|
Angilbert II
Angilbert II (called ''Angilberto da Pusterla'') was the Archbishop of Milan from 27 or 28 June 824 to his death on the 13 December 859. He succeeded Angilbert I. Like his predecessor Anselm I, who counselled Bernard to rebel in 817, Angilbert counselled the King of Italy, this time Lothair I, to revolt against his imperial sovereign in 833. In 837, he acted as an intermediary between Lothair and the emperor Louis the Pious. In 844 and again in May 859, after Lothair had attained the emperorship, Anselm was appointed to act as ''missus dominicus'' in his province. In the former year, he was in Rome for the coronation of Louis II as ''rex Langobardorum'' on 15 June. He was there again in April 850 for Louis's imperial coronation. In that year, he attended the reforming Synod of Pavia. Angilbert also championed the cause of the deacon Anspert, later archbishop, on 20 June 857. Angilbert was the donor of a golden altar for the church of Sant'Ambrogio Sant'Ambrogio may refer to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Milan
The Archdiocese of Milan ( it, Arcidiocesi di Milano; la, Archidioecesis Mediolanensis) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Italy which covers the areas of Milan, Monza, Lecco and Varese. It has long maintained its own Latin liturgical rite usage, the Ambrosian rite, which is still used in the greater part of the diocesan territory. Among its past archbishops, the better known are Ambrose, Charles Borromeo, Pope Pius XI and Pope Paul VI. The Archdiocese of Milan is the metropolitan see of the ecclesiastical province of Milan, which includes the suffragan dioceses of Bergamo, Brescia, Como, Crema, Cremona, Lodi, Mantova, Pavia, and Vigevano."Archdiocese of Milano " '' |
Louis II, Holy Roman Emperor
Louis II (825 – 12 August 875), sometimes called the Younger, was the king of Italy and emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 844, co-ruling with his father Lothair I until 855, after which he ruled alone. Louis's usual title was ''imperator augustus'' ("august emperor"), but he used ''imperator Romanorum'' ("emperor of the Romans") after his conquest of Bari in 871, which led to poor relations with the Eastern Roman Empire. He was called ''imperator Italiae'' ("emperor of Italy") in West Francia while the Byzantines called him ''Basileus Phrangias'' ("Emperor of Francia"). The chronicler Andreas of Bergamo, who is the main source for Louis's activities in southern Italy, notes that "after his death a great tribulation came to Italy." Childhood Louis was born in 825, the eldest son of the junior emperor Lothair I and his wife Ermengarde of Tours. His father was the son of the reigning emperor, Louis the Pious. Little is known about his early life, except that he grew up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishops Of Milan
The Archdiocese of Milan ( it, Arcidiocesi di Milano; la, Archidioecesis Mediolanensis) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Italy which covers the areas of Milan, Monza, Lecco and Varese. It has long maintained its own Latin liturgical rite usage, the Ambrosian rite, which is still used in the greater part of the diocesan territory. Among its past archbishops, the better known are Ambrose, Charles Borromeo, Pope Pius XI and Pope Paul VI. The Archdiocese of Milan is the metropolitan see of the ecclesiastical province of Milan, which includes the suffragan dioceses of Bergamo, Brescia, Como, Crema, Cremona, Lodi, Mantova, Pavia, and Vigevano."Archdiocese of Milano " '' |
859 Deaths
__FORCETOC__ Year 859 ( DCCCLIX) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events By place Europe * January 15 – Battle of St. Quentin: Frankish forces, led by Humfrid, defeat King Louis the German at Saint-Quentin (Northern France). Humfrid is enfeoffed with the County of Autun, and appointed Margrave of Burgundy, by King Charles the Bald. * Summer – The Viking chieftains Hastein and Björn Ironside (a son of Ragnar Lodbrok) begin an expedition, and sail from the Loire River with a fleet of 62 ships, to raid cities and monasteries in the Mediterranean Sea. * Viking raiders invade the Kingdom of Pamplona (Western Pyrenees), and capture King García Íñiguez I, somewhere in the Andalusian heartland. They extort a ransom, rising to around 70,000 gold dinars. * The Russian city of Novgorod is first mentioned in the Sofia Chronicles. * Winter – The weather is so severe that the Adriatic Sea freezes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Footnotes
A note is a string of text placed at the bottom of a page in a book or document or at the end of a chapter, volume, or the whole text. The note can provide an author's comments on the main text or citations of a reference work in support of the text. Footnotes are notes at the foot of the page while endnotes are collected under a separate heading at the end of a chapter, volume, or entire work. Unlike footnotes, endnotes have the advantage of not affecting the layout of the main text, but may cause inconvenience to readers who have to move back and forth between the main text and the endnotes. In some editions of the Bible, notes are placed in a narrow column in the middle of each page between two columns of biblical text. Numbering and symbols In English, a footnote or endnote is normally flagged by a superscripted number immediately following that portion of the text the note references, each such footnote being numbered sequentially. Occasionally, a number between brack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
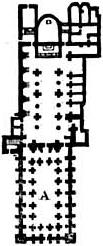
Sant'Ambrogio, Milan
The Basilica of Sant'Ambrogio (official name: ''Basilica romana minore collegiata abbaziale prepositurale di Sant'Ambrogio'') is a church in the center of Milan, northern Italy. History One of the most ancient churches in Milan, it was built by St. Ambrose in 379–386, in an area where numerous martyrs of the Roman persecutions had been buried. The first name of the church was in fact ''Basilica Martyrum''. When St. Ambrose arrived in Milan, the local churches were in conflict with each other over the conflict between Arianism and the Nicene Creed as well as numerous local issues. He was firmly in support of the First Council of Nicaea, Nicene side of the conflict and wanted to make northern Italy into a pro-Rome stronghold. He did this through both preaching and construction. He built three or four churches surrounding the city; Basilica Apostolorum (now San Nazaro in Brolo), Basilica Virginum (now Basilica of San Simpliciano, San Simpliciano), and Basilica Martyrum (which w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Pavia (850)
Council of Pavia or Synod of Pavia may refer to: *Council of Pavia (698), ended the schism of the Three Chapters in northern Italy * Council of Pavia (850), prohibited bishops from hunting * Council of Pavia (962), attended by Otto the Great * Council of Pavia (997), dealt with the illegal transfer of archbishop of Mainz and the bigamous marriage of Robert II of France * Council of Pavia (998), held by the Emperor Otto III * Council of Pavia (1018), dealt with church reform * Council of Pavia (1022), dealt with church reform * Council of Pavia (1046), held by the Henry III of Germany on his way to be crowned emperor * Council of Pavia (1160), convened by Frederick Barbarossa to end a papal schism *Council of Siena In the Catholic Church, the Council of Siena (1423–1424) marked a somewhat inconclusive stage in the Conciliar movement that was attempting reforms in the Church. If it had continued, it would have qualified as an ecumenical council. In the of ... (1423–1424), whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
, established_title = Founded , established_date = 753 BC , founder = King Romulus (legendary) , image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg , map_caption = The territory of the ''comune'' (''Roma Capitale'', in red) inside the Metropolitan City of Rome (''Città Metropolitana di Roma'', in yellow). The white spot in the centre is Vatican City. , pushpin_map = Italy#Europe , pushpin_map_caption = Location within Italy##Location within Europe , pushpin_relief = yes , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Italy , subdivision_type2 = Region , subdivision_name2 = Lazio , subdivision_type3 = Metropolitan city , subdivision_name3 = Rome Capital , government_footnotes= , government_type = Strong Mayor–Council , leader_title2 = Legislature , leader_name2 = Capitoline Assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missus Dominicus
A ''missus dominicus'' (plural ''missi dominici''), Latin for "envoy of the lord uler or ''palace inspector'', also known in Dutch as Zendgraaf (German: ''Sendgraf''), meaning "sent Graf", was an official commissioned by the Frankish king or Holy Roman Emperor to supervise the administration, mainly of justice, in parts of his dominions too remote for frequent personal visits. As such, the ''missus'' performed important intermediary functions between royal and local administrations. There are superficial points of comparison with the original Roman ''corrector'', except that the ''missus'' was sent out on a regular basis. Four points made the ''missi'' effective as instruments of the centralized monarchy: the personal character of the ''missus'', yearly change, isolation from local interests and the free choice of the king. Reign of Charlemagne Based on Merovingian ''ad hoc'' arrangements, using the form ''missus regis'' (the "king's envoy") and sending a layman and an ecclesias ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis The Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquitaine from 781. As the only surviving son of Charlemagne and Hildegard, he became the sole ruler of the Franks after his father's death in 814, a position which he held until his death, save for the period 833–34, during which he was deposed. During his reign in Aquitaine, Louis was charged with the defence of the empire's southwestern frontier. He conquered Barcelona from the Emirate of Córdoba in 801 and asserted Frankish authority over Pamplona and the Basques south of the Pyrenees in 812. As emperor he included his adult sons, Lothair, Pepin and Louis, in the government and sought to establish a suitable division of the realm among them. The first decade of his reign was characterised by several tragedies and embarrassments, no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |