|
Agate Lake
Agate Lake is a reservoir located above sea level in Jackson County, Oregon, United States. It is northeast of Medford, just north of Roxy Ann Peak. The lake is formed by the tall Agate Dam, which impounds Dry Creek, in the Rogue River watershed. History Construction of Agate Dam was authorized in 1962, started in 1965, and completed in 1966. The tall earth-fill embankment dam was completed by the Talent Division of the Rogue River Basin Project, impounding Dry Creek. Two canals were also built, one a feeder canal diverting seasonal runoff water from Hopkins canal fed from nearby Antelope Creek. The second is the Dry Creek Diversion Canal through which the reservoir water is released at a controlled rate beginning in the summer months supplementing the water supplies of Dry Creek, Antelope Creek, and eventually Little Butte Creek. This water is mainly used for irrigation and the demand for it downstream is normally enough to reduce the reservoir to its minimum allowabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roxy Ann Peak
Roxy Ann Peak, also known as Roxy Ann Butte, is a mountain in the Western Cascade Range at the eastern edge of Medford, Oregon. Composed of several geologic layers, the majority of the peak is of volcanic origin and dates to the early Oligocene epoch. It is primarily covered by oak savanna and open grassland on its lower slopes, and mixed coniferous forest on its upper slopes and summit, stopping short of the summit. Despite the peak's relatively small topographic prominence of , it rises above Medford and is visible from most of the Rogue Valley. The mountain is Medford's most important viewshed, open space reserve, and recreational resource. The area was originally inhabited beginning 8,000 to 10,000 years ago by ancestral Native Americans. The Latgawa Native American tribe was present in the early 1850s when the sudden influx of non-indigenous settlers resulted in the Rogue River Wars. After the wars, the Latgawa were forced away from the region onto reservations. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandalism
Vandalism is the action involving deliberate destruction of or damage to public or private property. The term includes property damage, such as graffiti and defacement directed towards any property without permission of the owner. The term finds its roots in an Enlightenment view that the Germanic Vandals were a uniquely destructive people. Etymology The Vandals, an ancient Germanic people, are associated with senseless destruction as a result of their sack of Rome under King Genseric in 455. During the Enlightenment, Rome was idealized, while the Goths and Vandals were blamed for its destruction. The Vandals may not have been any more destructive than other invaders of ancient times, but they did inspire English poet John Dryden to write, ''Till Goths, and Vandals, a rude Northern race, Did all the matchless Monuments deface'' (1694). However, the Vandals did intentionally damage statues, which may be why their name is associated with the vandalism of art. The ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alder
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few species extending into Central America, as well as the northern and southern Andes. Description With a few exceptions, alders are deciduous, and the leaves are alternate, simple, and serrated. The flowers are catkins with elongate male catkins on the same plant as shorter female catkins, often before leaves appear; they are mainly wind-pollinated, but also visited by bees to a small extent. These trees differ from the birches (''Betula'', another genus in the family) in that the female catkins are woody and do not disintegrate at maturity, opening to release the seeds in a similar manner to many conifer cones. The largest species are red alder (''A. rubra'') on the west coast of North America, and black alder (''A. glutinosa''), native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populus Trichocarpa
''Populus trichocarpa'', the black cottonwood, western balsam-poplar or California poplar, is a deciduous broadleaf tree species native to western North America. It is used for timber, and is notable as a model organism in plant biology. Description It is a large tree, growing to a height of and a trunk diameter over , which makes it the largest poplar species in the Americas. It is normally fairly short-lived, but some trees may live up to 400 years. A cottonwood in Willamette Mission State Park near Salem, Oregon, holds the national and world records. Last measured in April 2008, this black cottonwood was found to be standing at tall, around, with 527 points. The bark is grey and covered with lenticels, becoming thick and deeply fissured on old trees. The bark can become hard enough to cause sparks when cut with a chainsaw.Ewing, Susan. The Great Alaska Nature Factbook. Portland: Alaska Northwest Books, 1996. The stem is grey in the older parts and light brown in younge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions. Most species are known as willow, but some narrow-leaved shrub species are called osier, and some broader-leaved species are referred to as sallow (from Old English ''sealh'', related to the Latin word ''salix'', willow). Some willows (particularly arctic and alpine species) are low-growing or creeping shrubs; for example, the dwarf willow (''Salix herbacea'') rarely exceeds in height, though it spreads widely across the ground. Description Willows all have abundant watery bark sap, which is heavily charged with salicylic acid, soft, usually pliant, tough wood, slender branches, and large, fibrous, often stoloniferous roots. The roots are remarkable for their toughness, size, and tenacity to live, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of living fish species are ray-finned fish, belonging to the class Actinopterygii, with around 99% of those being teleosts. The earliest organisms that can be classified as fish were soft-bodied chordates that first appeared during the Cambrian period. Although they lacked a true spine, they possessed notochords which allowed them to be more agile than their invertebrate counterparts. Fish would continue to evolve through the Paleozoic era, diversifying into a wide variety of forms. Many fish of the Paleozoic developed external armor that protected them from predators. The first fish with jaws appeared in the Silurian period, after which many (such as sharks) became formidable marine predators rather than just the prey of arthropods. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stream
A stream is a continuous body of surface water flowing within the bed and banks of a channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to by a variety of local or regional names. Long large streams are usually called rivers, while smaller, less voluminous and more intermittent streams are known as streamlets, brooks or creeks. The flow of a stream is controlled by three inputs – surface runoff (from precipitation or meltwater), daylighted subterranean water, and surfaced groundwater ( spring water). The surface and subterranean water are highly variable between periods of rainfall. Groundwater, on the other hand, has a relatively constant input and is controlled more by long-term patterns of precipitation. The stream encompasses surface, subsurface and groundwater fluxes that respond to geological, geomorphological, hydrological and biotic controls. Streams are important as conduits in the water cycle, instruments in groundw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
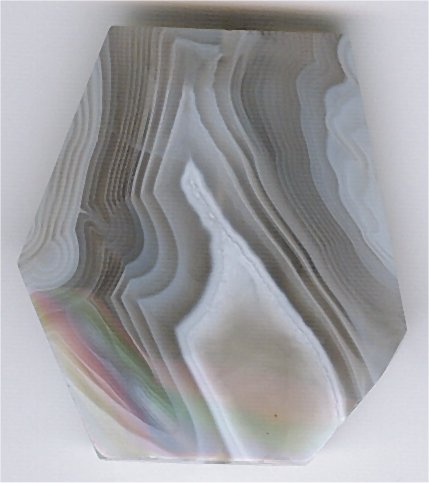
Agate Lake 2
Agate () is a common rock formation, consisting of chalcedony and quartz as its primary components, with a wide variety of colors. Agates are primarily formed within volcanic and metamorphic rocks. The ornamental use of agate was common in Ancient Greece, in assorted jewelry and in the seal stones of Greek warriors, while bead necklaces with pierced and polished agate date back to the 3rd millennium BCE in the Indus Valley civilisation. Etymology The stone was given its name by Theophrastus, a Greek philosopher and naturalist, who discovered the stone along the shore line of the Dirillo River or Achates ( grc, Ἀχάτης) in Sicily, sometime between the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE. Formation and properties Agate minerals have the tendency to form on or within pre-existing rocks, creating difficulties in accurately determining their time of formation. Their host rocks have been dated to have formed as early as the Archean Eon. Agates are most commonly found as nodules with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
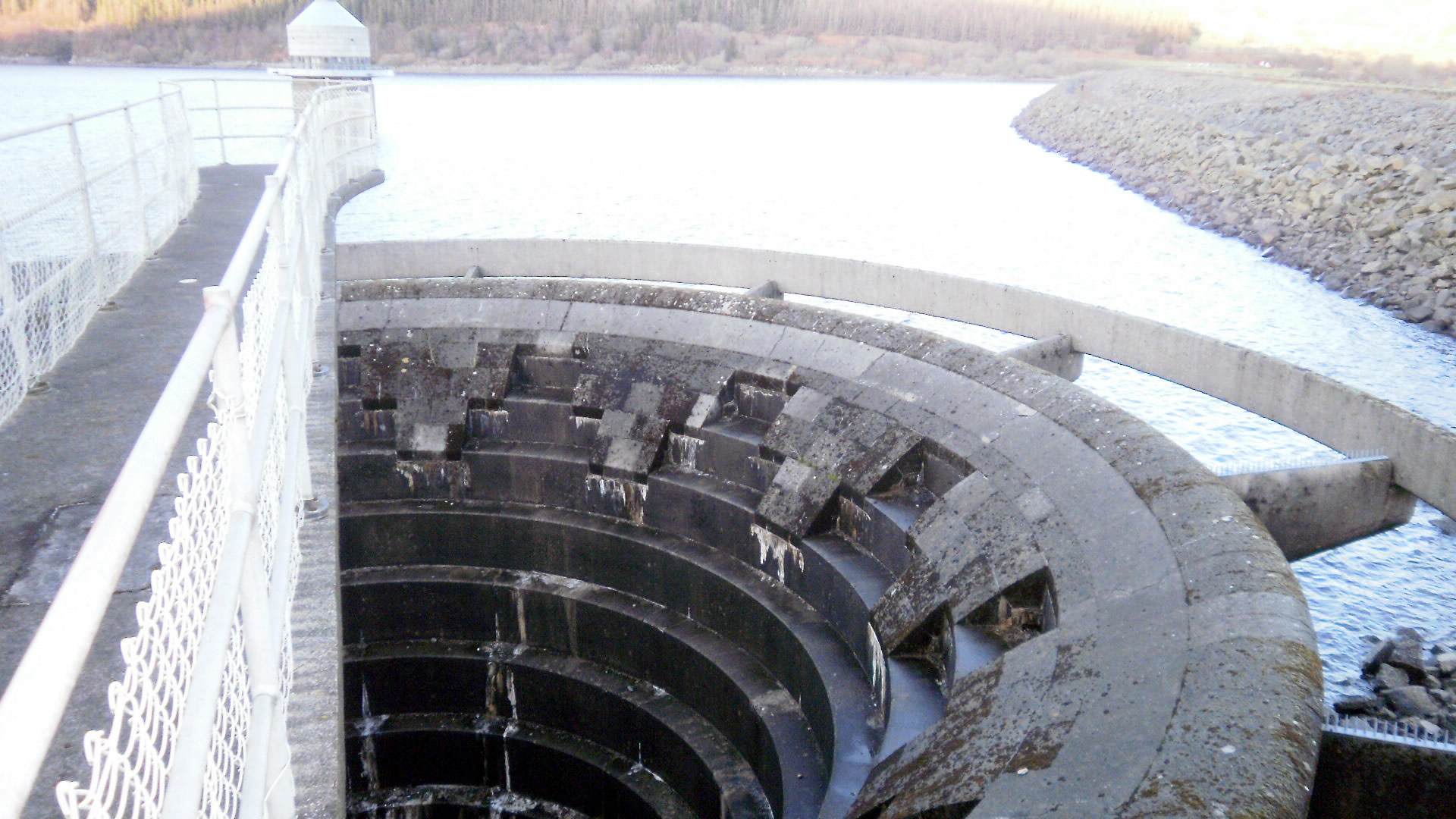
Spillway
A spillway is a structure used to provide the controlled release of water downstream from a dam or levee, typically into the riverbed of the dammed river itself. In the United Kingdom, they may be known as overflow channels. Spillways ensure that water does not damage parts of the structure not designed to convey water. Spillways can include floodgates and fuse plugs to regulate water flow and reservoir level. Such features enable a spillway to regulate downstream flow—by releasing water in a controlled manner before the reservoir is full, operators can prevent an unacceptably large release later. Other uses of the term "spillway" include bypasses of dams and outlets of channels used during high water, and outlet channels carved through natural dams such as moraines. Water normally flows over a spillway only during flood periods, when the reservoir has reached its capacity and water continues entering faster than it can be released. In contrast, an intake tower is a stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
