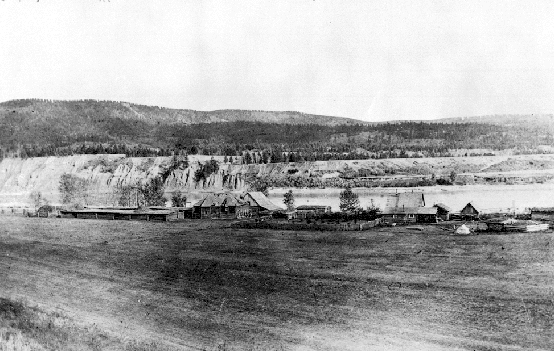|
Alexandria, British Columbia
Alexandria or Fort Alexandria is a National Historic Site of Canada on the Fraser River in British Columbia, and was the end of the Old Cariboo Road and the Cariboo Wagon Road. It is located on Highway 97, north of 100 Mile House and south of Quesnel. History On June 21, 1793, explorer Alexander MacKenzie reached the shores of the First Nations village at what would become Alexandria. He was told by the people of the village that the river was not safe for navigation beyond that point. Mackenzie heeded their advice and he and his party turned around and returned upriver to what would become the town of Quesnellemouth, (later Quesnel) and continued on to Bella Coola. In 1821, the North West Company erected a fort at Alexandria, the last the company would build before it was merged the same year with the Hudson's Bay Company. The fort was named Alexandria in honour of Alexander Mackenzie. They also built a granary and wintered their horses there. Alexandria became a key way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Alexandria
Alexandria or Fort Alexandria is a National Historic Site of Canada on the Fraser River in British Columbia, and was the end of the Old Cariboo Road and the Cariboo Wagon Road. It is located on Highway 97, north of 100 Mile House and south of Quesnel. History On June 21, 1793, explorer Alexander MacKenzie reached the shores of the First Nations village at what would become Alexandria. He was told by the people of the village that the river was not safe for navigation beyond that point. Mackenzie heeded their advice and he and his party turned around and returned upriver to what would become the town of Quesnellemouth, (later Quesnel) and continued on to Bella Coola. In 1821, the North West Company erected a fort at Alexandria, the last the company would build before it was merged the same year with the Hudson's Bay Company. The fort was named Alexandria in honour of Alexander Mackenzie. They also built a granary and wintered their horses there. Alexandria became a key way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cariboo Gold Rush
The Cariboo Gold Rush was a gold rush in the Colony of British Columbia, which later joined the Canadian province of British Columbia. The first gold discovery was made at Hills Bar in 1858, followed by more strikes in 1859 on the Horsefly River, and on Keithley Creek and Antler Creek in 1860. The actual rush did not begin until 1861, when these discoveries were widely publicized. By 1865, following the strikes along Williams Creek, the rush was in full swing. Towns grew up, the most famous of these being Barkerville, now preserved as a heritage site and tourist attraction. Other important towns of the Cariboo gold rush era were Keithley Creek, Quesnel Forks or simply "the Forks", Antler, Richfield, Quesnellemouthe (which would later be shortened to Quesnel), Horsefly and, around the site of the Hudson's Bay Company's fort of the same name, Alexandria. Williams Creek Richfield Richfield was the first strike on Williams Creek, and became the seat of government in the reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of National Historic Sites Of Canada
National Historic Sites of Canada (french: Lieux historiques nationaux du Canada) are places that have been designated by the federal Minister of the Environment on the advice of the Historic Sites and Monuments Board of Canada (HSMBC), as being of national historic significance. Parks Canada, a federal agency, manages the National Historic Sites program. As of July 2021, there were 999 National Historic Sites, 172 of which are administered by Parks Canada; the remainder are administered or owned by other levels of government or private entities. The sites are located across all ten provinces and three territories, with two sites located in France (the Beaumont-Hamel Newfoundland Memorial and Canadian National Vimy Memorial). There are related federal designations for National Historic Events and National Historic Persons. Sites, Events and Persons are each typically marked by a federal plaque of the same style, but the markers do not indicate which designation a subject has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ghost Towns In British Columbia ...
