|
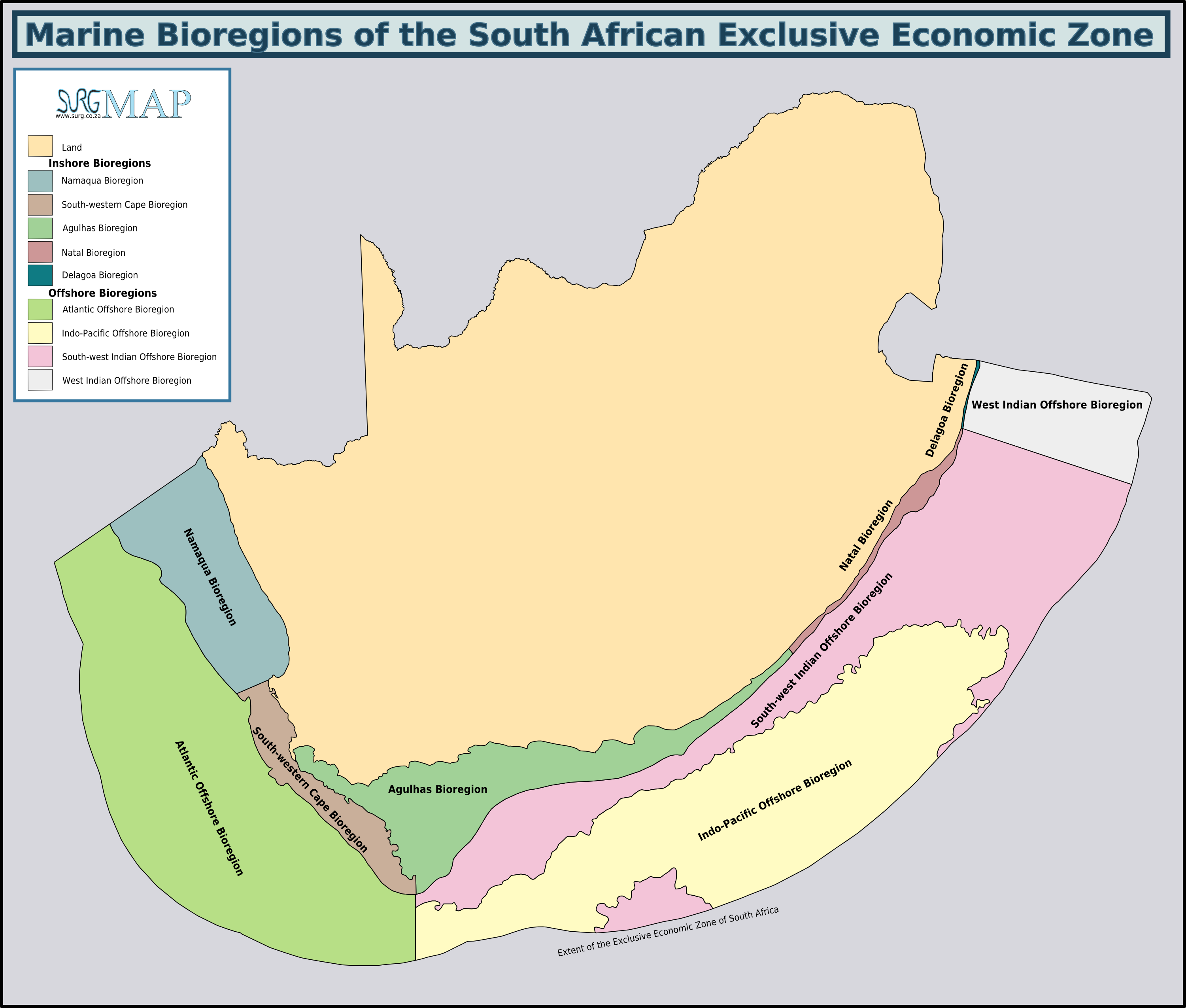
Agulhas Bank
The Agulhas Bank (, from Portuguese for Cape Agulhas, ''Cabo das Agulhas'', "Cape of Needles") is a broad, shallow part of the southern African continental shelf which extends up to south of Cape Agulhas before falling steeply to the abyssal plain. It is the ocean region where the warm Indian Ocean and the cold Atlantic Ocean meet. This convergence leads to treacherous sailing conditions, accounting for numerous wrecked ships in the area over the years. However, the meeting of the oceans here also fuels the nutrient cycle for marine life, making it one of the best fishing grounds in South Africa. Extent and characteristics South African marine ecoregions from the 2011 classification The Agulhas Bank stretches approximately along the African coast, from off Cape Peninsula (18°E) to Port Alfred (26°E), and up to from it. The bank slopes down relatively steeply from the coast to about deep and reaches before dropping steeply to on its southern edge. The shelf spans a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Agulhas
Cape Agulhas (; pt, Cabo das Agulhas , "Cape of the Needles") is a rocky headland in Western Cape, South Africa. It is the geographic southern tip of the African continent and the beginning of the dividing line between the Atlantic and Indian Oceans according to the International Hydrographic Organization. Historically, the cape has been known to sailors as a major hazard on the traditional clipper route. It is sometimes regarded as one of the great capes. It was most commonly known in English as Cape L'Agulhas until the 20th century. The town of L'Agulhas is located near to the cape. Geography Cape Agulhas is located in the Overberg region, 170 kilometres (105 mi) southeast of Cape Town. The cape was named by Portuguese navigators, who called it ''Cabo das Agulhas''—Portuguese for "Cape of Needles"—after noticing that around the year 1500 the direction of magnetic north (and therefore the compass needle) coincided with true north in the region. The cape is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
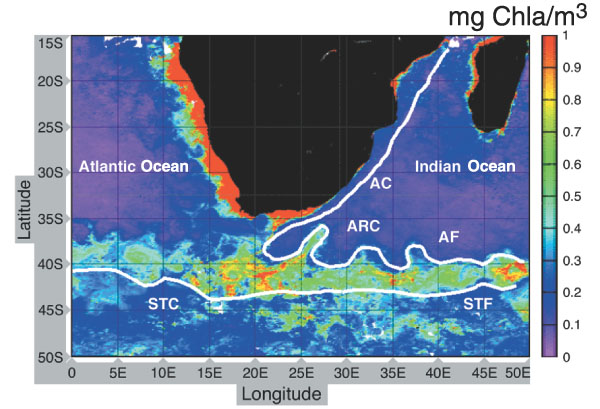
Agulhas Return Current
The Agulhas Return Current (ARC) is an ocean current in the South Indian Ocean. The ARC contributes to the water exchange between oceans by forming a link between the South Atlantic Current and the South Indian Ocean Current. It can reach velocities of up to and is therefore popular among participants in Yacht racing, trans-oceanic sailing races. Oceanography The ARC originates from the Agulhas Current, the western boundary current of the Indian Ocean, at the Agulhas Retroflection south of Africa and flows east along the Subtropical Front, roughly around 39°S, north of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current. The Agulhas Current follows the continental shelf of the African east-coast, pass through the Agulhas Passage until it leaves the Agulhas Bank and reaches the Agulhas Basin south of South Africa. From there it retroflects almost completely back into the south Indian Ocean as the ARC, and only a smaller part, known as Agulhas leakage, is shed into the South Atlantic. The water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natal Province
The Province of Natal (), commonly called Natal, was a province of South Africa from May 1910 until May 1994. Its capital was Pietermaritzburg. During this period rural areas inhabited by the black African population of Natal were organized into the bantustan of KwaZulu, which was progressively separated from the province, becoming partially autonomous in 1981. Of the white population, the majority were English-speaking people of British descent, causing Natal to become the only province to vote "No" to the creation of a republic in the referendum of 1960, due to very strong monarchist, pro-British Commonwealth, and anti-secessionist sentiment. In the latter part of the 1980s, Natal was in a state of violence between the Inkatha Freedom Party and the African National Congress, with violence subsidising soon after the first non-racial election in 1994.Taylor, Rupert. "Justice denied: political violence in Kwazulu‐Natal after 1994." African Affairs 101, no. 405 (2002): 473-508. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a thin but distinct layer in a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) in which temperature changes more drastically with depth than it does in the layers above or below. In the ocean, the thermocline divides the upper mixed layer from the calm deep water below. Depending largely on season, latitude, and turbulent mixing by wind, thermoclines may be a semi-permanent feature of the body of water in which they occur, or they may form temporarily in response to phenomena such as the radiative heating/cooling of surface water during the day/night. Factors that affect the depth and thickness of a thermocline include seasonal weather variations, latitude, and local environmental conditions, such as tides and currents. Oceans Most of the heat energy of the sunlight that strikes the Earth is absorbed in the first few centimeters at the ocean's surface, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ekman Layer
The Ekman layer is the layer in a fluid where there is a force balance between pressure gradient force, Coriolis force and turbulent drag. It was first described by Vagn Walfrid Ekman. Ekman layers occur both in the atmosphere and in the ocean. There are two types of Ekman layers. The first type occurs at the surface of the ocean and is forced by surface winds, which act as a drag on the surface of the ocean. The second type occurs at the bottom of the atmosphere and ocean, where frictional forces are associated with flow over rough surfaces. History Ekman developed the theory of the Ekman layer after Fridtjof Nansen observed that ice drifts at an angle of 20°–40° to the right of the prevailing wind direction while on an Arctic expedition aboard the Fram. Nansen asked his colleague, Vilhelm Bjerknes to set one of his students upon study of the problem. Bjerknes tapped Ekman, who presented his results in 1902 as his doctoral thesis. Mathematical formulation The mathemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upwelling
Upwelling is an oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted surface water. The nutrient-rich upwelled water stimulates the growth and reproduction of primary producers such as phytoplankton. The biomass of phytoplankton and the presence of cool water in those regions allow upwelling zones to be identified by cool sea surface temperatures (SST) and high concentrations of chlorophyll-a. The increased availability of nutrients in upwelling regions results in high levels of primary production and thus fishery production. Approximately 25% of the total global marine fish catches come from five upwellings, which occupy only 5% of the total ocean area.Jennings, S., Kaiser, M.J., Reynolds, J.D. (2001) "Marine Fisheries Ecology." Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd. Upwellings that are driven by coastal currents or diverging open oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Gyre
In oceanography, a gyre () is any large system of circulating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determine the circulatory patterns from the ''wind stress curl'' (torque). ''Gyre'' can refer to any type of vortex in an atmosphere or a sea, even one that is human-created, but it is most commonly used in terrestrial oceanography to refer to the major ocean systems. Major gyres The following are the five most notable ocean gyres:The five most notable gyres PowerPoint Presentation * * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eddy (fluid Dynamics)
