|
Almen Strip
An Almen strip is a thin strip of SAE 1070 steel used to quantify the intensity of a shot peening process. Developed and patented by John O. Almen, the strip was originally supported by 2 knife edges; later improvements see it being supported on 4 small balls. The strip is placed in the chamber in place of the item to be shot peened, usually near to an area of the item where the result is deemed critical, sometimes located by a special fixture. Compressive stress introduced by the peening operation causes the strip to deform into an arch, which is measured using a gauge. Almen strips are classified into 3 types: 'A', 'N', and 'C'. They differ in their thickness, while they have the same width and length. *Almen strip of "A" type is predominantly used for shot peening with cast shot or cut wire shot. *"N" type strips are used usually for glass bead peen and ceramic bead peen. *"C" type almen strips are used more rarely and are thicker than the other types. Although similar, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAE Steel Grades
The SAE steel grades system is a standard alloy numbering system (SAE J1086 - Numbering Metals and Alloys) for steel grades maintained by SAE International. In the 1930s and 1940s, the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) and SAE were both involved in efforts to standardize such a numbering system for steels. These efforts were similar and overlapped significantly. For several decades the systems were united into a joint system designated the AISI/SAE steel grades. In 1995 the AISI turned over future maintenance of the system to SAE because the AISI never wrote any of the specifications. Today steel quotes and certifications commonly make reference to both SAE and AISI, not always with precise differentiation. For example, in the alloy/grade field, a certificate might refer to "4140", "AISI 4140", or "SAE 4140", and in most light-industrial applications any of the above is accepted as adequate, and considered equivalent, for the job at hand, as long as the specific specificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant typically need an additional 11% chromium. Because of its high tensile strength and low cost, steel is used in buildings, infrastructure, tools, ships, trains, cars, machines, electrical appliances, weapons, and rockets. Iron is the base metal of steel. Depending on the temperature, it can take two crystalline forms (allotropic forms): body-centred cubic and face-centred cubic. The interaction of the allotropes of iron with the alloying elements, primarily carbon, gives steel and cast iron their range of unique properties. In pure iron, the crystal structure has relatively little resistance to the iron atoms slipping past one another, and so pure iron is quite ductile, or soft and easily formed. In steel, small amounts of carbon, other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shot Peening
Shot peening is a cold working process used to produce a compressive residual stress layer and modify the mechanical properties of metals and composites. It entails striking a surface with shot (round metallic, glass, or ceramic particles) with force sufficient to create plastic deformation."Shot Peening," ''Tool and Manufacturing Engineers Handbook'' (TMEH), Volume 3, Society of Manufacturing Engineers, 1985 In machining, shot peening is used to strengthen and relieve stress in components like steel automobile crankshafts and connecting rods. In architecture it provides a muted finish to metal. Shot peening is similar mechanically to sandblasting, though its purpose is not to remove material, but rather it employs the mechanism of plasticity to achieve its goal, with each particle functioning as a ball-peen hammer. Details Peening a surface spreads it plastically, causing changes in the mechanical properties of the surface. Its main application is to avoid the propagation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cut Wire Shot
Shot peening is a cold working process used to produce a compressive residual stress layer and modify the mechanical properties of metals and composites. It entails striking a surface with shot (round metallic, glass, or ceramic particles) with force sufficient to create plastic deformation."Shot Peening," ''Tool and Manufacturing Engineers Handbook'' (TMEH), Volume 3, Society of Manufacturing Engineers, 1985 In machining, shot peening is used to strengthen and relieve stress in components like steel automobile crankshafts and connecting rods. In architecture it provides a muted finish to metal. Shot peening is similar mechanically to sandblasting, though its purpose is not to remove material, but rather it employs the mechanism of plasticity (physics), plasticity to achieve its goal, with each particle functioning as a ball-peen hammer. Details Peening a surface spreads it plastically, causing changes in the mechanical properties of the surface. Its main application is to av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
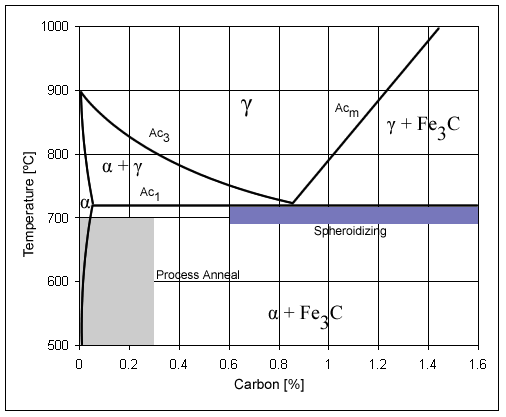
Plain Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is a steel with carbon content from about 0.05 up to 2.1 percent by weight. The definition of carbon steel from the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) states: * no minimum content is specified or required for chromium, cobalt, molybdenum, nickel, niobium, titanium, tungsten, vanadium, zirconium, or any other element to be added to obtain a desired alloying effect; * the specified minimum for copper does not exceed 0.40%; * or the maximum content specified for any of the following elements does not exceed the percentages noted: manganese 1.65%; silicon 0.60%; copper 0.60%. The term ''carbon steel'' may also be used in reference to steel which is not stainless steel; in this use carbon steel may include alloy steels. High carbon steel has many different uses such as milling machines, cutting tools (such as chisels) and high strength wires. These applications require a much finer microstructure, which improves the toughness. Carbon steel is a popular metal choic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AISI Steel Grades
The SAE steel grades system is a standard alloy numbering system (SAE J1086 - Numbering Metals and Alloys) for steel grades maintained by SAE International. In the 1930s and 1940s, the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI) and SAE were both involved in efforts to standardize such a numbering system for steels. These efforts were similar and overlapped significantly. For several decades the systems were united into a joint system designated the AISI/SAE steel grades. In 1995 the AISI turned over future maintenance of the system to SAE because the AISI never wrote any of the specifications. Today steel quotes and certifications commonly make reference to both SAE and AISI, not always with precise differentiation. For example, in the alloy/grade field, a certificate might refer to "4140", "AISI 4140", or "SAE 4140", and in most light-industrial applications any of the above is accepted as adequate, and considered equivalent, for the job at hand, as long as the specific specificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation induced by either mechanical indentation or abrasion. In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard metals such as titanium and beryllium are harder than soft metals such as sodium and metallic tin, or wood and common plastics. Macroscopic hardness is generally characterized by strong intermolecular bonds, but the behavior of solid materials under force is complex; therefore, hardness can be measured in different ways, such as scratch hardness, indentation hardness, and rebound hardness. Hardness is dependent on ductility, elastic stiffness, plasticity, strain, strength, toughness, viscoelasticity, and viscosity. Common examples of hard matter are ceramics, concrete, certain metals, and superhard materials, which can be contrasted with soft matter. Measuring hardness There are three main types of hardness measurements: ''scratch' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
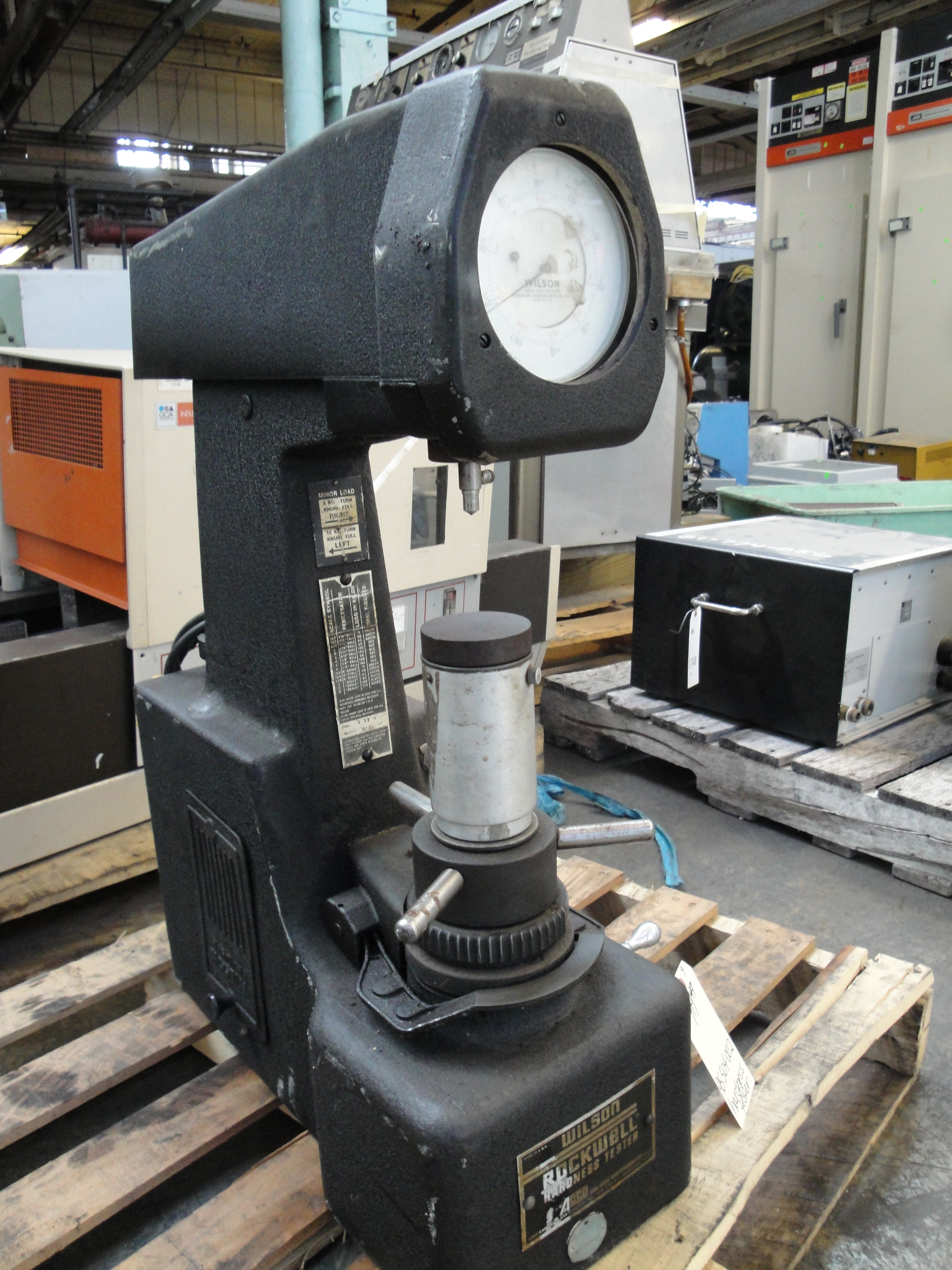
Rockwell Scale
The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). There are different scales, denoted by a single letter, that use different loads or indenters. The result is a dimensionless number noted as HRA, HRB, HRC, etc., where the last letter is the respective Rockwell scale. When testing metals, indentation hardness correlates linearly with tensile strength. History The differential depth hardness measurement was conceived in 1908 by Viennese professor Paul Ludwik in his book ''Die Kegelprobe'' (crudely, "the cone test"). The differential-depth method subtracted out the errors associated with the mechanical imperfections of the system, such as backlash and surface imperfections. The Brinell hardness test, invented in Sweden, was developed earlier – in 1900 – but it was slow, not use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Automotive Engineers
SAE International, formerly named the Society of Automotive Engineers, is a United States-based, globally active professional association and standards developing organization for engineering professionals in various industries. SAE International's world headquarters is in Warrendale, Pennsylvania, 20 miles north of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Principal emphasis is placed on global transport industries such as aerospace, automotive, and commercial vehicles. The organization adopted the name SAE International to reflect the broader emphasis on mobility. SAE International has over 138,000 global members. Membership is granted to individuals, rather than companies. Aside from its standardization efforts, SAE International also devotes resources to projects and programs in STEM education, professional certification, and collegiate design competitions. For historical legacy reasons, the label "SAE" is commonly used on tools and hardware in North America to indicate United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almen Round
An Almen round is a thin round disk used to quantify the intensity of a shot peening process. Developed in 1994 by Rudolf Bosshard in Switzerland, it is a modification of the Almen strip method, which is used worldwide as a surface treatment testing method in the field of shot peening. The basic principle is the same, but due to the simple shape and minimized size, the Almen round is more suitable for automated processing and installation on dummy rigs. Also instead of the Almen block according SAE International, SAE J442, here a matching device is used and if connected to electronic processing unit, the Almen value according AMS-S-13165 (predecessor MIL-S-13165 Rev.C) can be evaluated in one run. Test specimen The Almen round is a circular cutting from an original Almen strip normally in material SAE 1070. It can be either of a "A", "C" or "N" type offered in various quality grades. The standard strip allows the splitting into four pieces rounds, which have a diameter of 18.7&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shot Peening
Shot peening is a cold working process used to produce a compressive residual stress layer and modify the mechanical properties of metals and composites. It entails striking a surface with shot (round metallic, glass, or ceramic particles) with force sufficient to create plastic deformation."Shot Peening," ''Tool and Manufacturing Engineers Handbook'' (TMEH), Volume 3, Society of Manufacturing Engineers, 1985 In machining, shot peening is used to strengthen and relieve stress in components like steel automobile crankshafts and connecting rods. In architecture it provides a muted finish to metal. Shot peening is similar mechanically to sandblasting, though its purpose is not to remove material, but rather it employs the mechanism of plasticity to achieve its goal, with each particle functioning as a ball-peen hammer. Details Peening a surface spreads it plastically, causing changes in the mechanical properties of the surface. Its main application is to avoid the propagation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |