|
Alemannic Separatism
Alemannic Separatism is a historical movement of separatism of the Alemannic-German-speaking areas of Austria, France, and Germany (viz., South Baden, Swabia (viz. most of Württemberg and Bavarian Swabia), Alsace and Vorarlberg), aiming at a unification with the Swiss Confederacy (later Switzerland). The historic origins of the movement lay in the Napoleonic era (ca. 1805–1815) and it was briefly revived both after the end of World War I (1919) and after the end of World War II (1946–1952). Alemannic dialects The term "Alemannic" for the group of High German dialects was introduced by Johann Peter Hebel in 1803, who named them for the Alamanni tribes of the Migration period. The Alemannic-speaking areas of Germany were separated into Baden and Württemberg, parts of Swabia were integrated into Bavaria in 1805; the Alemannic dialects were not the only dialects in those states (e.g. in Baden and Württemberg the Northern parts speak a Rhine Franconian dialects, E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alemannic Language Location Map In 1950-de
Alemannic (''Alamannic'') or Alamanni may refer to: * Alemannic German, a dialect family in the Upper German branch of the German languages and its speakers * Alemanni, a confederation of Suebian Germanic tribes in the Roman period * Alamanni (surname) See also *Alemannia (other) *Alemannic separatism Alemannic Separatism is a historical movement of separatism of the Alemannic-German-speaking areas of Austria, France, and Germany (viz., South Baden, Swabia (viz. most of Württemberg and Bavarian Swabia), Alsace and Vorarlberg), aiming at ... * Allemand (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Peter Hebel
Johann Peter Hebel (10 May 1760 – 22 September 1826) was a German short story writer, dialectal poet, Lutheranism, Lutheran theologian and pedagogue, most famous for a collection of Alemannic German, Alemannic lyric poems (''Allemannische Gedichte'') and one of German tales (''Schatzkästlein des rheinischen Hausfreundes''"Treasure Chest of Rhenish Tales"). Born in Basel, Hebel entered primary school in 1766 and joined a Latin school three years later; he visited the schools in Basel during summer and in Hausen and Schopfheim respectively in the nearby Wiesental during winter. After the death of his mother in 1773, he remained at school, graduating with the help of friends from the ''Gymnasium illustre'' of Karlsruhe in 1778 and going on to study theology. He became a home tutor, an assistant preacher, an assistant teacher, a subdeacon and, in 1798, a professor and court deacon. Hebel was interested in botany, natural history and other subjects. His literary work began ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nazi Regime
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a dictatorship. Under Hitler's rule, Germany quickly became a totalitarian state where nearly all aspects of life were controlled by the government. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", alluded to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which Hitler and the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945 after just 12 years when the Allies defeated Germany, ending World War II in Europe. On 30 January 1933, Hitler was appointed chancellor of Germany, the head of government, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vienna
en, Viennese , iso_code = AT-9 , registration_plate = W , postal_code_type = Postal code , postal_code = , timezone = CET , utc_offset = +1 , timezone_DST = CEST , utc_offset_DST = +2 , blank_name = Vehicle registration , blank_info = W , blank1_name = GDP , blank1_info = € 96.5 billion (2020) , blank2_name = GDP per capita , blank2_info = € 50,400 (2020) , blank_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank_info_sec1 = 0.947 · 1st of 9 , blank3_name = Seats in the Federal Council , blank3_info = , blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD , blank_info_sec2 = .wien , website = , footnotes = , image_blank_emblem = Wien logo.svg , blank_emblem_size = Vienna ( ; german: Wien ; ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Austria
The Republic of German-Austria (german: Republik Deutschösterreich or ) was an unrecognised state that was created following World War I as an initial rump state for areas with a predominantly German-speaking and ethnic German population within what had been the Austro-Hungarian Empire, with plans for eventual unification with Germany. The territories covered an area of , with 10.4 million inhabitants. In practice, however, its authority was limited to the Danubian and Alpine provinces which had been the core of Cisleithania. Much of its claimed territory was ''de facto'' administered by the newly formed Czechoslovakia, and internationally recognized as such. Attempts to create German-Austria under these auspices were ultimately unsuccessful, especially since union with Germany was forbidden in the Treaty of Versailles, and the new state of the First Austrian Republic was created in 1919. Background The Austrian Empire of the Habsburgs had been reconstituted as a dual mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederation Of The Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine, also known as Napoleonic Germany, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria and Russia at the Battle of Austerlitz. Its creation brought about the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire shortly afterward. The Confederation of the Rhine lasted from 1806 to 1813.Hans A. Schmitt. "Germany Without Prussia: A Closer Look at the Confederation of the Rhine". ''German Studies Review'' 6, No. 4 (1983), pp 9–39. The founding members of the confederation were German princes of the Holy Roman Empire. They were later joined by 19 others, altogether ruling a total of over 15 million subjects. This granted a significant strategic advantage to the French Empire on its eastern frontier by providing a buffer between France and the two largest German states, Prussia and Austria (which also controlled substantial non-German lands). Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the Revolutionary Wars. He was the ''de facto'' leader of the French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814 and again in 1815. Napoleon's political and cultural legacy endures to this day, as a highly celebrated and controversial leader. He initiated many liberal reforms that have persisted in society, and is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. His wars and campaigns are studied by militaries all over the world. Between three and six million civilians and soldiers perished in what became known as the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon was born on the island of Corsica, not long af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Bavarian Language
Bavarian (german: Bairisch , Bavarian: ''Boarisch'') or alternately Austro-Bavarian, is a West Germanic language, part of the Upper German family, together with Alemannic and East Franconian. Bavarian is spoken by approximately 12 million people in an area of around , making it the largest of all German dialects. It can be found in the German state of Bavaria (especially Old Bavaria), most of the Republic of Austria (excluding Vorarlberg) and the Italian region of South Tyrol.Rowley (2011), p. 300; In 2008, 45 percent of Bavarians claimed to use only dialect in everyday communication. Prior to 1945, Bavarian was also prevalent in parts of the southern Czech Republic and western Hungary. The difference between Bavarian and Standard High German is larger than the difference between Danish and Norwegian or between Czech and Slovak (Prof Dr. Robert Hinderling); as such, there is disagreement regarding its classification. The International Organization for Standardization classifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Franconian German
South Franconian (german: Südfränkisch) or South Rhine Franconian (german: Südrheinfränkisch) is an Upper German dialect which is spoken in the northernmost part of Baden-Württemberg in Germany, around Karlsruhe, Mosbach and Heilbronn. Like closely related East Franconian it is a transitional dialect, which unites elements of Central German and Upper German. The language area is located in the transient zone between Rhine Franconian dialects (Hessian and Palatinate German) in the north and Alemannic German ( Low Alemannic and Swabian German) in the south. South Franconian is one of the High German The High German dialects (german: hochdeutsche Mundarten), or simply High German (); not to be confused with Standard High German which is commonly also called ''High German'', comprise the varieties of German spoken south of the Benrath and ... dialects with the lowest number of speakers. South Franconian is not considered a separate dialect by some observers. The scope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
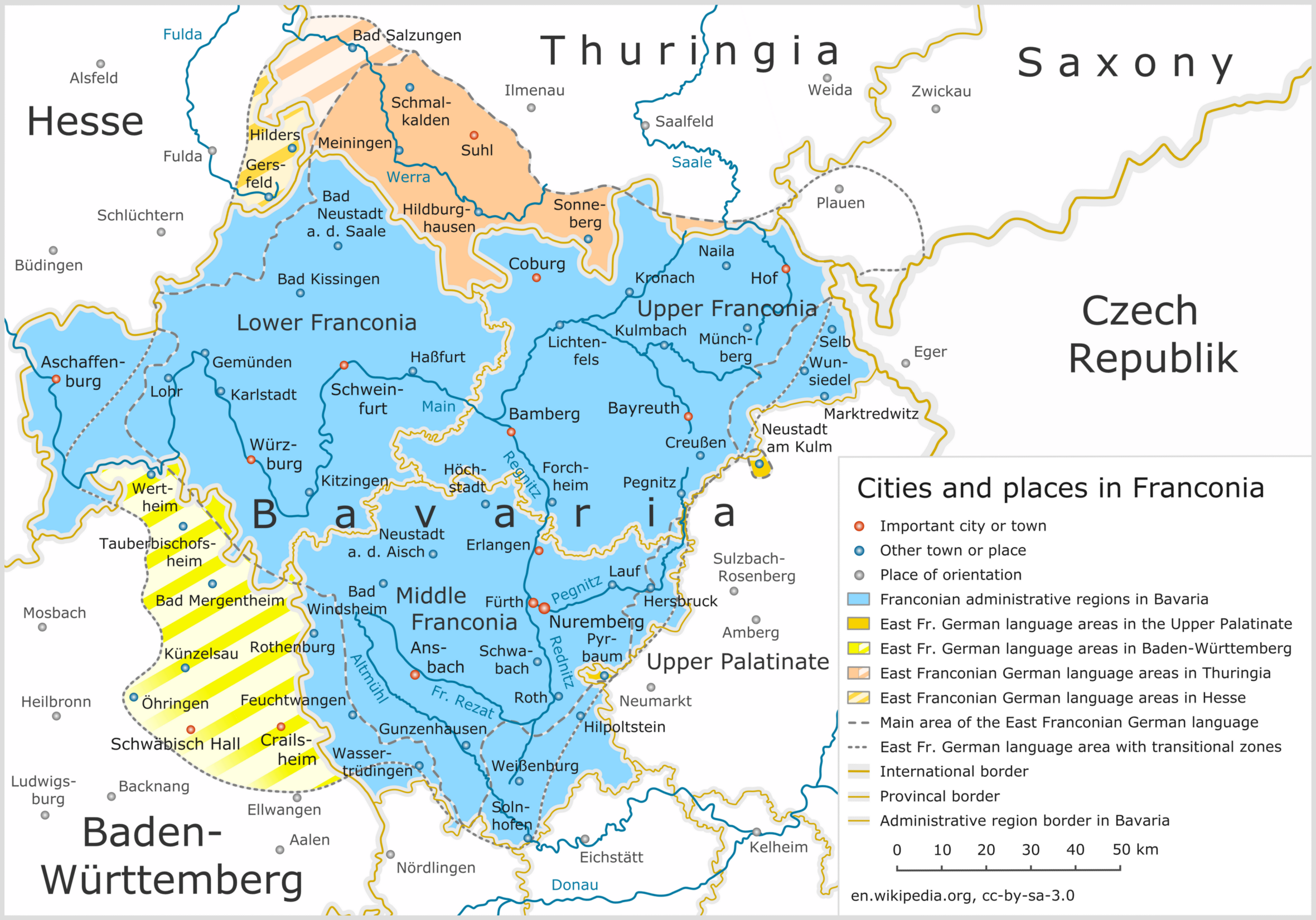
East Franconian German
East Franconian (german: Ostfränkisch) or Mainfränkisch, usually referred to as Franconian (') in German, is a dialect which is spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Meiningen, Bad Mergentheim, and Crailsheim. The major subgroups are ' (spoken in Lower Franconia and southern Thuringia), ' (spoken in Upper and Middle Franconia) and ' (spoken in some parts of Middle Franconia and Hohenlohe). In the transitional area between Rhine Franconian in the northwest and the Austro-Bavarian dialects in the southeast, East Franconian has elements of Central German and Upper German. The same goes only for South Franconian German in adjacent Baden-Württemberg. East Franconian is one of the German dialects with the highest number of speakers. The scope of East Franconian is disputed, because it overlaps with neighbouring dialects like Bavarian and Swabian in the sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine Franconian Dialects
__NOTOC__ Rhenish Franconian or Rhine Franconian (german: Rheinfränkisch ) is a dialect chain of West Central German. It comprises the varieties of German spoken across the western regions of the states of Saarland, Rhineland-Palatinate, northwest Baden-Württemberg, and Hesse in Germany. It is also spoken in northeast France, in the eastern part of the of Moselle in the Lorraine region, and in the north-west part of Bas-Rhin in Alsace. To the north, it is bounded by the Sankt Goar line (or '' line'') which separates it from Moselle Franconian; to the south, it is bounded by the Main line which is also referred to as the ''Speyer line'' which separates it from the Upper German dialects. Subgroups Cornelia Stroh: ''Sprachkontakt und Sprachbewußtsein: Eine soziolinguistische Studie am Beispiel Ost-Lothringens.'' Gunter Narr Verlag Tübingen, Tübingen, 1993, p. 34 * or Hessian * ** or Palatinate German ** or Lorraine Franconian See also * Saarland (section ''Local dialec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is second in population only to North Rhine-Westphalia, but due to its large size its population density is below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, became an ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)