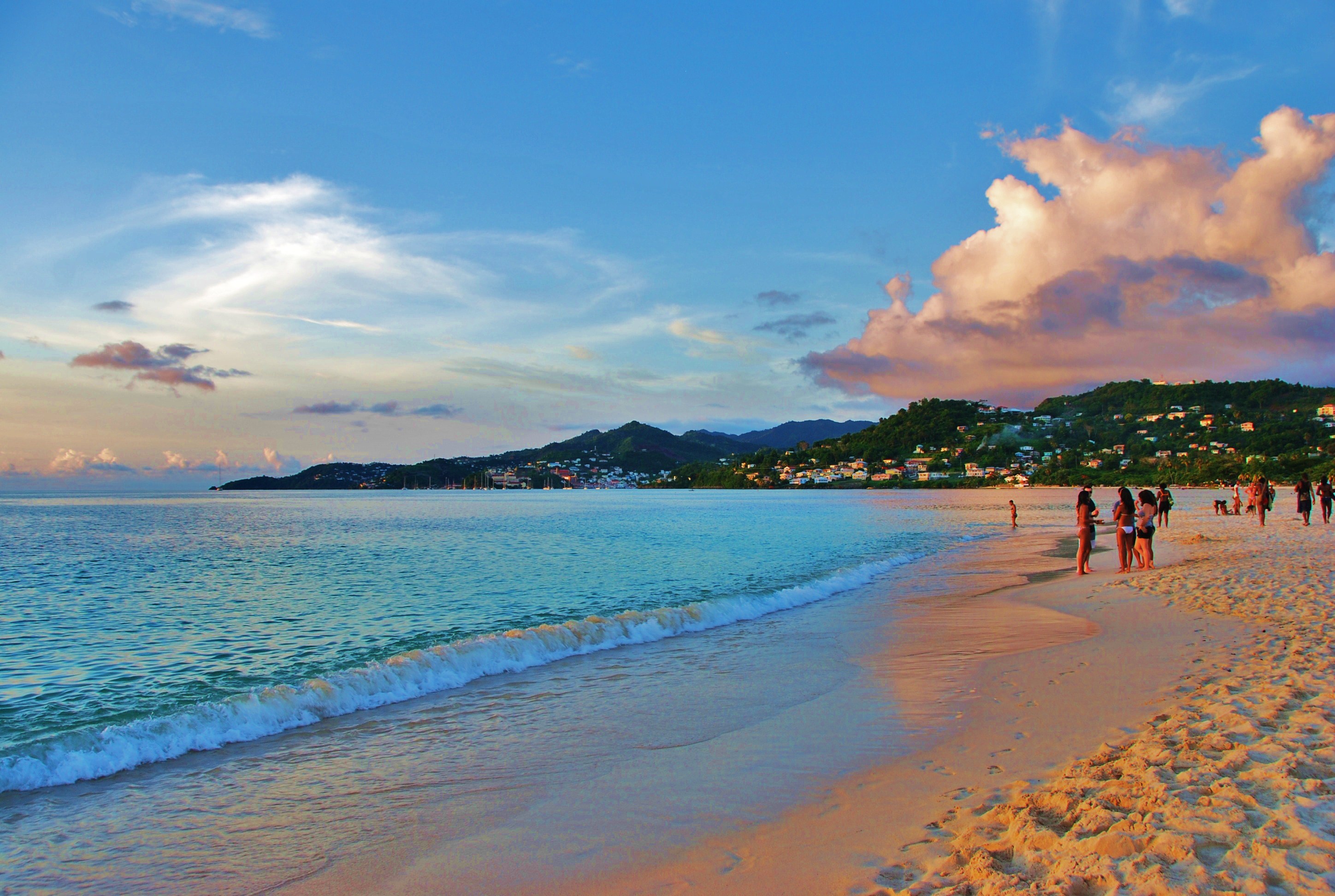
Shore
A shore or a shoreline is the fringe of land at the edge of a large body of water, such as an ocean, sea, or lake. In physical oceanography, a shore is the wider fringe that is geologically modified by the action of the body of water past and present, while the beach is at the edge of the shore, representing the intertidal zone where there is one. In contrast to a coast, a shore can border any body of water, while the coast must border an ocean or a sea. Therefore, in that sense, a coast is a type of shore. However, the word "coast" often refers to an area far wider than the shore, often stretching miles into the interior. Shores are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape, as well as by water induced erosion, such as waves. The geological composition of rock and soil dictates the type of shore which is created. Rivieras ''Riviera'' is an Italian word for "shoreline", ultimately derived from Latin ''ripa'' ("riverbank"). It came to be applied as a proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Speed
In meteorology, wind speed, or wind flow speed, is a fundamental atmospheric quantity caused by air moving from high to low pressure, usually due to changes in temperature. Wind speed is now commonly measured with an anemometer. Wind speed affects weather forecasting, aviation and maritime operations, construction projects, growth and metabolism rate of many plant species, and has countless other implications. Note that wind direction is usually almost parallel to isobars (and not perpendicular, as one might expect), due to Earth's rotation. Units Metres per second (m/s) is the SI unit for velocity and the unit recommended by the World Meteorological Organization for reporting wind speeds, and is amongst others used in weather forecasts in the Nordic countries. Since 2010 the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) also recommends meters per second for reporting wind speed when approaching runways, replacing their former recommendation of using kilometres per h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultures define different dates as the start of winter, and some use a definition based on weather. When it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere, it is summer in the Southern Hemisphere, and vice versa. In many regions, winter brings snow and freezing temperatures. The moment of winter solstice is when the Sun's elevation with respect to the North or South Pole is at its most negative value; that is, the Sun is at its farthest below the horizon as measured from the pole. The day on which this occurs has the shortest day and the longest night, with day length increasing and night length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice. The earliest sunset and latest sunrise dates outside the polar regions differ from the date of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_nahe_dem_Weiherdamm_in_Wildbergerhütte.jpg)