|
Ancylostoma Braziliense
''Ancylostoma braziliense'' is a species of hookworm belonging to the genus ''Ancylostoma''. It is an intestinal parasite of domestic cats and dogs. Severe infection is often fatal to these pets, especially in puppies and kittens. The infection is particularly endemic in the southern United States. It is most often confused with the zoonotic hookworm species '' Ancylostoma ceylanicum'' because of their uncanny resemblance. ''Ancyclostoma braziliense'' larvae can cause accidental infection in humans called cutaneous larval migration or creeping eruption, which produces severe itching in the skin. It is the most common skin infection in tropical region, particularly along the beaches of the Caribbean. Discovery and history When ''A. braziliense'' was described by Gomes de Faria in 1910, and ''A. ceylanicum'' by Arthur Looss in 1911, the two species were regarded as synonymous because of their apparent similarities in almost all respect. Especially in 1913, comparison of specimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hookworm
Hookworms are intestinal, blood-feeding, parasitic roundworms that cause types of infection known as helminthiases. Hookworm infection is found in many parts of the world, and is common in areas with poor access to adequate water, sanitation, and hygiene. In humans, infections are caused by two main species of roundworm, belonging to the genera ''Ancylostoma'' and '' Necator''. In other animals the main parasites are species of ''Ancylostoma''. Species The two most common types of hookworm that infect humans are ''Ancylostoma duodenale'' and '' Necator americanus''. Hookworm species that are known to infect domestic cats are '' Ancylostoma braziliense'' and '' Ancylostoma tubaeforme''. Wild cats are infected by '' Ancylostoma pluridentatum''. Dogs are commonly infected by '' Ancylostoma caninum'', but may also be infected by '' Uncinaria stenocephala'' and ''Ancylostoma braziliense''. In Asia, '' Ancylostoma ceylanicum'' is endemic among dogs and cats and infects humans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and east of Sumatra. The island is politically divided among three countries: Malaysia and Brunei in the north, and Indonesia to the south. Approximately 73% of the island is Indonesian territory. In the north, the East Malaysian states of Sabah and Sarawak make up about 26% of the island. The population in Borneo is 23,053,723 (2020 national censuses). Additionally, the Malaysian federal territory of Labuan is situated on a small island just off the coast of Borneo. The sovereign state of Brunei, located on the north coast, comprises about 1% of Borneo's land area. A little more than half of the island is in the Northern Hemisphere, including Brunei and the Malaysian portion, while the Indonesian portion spans the Northern and Southern he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzimidazole
Benzimidazole is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound. This bicyclic compound may be viewed as fused rings of the aromatic compounds benzene and imidazole. It is a colorless solid. Preparation Benzimidazole is produced by condensation of o-phenylenediamine with formic acid,. or the equivalent trimethyl orthoformate: :C6H4(NH2)2 + HC(OCH3)3 → C6H4N(NH)CH + 3 CH3OH 2-substituted derivatives are obtained when the condensation is conducted with aldehydes in place of formic acid, followed by oxidation.Robert A. Smiley "Phenylene- and Toluenediamines" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Reactions Benzimidazole is a base: :C6H4N(NH)CH + H+ → 6H4(NH)2CHsup>+ It can also be deprotonated with stronger bases: :C6H4N(NH)CH + LiH → Li 6H4N2CH + H2 The imine can be alkylated and also serves as a ligand in coordination chemistry. The most prominent benzimidazole complex features ''N''-ribosyl-dimethylbenzimidazole as found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scatology
In medicine and biology, scatology or coprology is the study of feces. Scatological studies allow one to determine a wide range of biological information about a creature, including its diet (and thus where it has been), health and diseases such as tapeworms. A comprehensive study of scatology was documented by John Gregory Bourke under the title '' Rites of All Nations'' (1891), with a 1913 German translation including a foreword by Sigmund Freud. An abbreviated version of the work was published as ''The Portable Scatalog'' in 1994. Etymology The word derives from the Greek ( ) meaning "dung, feces"; ''coprology'' derives from the Greek of similar meaning. Psychology In psychology, a scatology is an obsession with excretion or excrement, or the study of such obsessions. In sexual fetishism, scatology (usually abbreviated ''scat'') refers to coprophilia, when a being is sexually aroused by fecal matter, whether in the use of feces in various sexual acts, watching so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Definitive Host
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' ( symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include animals playing host to parasitic worms (e.g. nematodes), cells harbouring pathogenic (disease-causing) viruses, a bean plant hosting mutualistic (helpful) nitrogen-fixing bacteria. More specifically in botany, a host plant supplies food resources to micropredators, which have an evolutionarily stable relationship with their hosts similar to ectoparasitism. The host range is the collection of hosts that an organism can use as a partner. Symbiosis Symbiosis spans a wide variety of possible relationships between organisms, differing in their permanence and their effects on the two parties. If one of the partners in an association is much larger than the other, it is generally known as the host. In parasitism, the parasite benefits at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatitis
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can vary from small to covering the entire body. Dermatitis is often called eczema, and the difference between those terms is not standardized. The exact cause of the condition is often unclear. Cases may involve a combination of allergy and poor venous return. The type of dermatitis is generally determined by the person's history and the location of the rash. For example, irritant dermatitis often occurs on the hands of those who frequently get them wet. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs upon exposure to an allergen, causing a hypersensitivity reaction in the skin. Prevention of atopic dermatitis is typically with essential fatty acids, and may be treated with moisturizers and steroid creams. The steroid creams should generally be o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creeping Eruption
Creep, Creeps or CREEP may refer to: People * Creep, a creepy person Politics * Committee for the Re-Election of the President (CRP), mockingly abbreviated as CREEP, an fundraising organization for Richard Nixon's 1972 re-election campaign Arts, entertainment, and media Films * ''Creeps'' (film), a 1956 short starring the Three Stooges * ''The Creeps'' (film), a 1997 film directed by Charles Band * ''Creep'' (2004 film), a 2004 British-German horror film * ''Creep'' (2014 film), an American found-footage horror film ** ''Creep 2'', 2017 American found-footage horror film; sequel to the 2014 film Gaming * "Creep", a carpet of bio-matter Zerg colonies produce in the ''StarCraft'' video game franchise Literature * ''Creeps'' (novel), 2013 young adult novel by Darren Hynes * '' The Creeping'', 2015 young adult novel by Alexandra Sirowy Music Groups * Creep (band), American electronic music band * Deli Creeps, an avant-garde band from San Francisco (1990–2007) * The Creeps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
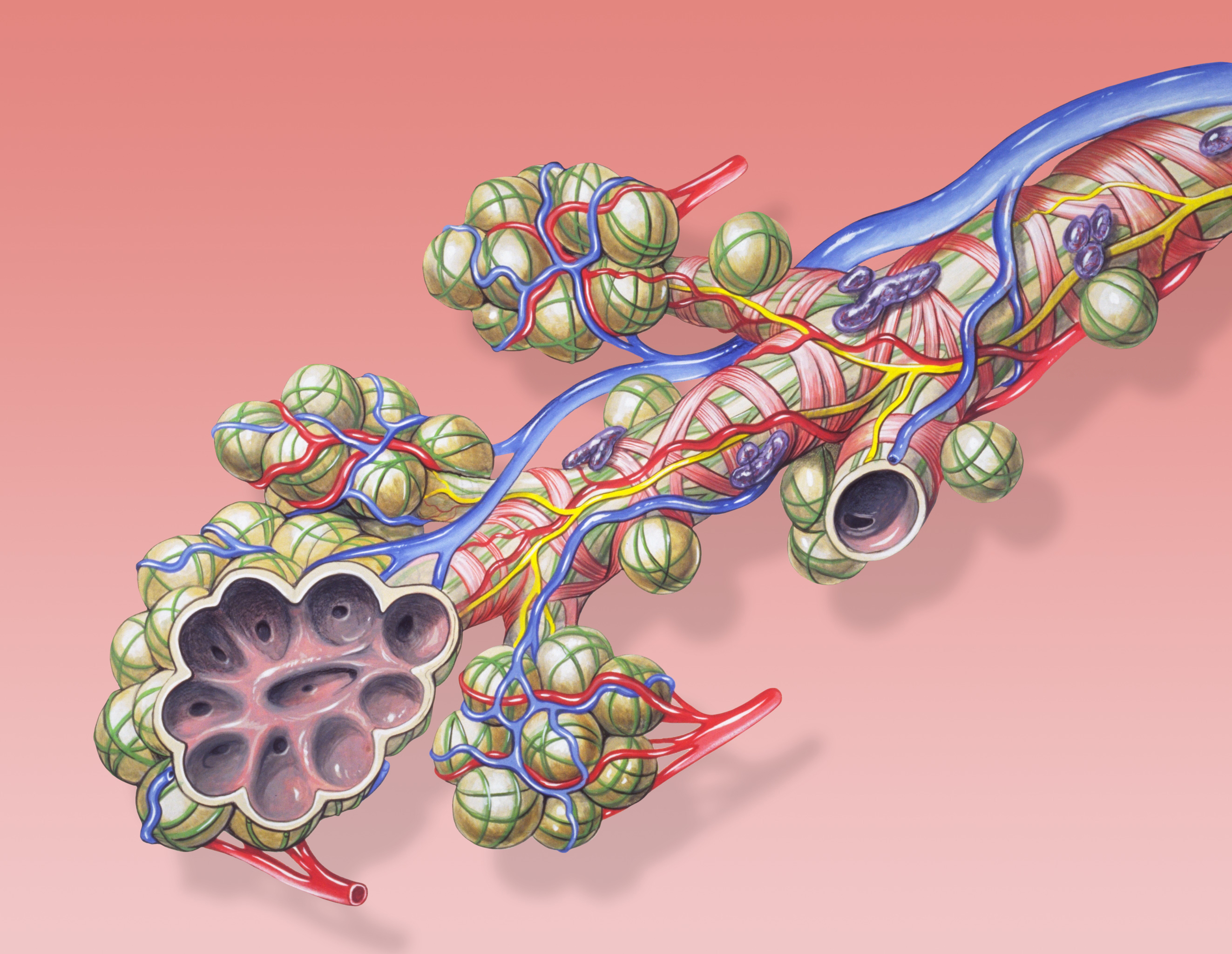
Pulmonary Alveolus
A pulmonary alveolus (plural: alveoli, from Latin ''alveolus'', "little cavity"), also known as an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume. Alveoli are first located in the respiratory bronchioles that mark the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely in these bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Across the membrane oxygen is diffused into the capillaries and carbon dioxide released from the capillaries into the alveoli to be breathed out. Alveoli are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the air and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In earlier tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible. Humans have two lungs, one on the left an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
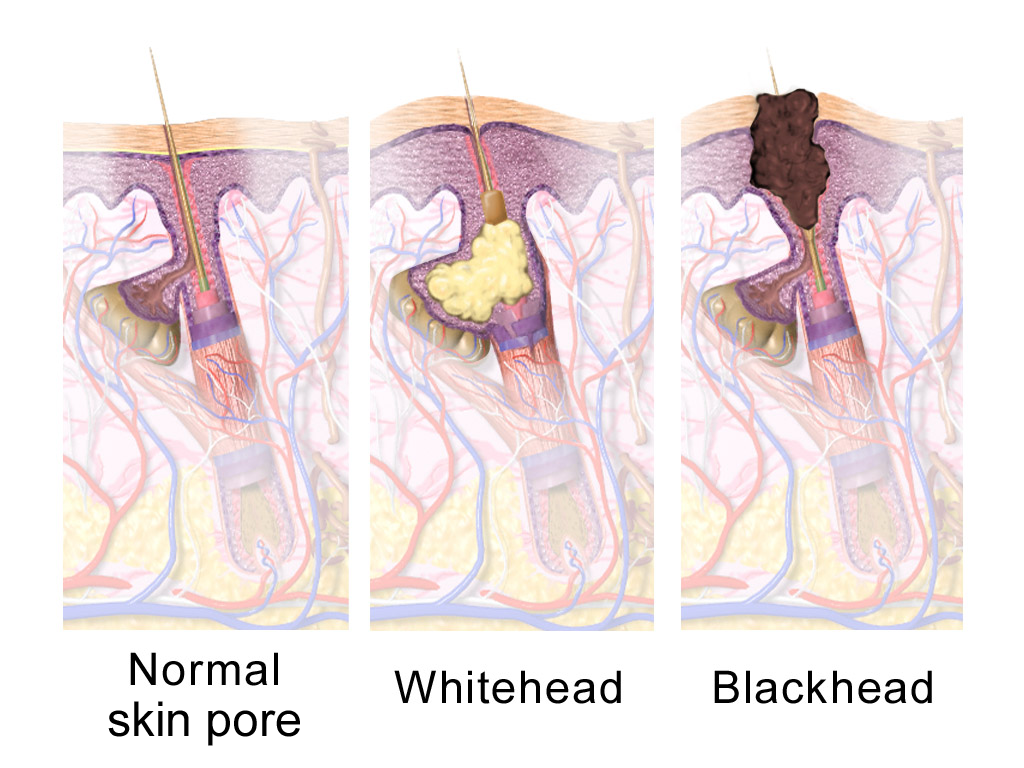
Sebaceous Gland
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number on the face and scalp, but also on all parts of the skin except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In the eyelids, meibomian glands, also called tarsal glands, are a type of sebaceous gland that secrete a special type of sebum into tears. Surrounding the female nipple, areolar glands are specialized sebaceous glands for lubricating the nipple. Fordyce spots are benign, visible, sebaceous glands found usually on the lips, gums and inner cheeks, and genitals. Structure Location Sebaceous glands are found throughout all areas of the skin, except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There are two types of sebaceous glands, those connected to hair follicles and those that exist independently. Sebaceous glands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)