|
Andrew Tracey
Andrew Tracey (born 5 May 1936, Durban, South Africa) is a South African ethnomusicologist, promoter of African music, composer, folk singer, band leader, and actor. His father, Hugh Tracey (1903–1977), pioneered the study of traditional African music in the 1920s–1970s, created the International Library of African Music (ILAM) in 1954, and started the company African Musical Instruments (AMI) which manufactured the first commercial kalimbas in the 1950s. Tracey continued and complemented the work of his father in a variety of ways. With brother Paul, he co-wrote and performed in the world musical revue ''Wait a Minim!'' which travelled around the world for seven years. With his father and brother, Tracey wrote the first instructional materials for the Hugh Tracey kalimbas which were being sent around the world in the 1960s. Upon his father's death in 1977, Tracey took over his father's role as director of ILAM, which he filled until his retirement in 2005, and his wife He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johnny Carson
John William Carson (October 23, 1925 – January 23, 2005) was an American television host, comedian, writer and producer. He is best known as the host of ''The Tonight Show Starring Johnny Carson'' (1962–1992). Carson received six Primetime Emmy Awards, the Television Academy's 1980 Governor's Award and a 1985 Peabody Award. He was inducted into the Television Academy Hall of Fame in 1987. Carson was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 1992 and received a Kennedy Center Honor in 1993.Johnny CarsonEncyclopædia Britannica Online (2009). In Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved July 30, 2009. During World War II, Carson served in the Navy. After the war, Carson started a career in radio. He moved from radio to TV and followed Jack Paar as the host of the late night talk show, ''Tonight''. Although his show was already successful by the end of the 1960s, during the 1970s, Carson became an American icon and remained so even after his retirement in 1992. He adopt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Zimbabwe
Zimbabwean music is heavily reliant on the use of instruments such as the mbira, Ngoma drums and hosho. Their music symbolizes much more than a simple rhythm, as the folk and pop style styled music was used as a symbol of hope for Zimbabweans looking to gain independence from Rhodesia. Music has played a significant role in the history of Zimbabwe, from a vital role in the traditional Bira ceremony used to call on ancestral spirits, to protest songs during the struggle for independence. The community in Zimbabwe used music to voice their resistance to their oppression, as one of the only weapons they had available to fight back with. In the eighties, the Music of Zimbabwe was at the center of the African Music scene thanks to genres such as Sungura and Jit. However, several performers were banned by state TV and radio leading to the closing of several music venues. Musical Genres Sungura Sungura is the most popular musical genre in Zimbabwe. It emerged in 1953, in a time w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Africa
Given the vastness of the African continent, its music is diverse, with regions and nations having many distinct musical traditions. African music includes the genres amapiano, Jùjú, Fuji, Afrobeat, Highlife, Makossa, Kizomba, and others. The music and dance of the African diaspora, formed to varying degrees on African musical traditions, include American music like Dixieland jazz, blues, jazz, and many Caribbean genres, such as calypso (see kaiso) and soca. Latin American music genres such as cumbia, conga, rumba, son cubano, salsa music, bomba, samba and zouk were founded on the music of enslaved Africans, and have in turn influenced African popular music. Like the music of Asia, India and the Middle East, it is a highly rhythmic music. The complex rhythmic patterns often involving one rhythm played against another to create a polyrhythm. The most common polyrhythm plays three beats on top of two, like a triplet played against straight notes. Sub-Saharan African mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodes University
Rhodes University is a public university, public research university located in Makhanda, Eastern Cape, Makhanda (Grahamstown) in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. It is one of four universities in the province. Established in 1904, Rhodes University is the province's oldest university, and it is the sixth oldest South African university in continuous operation, being preceded by the University of the Free State (1904), University of Witwatersrand (1896), University of South Africa (1873) as the University of the Cape of Good Hope, Stellenbosch University (1866) and the University of Cape Town (1829). Rhodes was founded in 1904 as Rhodes University College, named after Cecil Rhodes, through a grant from the Rhodes Trust. It became a constituent college of the University of South Africa in 1918 before becoming an independent university in 1951. The university had an enrolment of over 8,000 students in the 2015 academic year, of whom just over 3,600 lived in 51 residenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grahamstown
Makhanda, also known as Grahamstown, is a town of about 140,000 people in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. It is situated about northeast of Port Elizabeth and southwest of East London, Eastern Cape, East London. Makhanda is the largest town in the Makana Local Municipality, and the seat of the municipal council. It also hosts Rhodes University, the Eastern Cape Division of the High Court of South Africa, High Court, the South African Library for the Blind (SALB), Diocese of Grahamstown, a diocese of the Anglican Church of Southern Africa, and 6 South African Infantry Battalion. Furthermore, located approximately 3 km south-east of the town lies the world renowned Waterloo Farm lagerstätte, Waterloo Farm, the only estuarine fossil site in the world from 360 million years ago with exceptional soft-tissue preservation. The town's name-change from Grahamstown to Makhanda was officially gazetted on 29 June 2018. The town was officially renamed to Makhanda in memory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and east. Although Kazungula, it does not border Zimbabwe, less than 200 metres (660 feet) of the Botswanan right bank of the Zambezi, Zambezi River separates the two countries. Namibia gained independence from South Africa on 21 March 1990, following the Namibian War of Independence. Its capital and largest city is Windhoek. Namibia is a member state of the United Nations (UN), the Southern African Development Community (SADC), the African Union (AU) and the Commonwealth of Nations. The driest country in sub-Saharan Africa, Namibia has been inhabited since pre-historic times by the San people, San, Damara people, Damara and Nama people. Around the 14th century, immigration, immigrating Bantu peoples arrived as part of the Bantu expansion. Since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa: Due to the historical .... The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The southern part of the country includes a substantial portion of Lake Victoria, shared with Kenya and Tanzania. Uganda is in the African Great Lakes region. Uganda also lies within the Nile, Nile basin and has a varied but generally a modified equatorial climate. It has a population of around 49 million, of which 8.5 million live in the Capital city, capital and largest city of Kampala. Uganda is named after the Buganda kingdom, which encompasses a large portion of the south of the country, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the north, Tanzania to the northeast, Malawi to the east, Mozambique to the southeast, Zimbabwe and Botswana to the south, Namibia to the southwest, and Angola to the west. The capital city of Zambia is Lusaka, located in the south-central part of Zambia. The nation's population of around 19.5 million is concentrated mainly around Lusaka in the south and the Copperbelt Province to the north, the core economic hubs of the country. Originally inhabited by Khoisan peoples, the region was affected by the Bantu expansion of the thirteenth century. Following the arrival of European exploration of Africa, European explorers in the eighteenth century, the British colonised the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

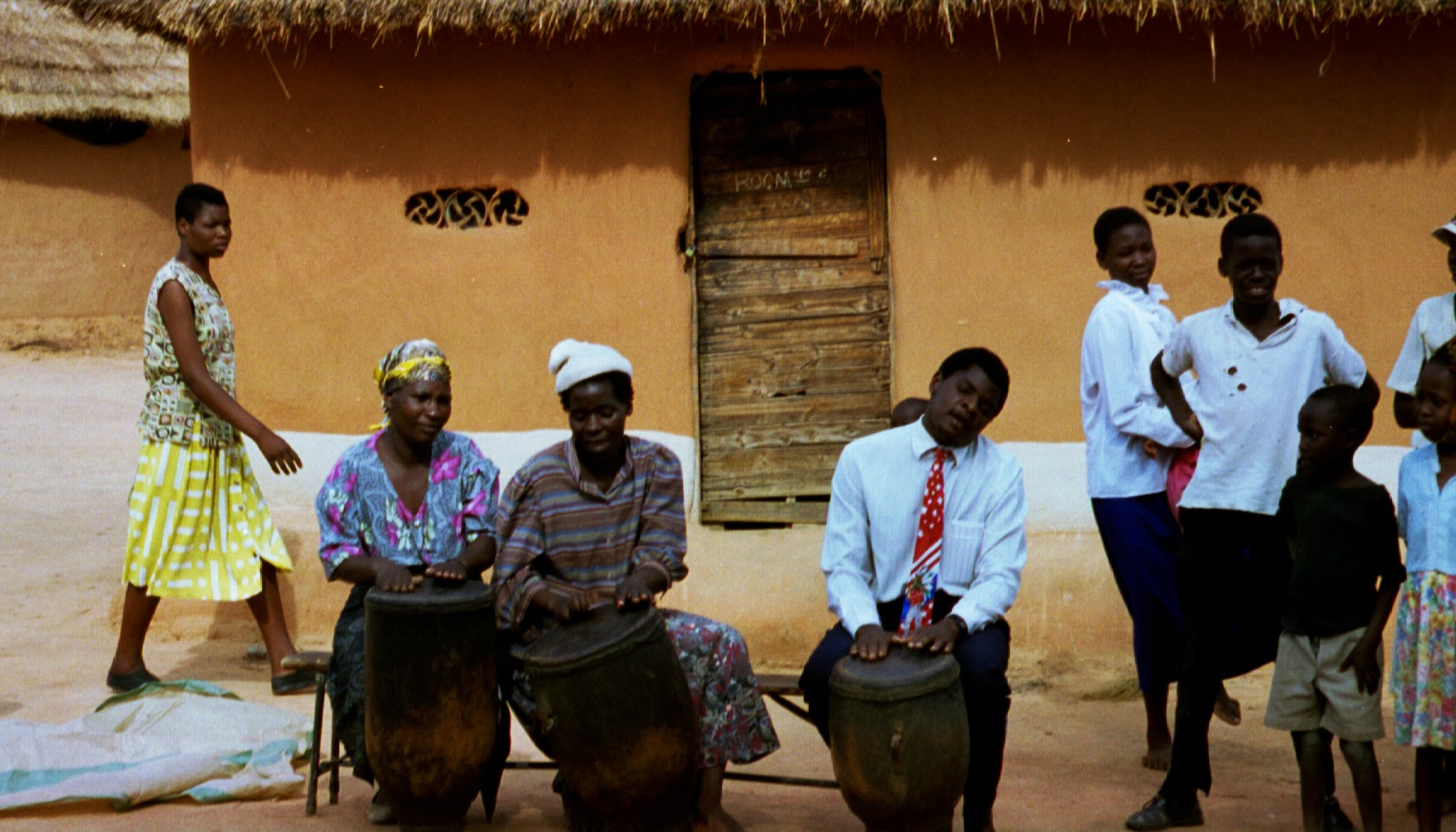


_-_Copy.jpg)