Agulhas Return Current on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
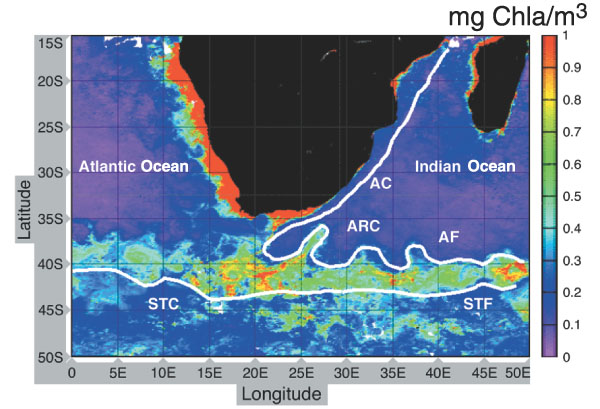 The Agulhas Return Current (ARC) is an
The Agulhas Return Current (ARC) is an
 The Agulhas Return Current (ARC) is an
The Agulhas Return Current (ARC) is an ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, sh ...
in the South Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
. The ARC contributes to the water exchange between oceans by forming a link between the South Atlantic Current and the South Indian Ocean Current. It can reach velocities of up to and is therefore popular among participants in trans-oceanic sailing races.
Oceanography
The ARC originates from the Agulhas Current, the western boundary current of the Indian Ocean, at the Agulhas Retroflection south of Africa and flows east along the Subtropical Front, roughly around 39°S, north of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current. The Agulhas Current follows the continental shelf of the African east-coast, pass through the Agulhas Passage until it leaves theAgulhas Bank
The Agulhas Bank (, from Portuguese for Cape Agulhas, ''Cabo das Agulhas'', "Cape of Needles") is a broad, shallow part of the southern African continental shelf which extends up to south of Cape Agulhas before falling steeply to the abyssal pla ...
and reaches the Agulhas Basin south of South Africa. From there it retroflect
Retroflection is the movement of an ocean current that doubles back on itself.
Usage history
More commonly used to describe the way the mammalian intestine or uterus might turn back on itself, retroflection was first used in an oceanographic sense ...
s almost completely back into the south Indian Ocean as the ARC, and only a smaller part, known as Agulhas leakage, is shed into the South Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for ...
.
The water mass loses a lot of heat at the Agulhas Retroflection, up to , while evaporation and precipitation change the composition of the upper layers. The ARC, therefore, has another composition than the Agulhas Current proper. It also loses velocity from and volume transport from 70 to 54 million m3/s. Furthermore, all traces of Indian Tropical Surface Water are gone.
Having left the retroflection, the ARC meanders east between 36°S and 41°S.
These meanders were described as Rossby waves in 1970 and are known to shed cold eddies equatorward and enhance the primary productivity
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Works
* ...
at the Subtropical Front.
The ARC makes a large, quasi-permanent northward meander around the Agulhas Plateau after which it loses more velocity and volume by leakage into the South Indian subtropical gyre. Over the Crozet Basin the last remnants of the ARC are gone.
As it enters the Crozet Basin at 53°E, the transport of the ARC is 35 Sv, most of which is recirculated northward before reaching the Kerguelen-Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Re ...
Passage.
The current east of the Crozet Basin, at 66°E-70°E, is called the South Indian Ocean Current and lacks the distinctive features of the ARC.
References
Notes
Sources
* * * * * * {{Refend Currents of the Indian Ocean