This is a list of ghost towns in the Canadian province of British Columbia, including those still partly inhabited or even overtaken by modern towns, as well as those completely abandoned or derelict. Region of location and associated events or enterprises are included. See also * Fisherman, British Columbia *List of mines in British Columbia * Paulson, British Columbia * Teepee, British Columbia References :*Bruce Ramsey, Ghost Towns of British Columbia, Mitchell Press, Vancouver, 1963, OCLC: 39371 :*T W Paterson, Encyclopedia of ghost towns & mining camps of British Columbia, Stagecoach Pub., Langley, 1979, ISBN {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Ghost Towns In British Columbia * British Columbia Ghost towns Ghost Town(s) or Ghosttown may refer to: * Ghost town, a town that has been abandoned Film and television * ''Ghost Town'' (1936 film), an American Western film by Harry L. Fraser * ''Ghost Town'' (1956 film), an American Western film by Alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chilcotin War
The Chilcotin War, the Chilcotin Uprising or the Bute Inlet Massacre was a confrontation in 1864 between members of the Tsilhqot'in (Chilcotin) people in British Columbia and white road construction workers. Fourteen men employed by Alfred Waddington in the building of a road from Bute Inlet were killed, as well as a number of men with a pack-train near Anahim Lake and a settler at Puntzi Lake. Background In 1862, Alfred Waddington began lobbying the press and his political allies for support to build a wagon road from Bute Inlet to Fort Alexandria, where it would connect to the Cariboo Road and continue on to the goldfields at Barkerville. He received approval for the construction early in 1863. According to Waddington, it would reduce land travel from to and the total days consumed in packing freight from 37 days to 22 compared to the route through Yale and the Fraser Canyon known as the Cariboo Road and favoured by Governor Douglas. The Bute Inlet Wagon Road was to foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klatsassin
Lhatŝ’aŝʔin (also known as Klatsassan or Klattasine; died 1864), a chief of the Chilcotin ( Tsilhqot'in) people, led a small group of warriors in attacks on road-building crews near Bute Inlet, British Columbia, in April and May 1864. The road crews had been starving and underpaying Tsilhqot'in workers, which provoked Lhatŝ’aŝʔin to declare war. On 29 April 1864, Lhatŝ’aŝʔin arrived at a ferry site up the Homathko River. He and his warriors killed ferry-keeper Tim Smith, plundering the food and stores kept there. The next day, Lhatŝ’aŝʔin attacked the unsuspecting and unarmed road workers at the main camp, killing 9. Further up the trail, the band came upon foreman William Brewster and three of his men. All were killed, Brewster's body being mutilated and left while the other three were thrown in the river. The band also killed William Manning, a settler at Puntzi Lake. Proceeding into the interior to escape justice, Lhatŝ’aŝʔin and his followers ambushed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) certified the global eradication of the disease in 1980, making it the only human disease to be eradicated. The initial symptoms of the disease included fever and vomiting. This was followed by formation of ulcers in the mouth and a skin rash. Over a number of days, the skin rash turned into the characteristic fluid-filled blisters with a dent in the center. The bumps then scabbed over and fell off, leaving scars. The disease was spread between people or via contaminated objects. Prevention was achieved mainly through the smallpox vaccine. Once the disease had developed, certain antiviral medication may have helped. The risk of death was about 30%, with higher rates among babies. Often, those who survived had extensive scarring of their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homathko River
The Homathko River is one of the major rivers of the southern Coast Mountains of the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is one of the few rivers that penetrates the range from the interior Chilcotin Country to the coastal inlets of the Pacific Ocean. The Homathko River reaches the sea at the head of Bute Inlet, just west of the mouth of the Southgate River. The Homathko River Valley is one of the most difficult to navigate. The frigid waters make crossing impossible and the valley itself is lined with devil's club. It is also home to many grizzly bears. Geography The mountains flanking the Homathko River are the highest in the Coast Mountains, and include Mount Waddington west of the river in the Waddington Range and Mount Queen Bess east of the river, adjacent to the Homathko Icefield. Also flanking the Homathko River on the west are the Niut Range, which is in the angle of the Homathko and its main west fork, Mosley Creek, and the Whitemantle Range, which is to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Waddington
Alfred Penderell Waddington (October 2, 1801 – February 26, 1872), during his later years, was actively involved in the Colony of Vancouver Island in what later became the province of British Columbia, Canada. From 1860 to 1861 he was a representative of the Victoria District in the House of Assembly of the Colony of Vancouver Island. He was also the first colonial Superintendent of Education from 1865 to 1867 and was an advocate of free public education. Waddington is also remembered for planning the ill-fated Waddington's Road at Bute Inlet. The road was intended to be a shorter route to the Cariboo Gold Rush goldfields and was intended to run from the Pacific Coast via Bute Inlet to Fort Alexandria, but instead resulted in the Chilcotin War. Early years Alfred Waddington completed his early education in England, attended a school in Paris and then attended the University of Göttingen in Germany. In 1850, he moved to California and joined a partnership of wholesale gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bute Inlet
, image = Bute Inlet.jpg , image_size = 260px , alt = , caption = , image_bathymetry = , alt_bathymetry = , caption_bathymetry = , location = Strathcona RD, British Columbia , group = , coordinates = , type = , etymology = , part_of = , inflow = Homathko River, Southgate River , rivers = , outflow = Cordero Channel (west) Calm Channel (south) , oceans = , catchment = , basin_countries = , agency = , designation = , date-built = , engineer = , date-flooded = , length = , width = , area = , depth = , max-depth = , volume = , residence_time = , salinity = , shore = , elevation = , temperature_high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
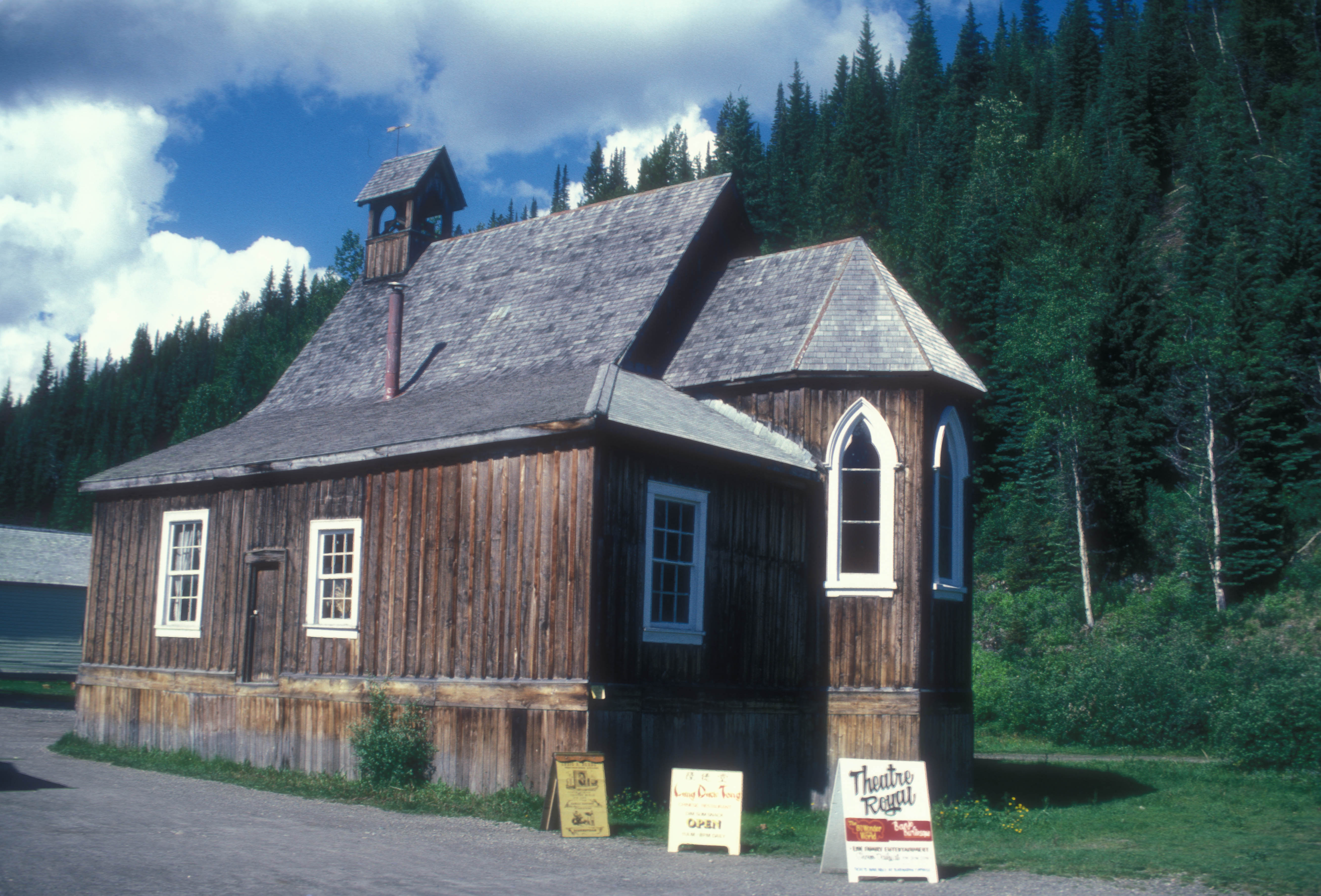
Barkerville
Barkerville was the main town of the Cariboo Gold Rush in British Columbia, Canada, and is preserved as a historic town. It is located on the north slope of the Cariboo Plateau near the Cariboo Mountains east of Quesnel. BC Highway 26, which follows the route of the Cariboo Wagon Road, the original access to Barkerville, goes through it. History Founding Barkerville is located on the western edge of the Cariboo Mountains in British Columbia. It was named after Billy Barker from Cambridgeshire, England, who was among those who first struck gold at the location in 1861. His claim was the richest and the most famous. Barkerville was built up almost overnight, and was a case of "growth via word of mouth". It grew as fast as the word of Barker's strike spread. His claim would eventually yield 37,500 ounces (1,065 kg/2,350 lb) of gold. Before the construction of the Cariboo Wagon Road, people hauled their own supplies to Barkerville, either on their backs or in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |