|
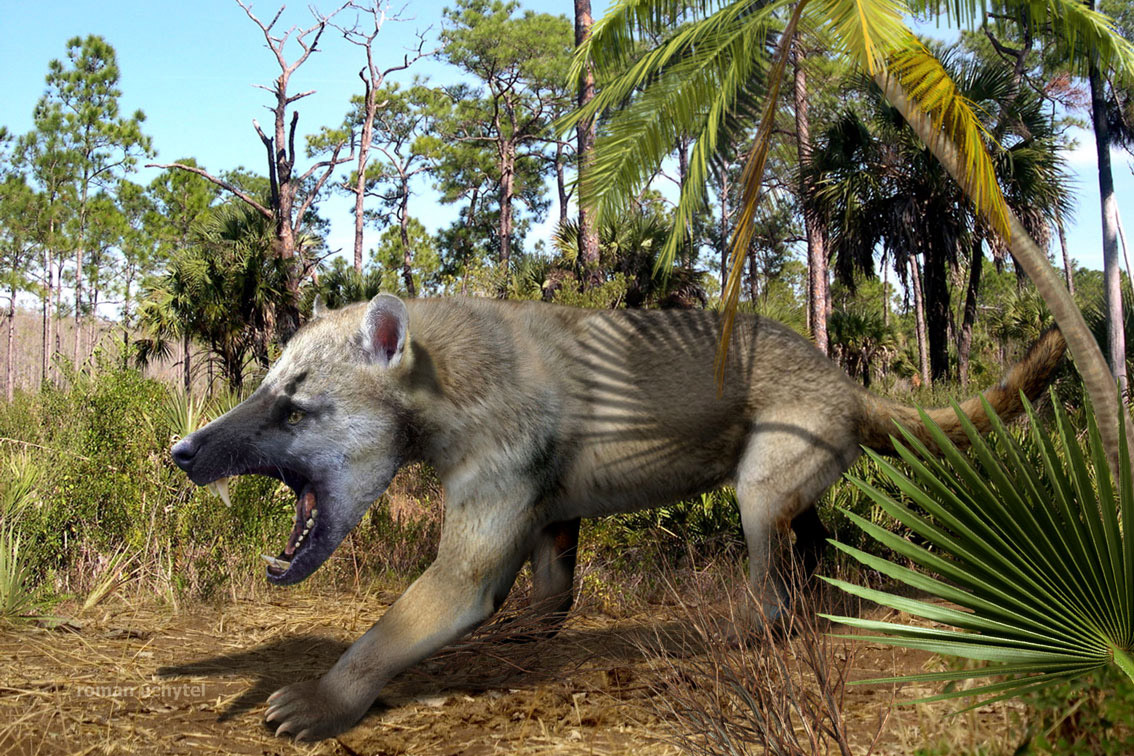
Amphicyonid
Amphicyonidae is an extinct family of terrestrial carnivorans belonging to the suborder Caniformia. They first appeared in North America in the middle Eocene (around 45 mya), spread to Europe by the late Eocene (35 mya), and appear in Asia, and Africa by the early Miocene (23 mya). They had largely disappeared worldwide by the late Miocene (8 mya), with the latest recorded species at the end of the Miocene in Pakistan. They were among the first carnivorans to evolve large body size. Later in their history, they came into competition with hesperocyonine and borophagine canids. As dogs evolved similar body sizes and cranial and dental adaptations, the rise of these groups may have led to their extinction. Amphicyonids are often colloquially referred to as "bear-dogs". Taxonomy The family was erected by Haeckel (1886) lso attributed to Trouessart (1885) Their exact position has long been disputed. Some early paleontologists defined them as members of the family Canidae, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thaumastocyoninae
Thaumastocyoninae is an extinct subfamily of amphicyonids, large terrestrial carnivores, which inhabited what is now Europe during the Miocene epoch. The subfamily was erected by Hürzeler (1940), and is defined by the complete suppression of m1 metaconid, reduction of the premolars, except the p4, which is reinforced, and the oblique abrasion of the teeth, and the possession of hypercarnivorous tendencies. Thaumastocyonines are poorly known, with only about 65 dental specimens, most of those isolated teeth, being known as of 2020,Morlo M, Bastl K, Habersetzer J, Engel T, Lischewsky B, Lutz H, von Berg A, Rabenstein R, Nagel D. 2020The apex of amphicyonid hypercarnivory: solving the riddle of ''Agnotherium antiquum'' Kaup, 1833 (Mammalia, Carnivora).Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 39(5):e1705848 DOI 10.1080/02724634.2019.1705848. although more complete remains have recently been discovered. Evolution and phylogeny The first thaumastocyonines appear during the earliest Miocen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphoenodon
''Daphoenodon'' is an extinct genus of terrestrial carnivore, which lived in the early Miocene and belonged to the family Amphicyonidae ("bear dogs") of the suborder Caniformia Caniformia is a suborder within the order Carnivora consisting of "dog-like" carnivorans. They include dogs (wolves, foxes, etc.), bears, raccoons, and mustelids. The Pinnipedia (seals, walruses and sea lions) are also assigned to this group. .... The species of ''Daphoenodon'' are characterized by limbs that are specialized in fore and aft movement, as well as a body alignment that results in a lengthened stride. Hunt, R.M. (2009). "Long-Legged Pursuit Carnivorans (Amphicyonidae, Daphoeninae) from the Early Miocene of North America". ''Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History.'' 318: 1-95. Species ''D.'' ''falkenbachi'' was a larger species that was found in northern Goshen, southeastern Platte Counties, Wyoming, and Nebraska. A smaller species, ''D. skinneri'', was found in southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caniformia