In fluid dynamics, an eddy is the swirling of a fluid and the reverse current created when the fluid is in a turbulent flow regime. The moving fluid creates a space devoid of downstream-flowing fluid on the downstream side of the object. Fluid behind the obstacle flows into the void creating a swirl of fluid on each edge of the obstacle, followed by a short reverse flow of fluid behind the obstacle flowing upstream, toward the back of the obstacle. This phenomenon is naturally observed behind large emergent rocks in swift-flowing rivers. An eddy is a movement of fluid that deviates from the general flow of the fluid. An example for an eddy is a vortex which produces such deviation. However, there are other types of eddies that are not simple vortices. For example, a Rossby wave is an eddy which is an undulation that is a deviation from mean flow, but doesn't have the local closed streamlines of a vortex. Swirl and eddies in engineering The propensity of a fluid to swirl is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retroflection
Retroflection is the movement of an ocean current that doubles back on itself. Usage history More commonly used to describe the way the mammalian intestine or uterus might turn back on itself, retroflection was first used in an oceanographic sense in 1970 by South African oceanographer Nils Bang, to describe the Agulhas Current which curves on itself at the southern tip of Africa to become the Aghulhas Return Current. Bang credited the inspiration for the metaphor to his wife, Alison Coombe Bang, a nursing sister, who mentioned the term during her midwifery studies. Bang's research, through the University of Cape Town, was done on a limited budget and with rudimentary equipment,Sciendaba, Vol XII No 48, 15 December 1977 yet his studies using closely spaced bathythermograph readings, were later corroborated by satellite thermal imagery. The term was then revived and is now common parlance among oceanographers. The Agulhas current's retroflection is now key to an understanding of its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agulhas Current NLOM ''
{{disambig ...
Agulhas (''needles'' in the Portuguese language — or ) may refer to: * Cape Agulhas, the southernmost point of Africa * L'Agulhas, a town near the Cape * Cape Agulhas Lighthouse, located at the Cape * Cape Agulhas Local Municipality, the municipality governing the area around Bredasdorp, including the Cape * Agulhas National Park, a national park protecting areas around Cape Agulhas * The Agulhas Bank, an area of ocean south of the Cape * The Agulhas Current, an ocean current off the east coast of South Africa * South African research ships: : **'' S. A. Agulhas'' **''S. A. Agulhas II ''S. A. Agulhas II'' is a South African icebreaking polar supply and research ship owned by the Department of Environmental Affairs (DEA). She was built in 2012 by STX Finland Rauma shipyard in Rauma, Finland, to replace the ageing '' S. A. Agu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean, also known as the Antarctic Ocean, comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60° S latitude and encircling Antarctica. With a size of , it is regarded as the second-smallest of the five principal oceanic divisions: smaller than the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans but larger than the Arctic Ocean. Over the past 30 years, the Southern Ocean has been subject to rapid climate change, which has led to changes in the marine ecosystem. By way of his voyages in the 1770s, James Cook proved that waters encompassed the southern latitudes of the globe. Since then, geographers have disagreed on the Southern Ocean's northern boundary or even existence, considering the waters as various parts of the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans, instead. However, according to Commodore John Leech of the International Hydrographic Organization (IHO), recent oceanographic research has discovered the importance of Southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |