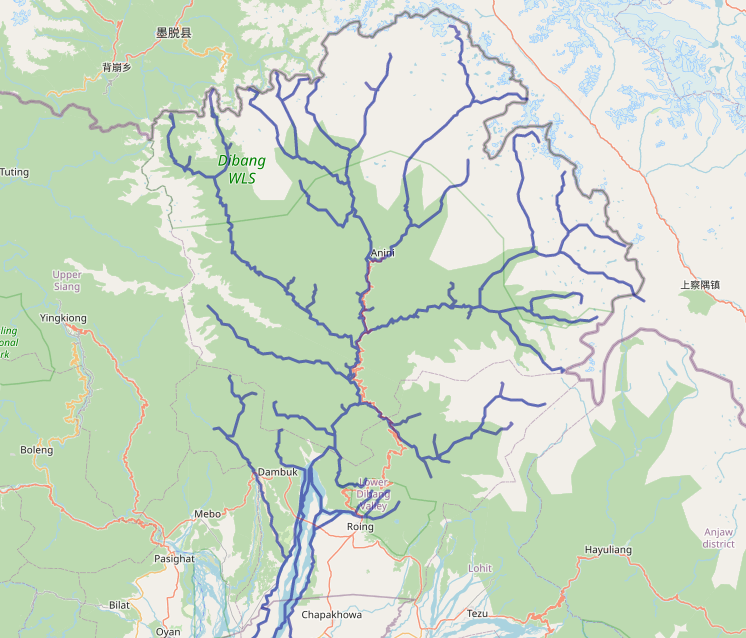
Anini is the headquarters of the Dibang Valley district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in Northeast India. Anini was also the district headquarters of the undivided Dibang Valley district. Most of this location's population consists of the Idu Mishmi tribal people. Due to its remote location, Anini remains a small and underdeveloped town. However, it still has basic road and air links to the rest of India. The town is fully dependent on the nearest major settlement, Roing, which is in the Lower Dibang Valley District, for most commercial needs. The Anini sub-division consists of six administrative circles— Anini, Mipi, Dambeun, Etalin, Anelih, and Arzoo. Etymology While there is no definite answer, Anini's name may have come from Inini or Innini. Historical maps of Arunachal Pradesh from times before the Lower Dibang Valley district were carved out of the Dibang Valley District in 2001. Before Roing was established, these maps indicate the capital of the Dibang Valley Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anini PrasadBasavaraj
Anini is the headquarters of the Dibang Valley district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in Northeast India. Anini was also the district headquarters of the undivided Dibang Valley district. Most of this location's population consists of the Idu Mishmi tribal people. Due to its remote location, Anini remains a small and underdeveloped town. However, it still has basic road and air links to the rest of India. The town is fully dependent on the nearest major settlement, Roing, which is in the Lower Dibang Valley District, for most commercial needs. The Anini sub-division consists of six administrative circles— Anini, Mipi, Dambeun, Etalin, Anelih, and Arzoo. Etymology While there is no definite answer, Anini's name may have come from Inini or Innini. Historical maps of Arunachal Pradesh from times before the Lower Dibang Valley district were carved out of the Dibang Valley District in 2001. Before Roing was established, these maps indicate the capital of the Dibang Valle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dibang Valley District
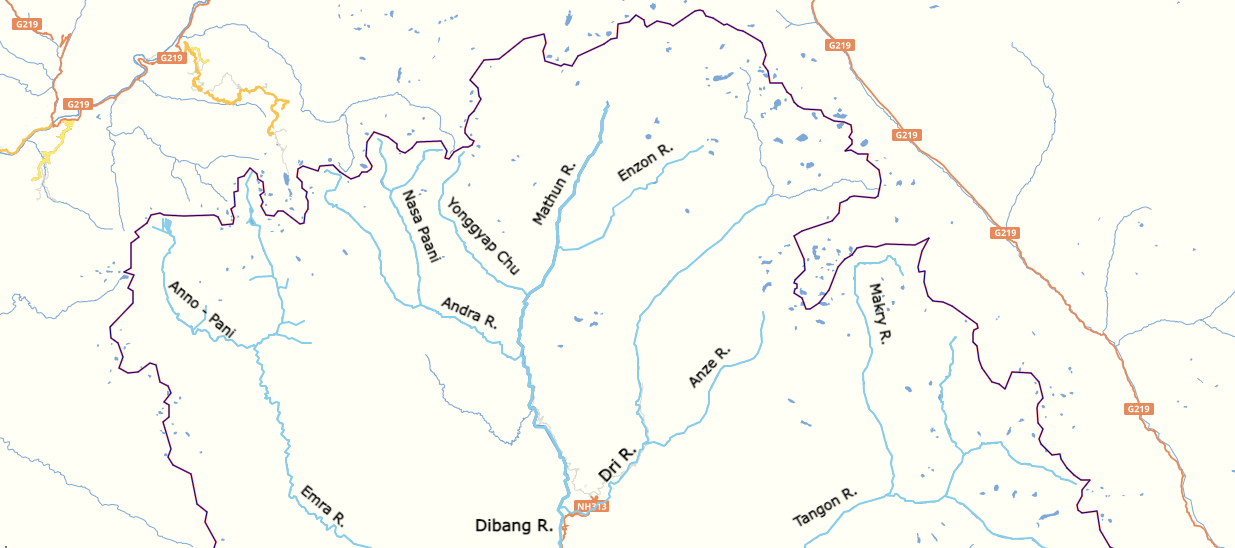
Dibang Valley (Pron:/dɪˈbæŋ/) is a district of Arunachal Pradesh named after the Dibang River or the Talon as the Mishmis call it. It is the least populated district in India and has an area of . History In June 1980, Dibang Valley district was created out of part of Lohit district. On 16 December 2001, Dibang Valley district was bifurcated into Dibang Valley district and Lower Dibang Valley district. Geography The Dibang River originates in the mountains of Arunachal Pradesh and flows through the length of the valley which is named after it. The Dibang has multiple tributaries and only once it debouches into the plains is it called by its name. Some of the major rivers of Dibang Valley District are: Ahui, Emra, Mathun, Dri, Tangon, Ithun, and Ange. The capital of this district, Anini, is the northernmost district capital in Northeast India. This district contains the northernmost point of Northeast India. Transport The proposed Mago-Thingbu to Vijaynagar Arunachal P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dibang Valley District
Dibang Valley (Pron:/dɪˈbæŋ/) is a district of Arunachal Pradesh named after the Dibang River or the Talon as the Mishmis call it. It is the least populated district in India and has an area of . History In June 1980, Dibang Valley district was created out of part of Lohit district. On 16 December 2001, Dibang Valley district was bifurcated into Dibang Valley district and Lower Dibang Valley district. Geography The Dibang River originates in the mountains of Arunachal Pradesh and flows through the length of the valley which is named after it. The Dibang has multiple tributaries and only once it debouches into the plains is it called by its name. Some of the major rivers of Dibang Valley District are: Ahui, Emra, Mathun, Dri, Tangon, Ithun, and Ange. The capital of this district, Anini, is the northernmost district capital in Northeast India. This district contains the northernmost point of Northeast India. Transport The proposed Mago-Thingbu to Vijaynagar Arunachal P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dibang Valley
Dibang Valley (Pron:/dɪˈbæŋ/) is a district of Arunachal Pradesh named after the Dibang River or the Talon as the Mishmis call it. It is the least populated district in India and has an area of . History In June 1980, Dibang Valley district was created out of part of Lohit district. On 16 December 2001, Dibang Valley district was bifurcated into Dibang Valley district and Lower Dibang Valley district. Geography The Dibang River originates in the mountains of Arunachal Pradesh and flows through the length of the valley which is named after it. The Dibang has multiple tributaries and only once it debouches into the plains is it called by its name. Some of the major rivers of Dibang Valley District are: Ahui, Emra, Mathun, Dri, Tangon, Ithun, and Ange. The capital of this district, Anini, is the northernmost district capital in Northeast India. This district contains the northernmost point of Northeast India. Transport The proposed Mago-Thingbu to Vijaynagar Arunachal P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etalin
Etalin is a village and the headquarters of an eponymous circle (subdistrict) in the Dibang Valley district in the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh.District Census Handbook – Dibang Valley, Part B Census of India, 2011. It is a rest stop used by those taking the route to Anini or Malinye. Etalin is approximately 52 km from Anini and approximately 42 km from Malinye. The nearest hospital is the |
Lower Dibang Valley District
The Lower Dibang Valley district (Pron:/dɪˈbæŋ/) is an administrative district in the state of Arunachal Pradesh in northeastern India. It is the tenth least populous district in the country. History In June 1980, the Dibang Valley district was created from part of the Lohit district. On 16 December 2001, the Dibang Valley district was bifurcated into Dibang Valley district and Lower Dibang Valley district. Geography and timeline The headquarters of the district is Roing. Before it was carved out of the district on 16 December 2001, Anini housed the district headquarters. Transport The proposed Arunachal Pradesh Frontier Highway goes along the McMahon Line, and will pass through the Lower Dibang Valley district. An alignment map can be seehereanhere It will intersect with the proposed East-West Industrial Corridor Highway. Divisions There are two Arunachal Pradesh Legislative Assembly constituencies located in this district: Dambuk and Roing. Both are part of the Aruna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh (, ) is a state in Northeastern India. It was formed from the erstwhile North-East Frontier Agency (NEFA) region, and became a state on 20 February 1987. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south. It shares international borders with Bhutan in the west, Myanmar in the east, and a disputed border with China in the north at the McMahon Line. Itanagar is the state capital of Arunachal Pradesh. Arunachal Pradesh is the largest of the Seven Sister States of Northeast India by area. Arunachal Pradesh shares a 1,129 km border with China's Tibet Autonomous Region. As of the 2011 Census of India, Arunachal Pradesh has a population of 1,382,611 and an area of . It is an ethnically diverse state, with predominantly Monpa people in the west, Tani people in the centre, Mishmi and Tai people in the east, and Naga people in the southeast of the state. About 26 major tribes and 100 sub-tribes live in the state. The main tribes of the state are Adi, Nyshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idu Mishmi Language
The Idu Mishmi language () is a small language spoken by the Mishmi people in Dibang Valley district, Lower Dibang Valley district, Lohit district, East Siang district, Upper Siang district of the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh and in Zayü County of the Tibet Autonomous Region, China. There were 8569 speakers in India in 1981 and 7000 speakers in China in 1994. It is considered an endangered language. Locations In China, Idu Mishmi is spoken in Xiba village 西巴村, which has just over 40 residents and is located at the foot of Xikong Mountain 习孔山. Xiba village is located 10 kilometers from the nearest administrative center, namely Migu village 米古村 (Jiang 2005:4). The Idu live in the Danba River 丹巴江 and E River 额河 watersheds in Zayü County, Tibet. They are officially classified by the Chinese government as ethnic Lhoba people. In India, the Idu are found in Arunachal Pradesh. Script The Idu Mishmi people did not usually have a script of their own. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assam
Assam (; ) is a state in northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . The state is bordered by Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh to the north; Nagaland and Manipur to the east; Meghalaya, Tripura, Mizoram and Bangladesh to the south; and West Bengal to the west via the Siliguri Corridor, a wide strip of land that connects the state to the rest of India. Assamese and Boro are the official languages of Assam, while Bengali is an additional official language in the Barak Valley. Assam is known for Assam tea and Assam silk. The state was the first site for oil drilling in Asia. Assam is home to the one-horned Indian rhinoceros, along with the wild water buffalo, pygmy hog, tiger and various species of Asiatic birds, and provides one of the last wild habitats for the Asian elephant. The Assamese economy is aided by wildlife tourism to Kaziranga National Park and Manas National Park, which are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roing
Roing is the district headquarter of Lower Dibang Valley district in the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh. It is the last major township at the north-eastern frontier of India. Demographics As of 2011 India census, Roing had a population of 11,389 of which 6,064 are males while 5,325 are females. Roing has an average literacy rate of 88.39%, higher than the national average of 65.38%: male literacy is 91.94%, and female literacy is 84.35%. The population of Children age 0-6 is 1157 which is 10.16% of the total population of Roing. The female Sex Ratio is 878 against the state average of 938. Moreover, the Child Sex Ratio in Roing is around 875 compared to the Arunachal Pradesh state average of 972. Roing has total administration over 2,617 houses to which it supplies basic amenities like water and sewerage. Both Adi and Mishmi ( Idu) are the principal indigenous dwellers of Roing. Notable tourist attractions arMehao wild life sanctuary [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ledo Road
The Ledo Road (from Ledo, Assam, India to Kunming, Yunnan, China) was an overland connection between India and China, built during World War II to enable the Western Allies to deliver supplies to China and aid the war effort against Japan. After the Japanese cut off the Burma Road in 1942 an alternative was required, hence the construction of the Ledo Road. It was renamed the Stilwell Road, after General Joseph Stilwell of the U.S. Army, in early 1945 at the suggestion of Chiang Kai-shek. It passes through the Burmese towns of Shingbwiyang, Myitkyina and Bhamo in Kachin state. Of the long road, are in Burma and in China with the remainder in India. The road had the Ledo-Pangsau Pass-Tanai (Danai)-Myitkyina--Bhamo-Mansi- Namhkam-Kunming route. To move supplies from the railheads to the Army fronts, three all-weather roads were constructed in record time during the autumn (fall) of 1943: Ledo Road in the north across three nations, which went on to connect to the Burma R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)


