|
Afrotragulus
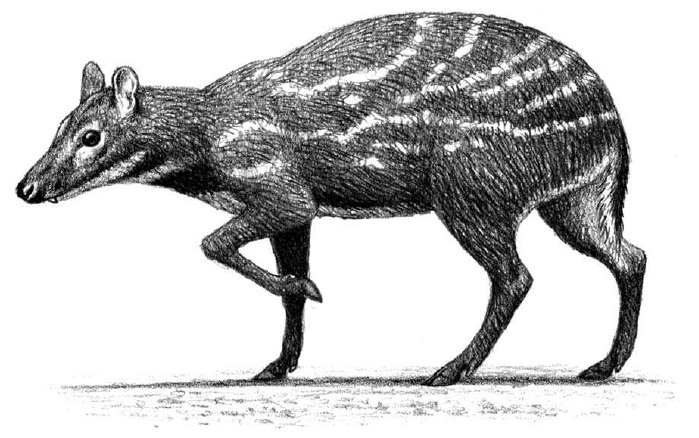
''Afrotragulus'' is an extinct genus of tragulid ruminant which existed in Kenya during the early Miocene period. It contains the species ''Afrotragulus moruorotensis'' and ''Afrotragulus parvus'', formerly classified in genus ''Dorcatherium ''Dorcatherium'' is an extinct genus of tragulid ruminant which existed in Europe, East Africa and the Siwaliks during the Miocene and Pliocene The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5 ...,'' as well as ''A. akhtari, A. megalomilos'', and ''A. moralesi''. References Chevrotains Miocene even-toed ungulates Fossil taxa described in 2010 Miocene mammals of Africa Prehistoric even-toed ungulate genera {{paleo-eventoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afrotragulus Moruorotensis
''Afrotragulus'' is an extinct genus of tragulid ruminant which existed in Kenya during the early Miocene period. It contains the species ''Afrotragulus moruorotensis'' and ''Afrotragulus parvus'', formerly classified in genus ''Dorcatherium ''Dorcatherium'' is an extinct genus of tragulid ruminant which existed in Europe, East Africa and the Siwaliks during the Miocene and Pliocene The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5 ...,'' as well as ''A. akhtari, A. megalomilos'', and ''A. moralesi''. References Chevrotains Miocene even-toed ungulates Fossil taxa described in 2010 Miocene mammals of Africa Prehistoric even-toed ungulate genera {{paleo-eventoedungulate-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chevrotains
Chevrotains, or mouse-deer, are small even-toed ungulates that make up the family Tragulidae, the only extant members of the infraorder Tragulina. The 10 extant species are placed in three genera, but several species also are known only from fossils. The extant species are found in forests in South and Southeast Asia, with a single species, the water chevrotain, in the rainforests of Central and West Africa. They are solitary or live in pairs, and feed almost exclusively on plant material. Chevrotains are the smallest hoofed mammals in the world. The Asian species weigh between , while the African chevrotain is considerably larger at . With an average length of and an average height of , the Java mouse-deer is the smallest extant (living) ungulate or hoofed mammal, as well as the smallest extant even-toed ungulate. In November 2019, conservation scientists announced that they had photographed silver-backed chevrotains (''Tragulus versicolor'') in a Vietnamese f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
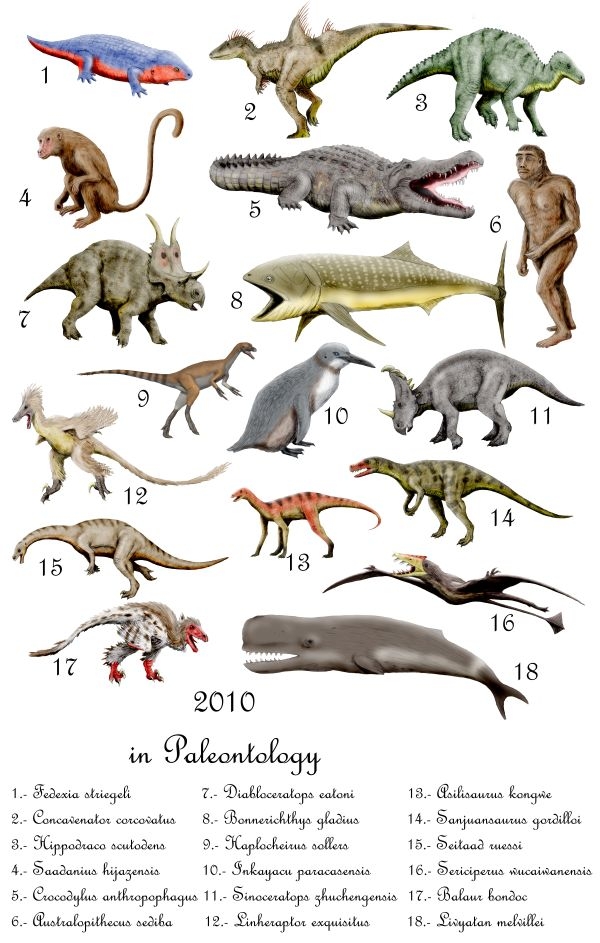
2010 In Paleontology
Plants Angiosperms Molluscs Newly named bivalves Arthropods Fishes Amphibians Newly named amphibians Basal reptiles Newly named basal reptiles Ichthyopterygians Newly named ichthyopterygians Lepidosauromorphs Newly named plesiosaurs Newly named basal lepidosaurs Newly named lizards Newly named snakes Turtles Newly named turtles Archosauromorphs Newly named basal archosauromorphs Archosaurs Synapsids Newly named non-mammalian synapsids Mammals Other animals Footnotes Complete author list As science becomes more collaborative, papers with large numbers of authors are becoming more common. To prevent the deformation of the tables, these footnotes list the contributors to papers that erect new genera and have many authors. References {{Reflist, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tragulidae
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star. Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as star (as, for example, in ''the A* search algorithm'' or ''C*-algebra''). In English, an asterisk is usually five- or six-pointed in sans-serif typefaces, six-pointed in serif typefaces, and six- or eight-pointed when handwritten. Its most common use is to call out a footnote. It is also often used to censor offensive words. In computer science, the asterisk is commonly used as a wildcard character, or to denote pointers, repetition, or multiplication. History The asterisk has already been used as a symbol in ice age cave paintings. There is also a two thousand-year-old character used by Aristarchus of Samothrace called the , , which he used when proofreading Homeric poetry to mark lines that were duplicated. Origen is know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenya
) , national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"() , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Nairobi , coordinates = , largest_city = Nairobi , official_languages = Constitution (2009) Art. 7 ational, official and other languages"(1) The national language of the Republic is Swahili. (2) The official languages of the Republic are Swahili and English. (3) The State shall–-–- (a) promote and protect the diversity of language of the people of Kenya; and (b) promote the development and use of indigenous languages, Kenyan Sign language, Braille and other communication formats and technologies accessible to persons with disabilities." , languages_type = National language , languages = Swahili , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2019 census , religion = , religion_year = 2019 census , demonym = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorcatherium
''Dorcatherium'' is an extinct genus of tragulid ruminant which existed in Europe, East Africa and the Siwaliks during the Miocene and Pliocene The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58Chevrotains Miocene even-toed ungulates Pliocene even-toed ungulates Cenozoic mammals of Afric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Even-toed Ungulates
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 2010
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene Mammals Of Africa
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)


_(2).jpg)