Caniformia is a suborder within the order Carnivora consisting of "dog-like" carnivorans. They include dogs (wolves, foxes, etc.), bears, raccoons, and mustelids. The Pinnipedia (seals, walruses and sea lions) are also assigned to this group. The center of diversification for the Caniformia is North America and northern Eurasia. Caniformia stands in contrast to the other suborder of Carnivora, the Feliformia ("cat-like" carnivorans), the center of diversification of which was in Africa and southern Asia. Description Most members of this group have nonretractile claws (the fisher, marten, sea otter ( forepaws only), red panda, and ringtail, and some foxes have retractile or semi-retractile claws) and tend to be plantigrade (with the exception of the Canidae). Other traits that separate the Caniformia from the Feliformia is that caniforms have longer jaws and more teeth, with less specialized carnassial teeth. They also tend more towards omnivory and opportunistic feeding, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphicyoninae
Amphicyoninae is a subfamily of extinct bear-dogs, large terrestrial carnivores belonging to the suborder Caniformia and which inhabited North America, Eurasia, and Africa from ~37.2—2.6 Ma. Amphicyoninae existed for approximately ~. Amphicyoninae was named by Trouessart (1885). It was assigned to Canidae by Matthew (1902); to Ursidae by Ginsburg (1977); and to Amphicyonidae by Hunt (1998). Genera include: *''Agnotherium'', found in both Europe and N. Africa *''Amphicyon'', found in both Europe and N. America *''Cynelos'', synonyms include ''Absonodaphoenus'' (from Florida) and ''Hecubides'' (from Africa), endemic to N. America *'' Cynodictis'' *''Ischyrocyon'', ''Hadrocyon'' is a synonym, endemic to N. America *''Goupilictis'' *''Magericyon'' *''Pliocyon'', endemic to N. America *''Pseudocyon'', ''Amphicyonopsis'' is a synonym, endemic to Europe and N. America *''Ysengrinia'', found in both Europe and N. America Fossil distribution Specimens have been recovered from: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family Ursidae. They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Northern Hemisphere and partially in the Southern Hemisphere. Bears are found on the continents of North America, South America, Europe, and Asia. Common characteristics of modern bears include large bodies with stocky legs, long snouts, small rounded ears, shaggy hair, plantigrade paws with five nonretractile claws, and short tails. While the polar bear is mostly carnivorous, and the giant panda feeds almost entirely on bamboo, the remaining six species are omnivorous with varied diets. With the exception of courting individuals and mothers with their young, bears are typically solitary animals. They may be diurnal or nocturnal and have an excellent sense of smell. Despite their heavy build and awkward gait, they are adept runners, cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemicyonidae
Hemicyoninae is an extinct subfamily of Ursidae, often called dog bears (literally "half dog" (Ancient Greek, Greek: )). They were bear-like carnivorans living in Europe, North America, Africa and Asia during the Oligocene through Miocene epochs 33.9–5.3 Annum, Ma, existing for approximately . They are sometimes classified as a separate family (biology), family.McKenna, Malcolm C., and Bell, Susan K. 1997. ''Classification of Mammals Above the Species Level.'' Columbia University Press, New York, 631 pp. Systematics * Subfamily †Hemicyoninae (Frick, 1926) ** Tribe †Cephalogalini (de Bonis, 2013) *** †''Adelpharctos'' (de Bonis, 1971) **** †''Adelpharctos ginsburgi'' (de Bonis, 2011) **** †''Adelpharctos mirus'' (de Bonis, 1971) *** †''Cyonarctos'' (de Bonis, 2013) **** †''Cyonarctos dessei'' (de Bonis, 2013) *** †''Phoberogale'' (Ginsburg & Morales, 1995) **** †''Phoberogale minor'' (Filhol, 1877) **** †''Phoberogale bonali'' (Helbing, 1928) **** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphoeninae
The Daphoeninae are an extinct subfamily of dog-like, terrestrial carnivores, which belonged to the family Amphicyonidae of the suborder Caniformia. The group inhabited North America from the Middle Eocene subepoch to the Middle Miocene subepoch 42—15.97 million years ago (Mya), existing for about . Fossil distribution ''Daphoenus'' fossils found in late Oligocene rocks in the Great Plains are dated about 28 million years old. ''Daphoenus'' survived to 27 Mya in the Pacific Northwest in the John Day beds of Oregon. Other sites include: Alachua County, Florida (Whitneyan) estimated at 31.1—24.3 Ma., Tecuya Canyon, California (Arikareean age) 30.8—20.6 Ma., Haystack Member Formation, Wheeler County, Oregon (Hemingfordian) 20.6—16.3 Mya, Lac Pelletier, Alberta, Canada (Duchesnean The Duchesnean North American Stage on the geologic timescale is a North American Land Mammal Age (NALMA), with an age from 42 to 38 million years BP, representing . It falls within the Eoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivora
Carnivora is a Clade, monophyletic order of Placentalia, placental mammals consisting of the most recent common ancestor of all felidae, cat-like and canidae, dog-like animals, and all descendants of that ancestor. Members of this group are formally referred to as carnivorans, and have evolved to specialize in eating flesh. The order is the fifth largest order of mammals, comprising at least 279 species. Carnivorans live on every major landmass and in a variety of habitats, ranging from the cold polar regions to the hyper-arid region of the Sahara Desert to the open seas. They come in a very large array of different body plans in contrasting shapes and sizes. Carnivora can be divided into two subclades: the cat-like Feliformia and the dog-like Caniformia, which are differentiated based on the structure of their ear bones and cranial features. The feliforms include families such as the felidae, cats, the hyenas, the mongooses and the viverridae, civets. The majority of felifor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borophaginae
The extinct Borophaginae form one of three subfamilies found within the canid family. The other two canid subfamilies are the extinct Hesperocyoninae and extant Caninae. Borophaginae, called "bone-crushing dogs", were endemic to North America during the Oligocene to Pliocene and lived roughly 34—2.5 million years ago, existing for about . Origin The Borophaginae descended from the subfamily Hesperocyoninae. The earliest and most primitive borophagine is the genus ''Archaeocyon'', which is a small fox-sized animal mostly found in the fossil beds in western North America. The borophagines soon diversified into several major groups. They evolved to become considerably larger than their predecessors, and filled a wide range of niches in late Cenozoic North America, from small omnivores to powerful, bear-sized carnivores, such as ''Epicyon''. Species There are 66 identified borophagine species, including 18 new ones that range from the Orellan to Blancan ages. A phylogenetic anal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canidae
Canidae (; from Latin, ''canis'', "dog") is a biological family of dog-like carnivorans, colloquially referred to as dogs, and constitutes a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). There are three subfamilies found within the canid family, which are the extinct Borophaginae and Hesperocyoninae, and the extant Caninae. The Caninae are known as canines, and include domestic dogs, wolves, coyotes, foxes, jackals and other extant and extinct species. Canids are found on all continents except Antarctica, having arrived independently or accompanied human beings over extended periods of time. Canids vary in size from the gray wolf to the fennec fox. The body forms of canids are similar, typically having long muzzles, upright ears, teeth adapted for cracking bones and slicing flesh, long legs, and bushy tails. They are mostly social animals, living together in family units or small groups and behaving cooperatively. Typically, only the dominant pair in a group bree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
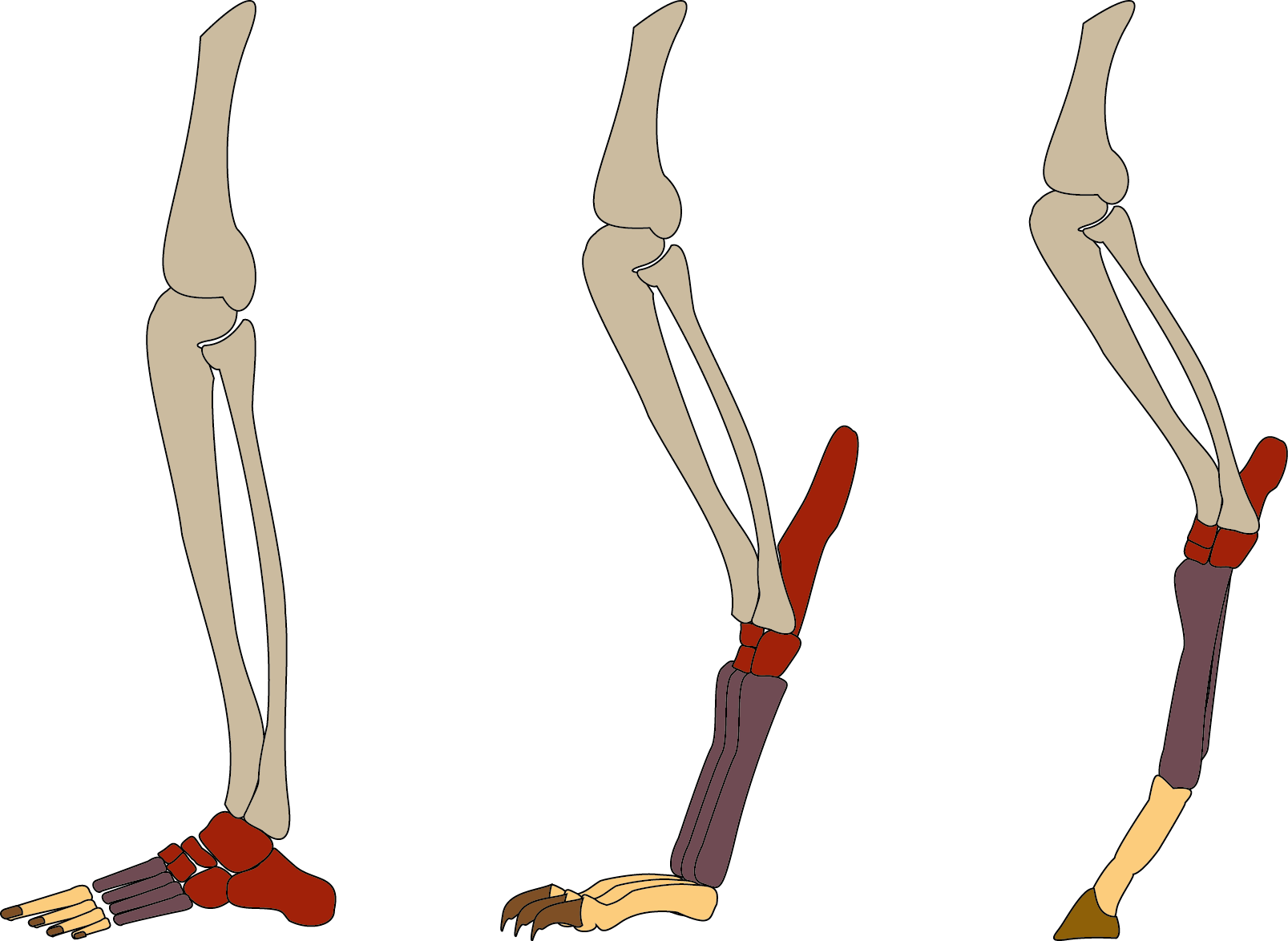
Digitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade () locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin ''digitus'', 'finger', and ''gradior'', 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (metatarsals) touching the ground, and the rest of its foot lifted. Digitigrades include walking birds (what many assume to be bird knees are actually ankles), cats, dogs, and many other mammals, but not plantigrades or unguligrades. Digitigrades generally move more quickly and quietly than other animals. There are anatomical differences between the limbs of plantigrades, like humans, and both unguligrade and digitigrade limbs. Digitigrade and unguligrade animals have relatively long carpals and tarsals, and the bones which would correspond to the human ankle are thus set much higher in the limb than in a human. In a digitigrade animal, this effectively lengthens the foot, so much so that what are often thought of as a digitigrade animal's "hands" and "feet" correspon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.jpg)